
Embryonic stage zygote
This fluid helps protect the embryo from injury. Milestones in the development of your fetus: 5 weeks: the heart starts to beat and most other organs begin to develop, followed by the brain and spinal cord. 10 weeks: the embryo is considered a fetus. 12 weeks: most organs are formed. 14 weeks: doctors can tell the sex of the fetus.
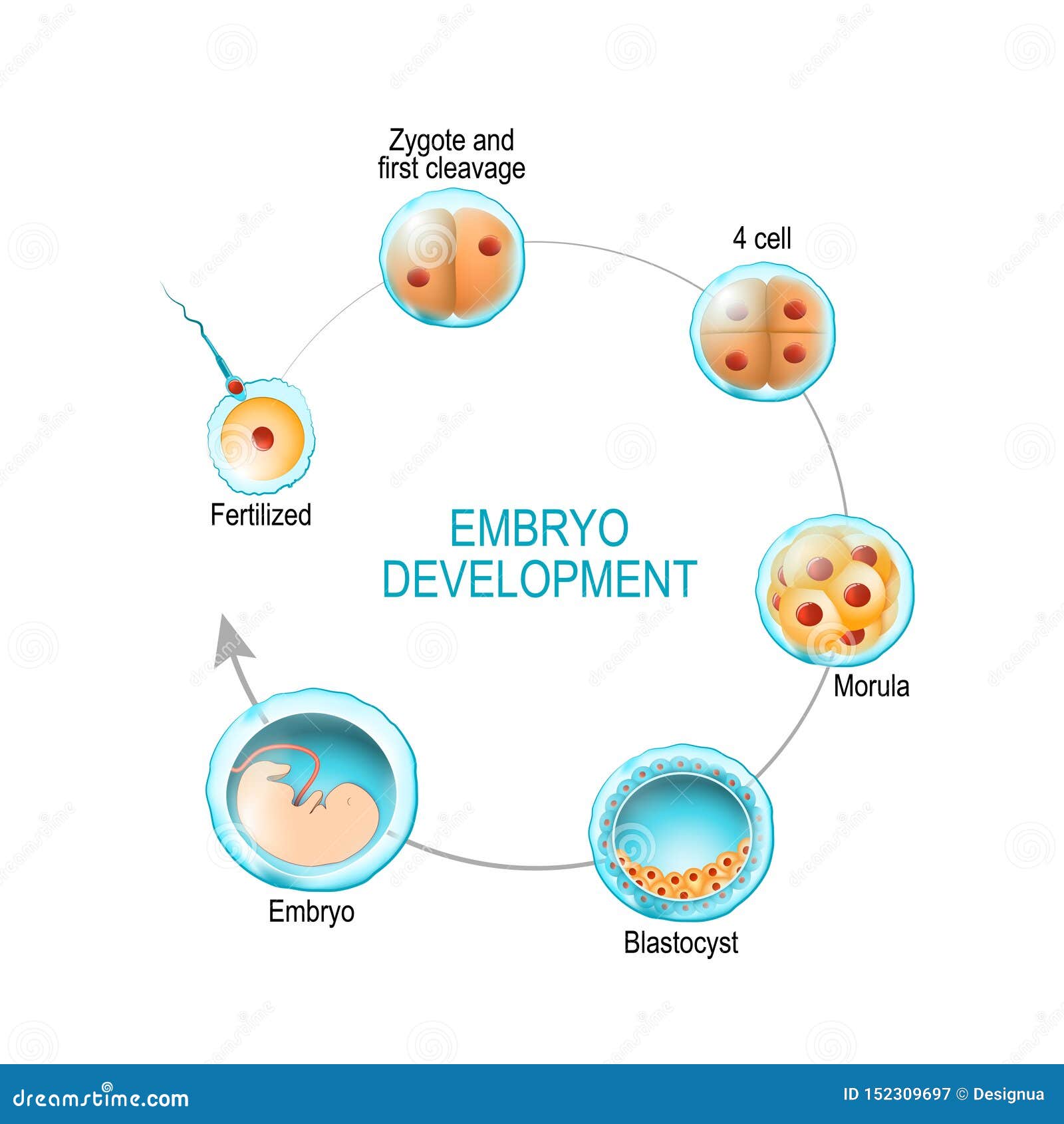
Zygote To Embryo Stages
Furthermore, the terms "zygote," "embryo," and "fetus" describe stages of biological human development and as such, do not describe the development into a human person. Proponents of the first hypothesis claim that personhood is attained from the moment of fertilization when a new zygotic genome is assembled, or even earlier when a.

Embryo on day 1 zygote
In general, pregnancy is divided into three trimesters. The first trimester lasts from week one through week 12. The second trimester is week 13 through week 28. The third trimester is week 29 through 40. During each trimester, your body and the baby go through many changes. The first trimester allows your baby's major organs to begin developing.
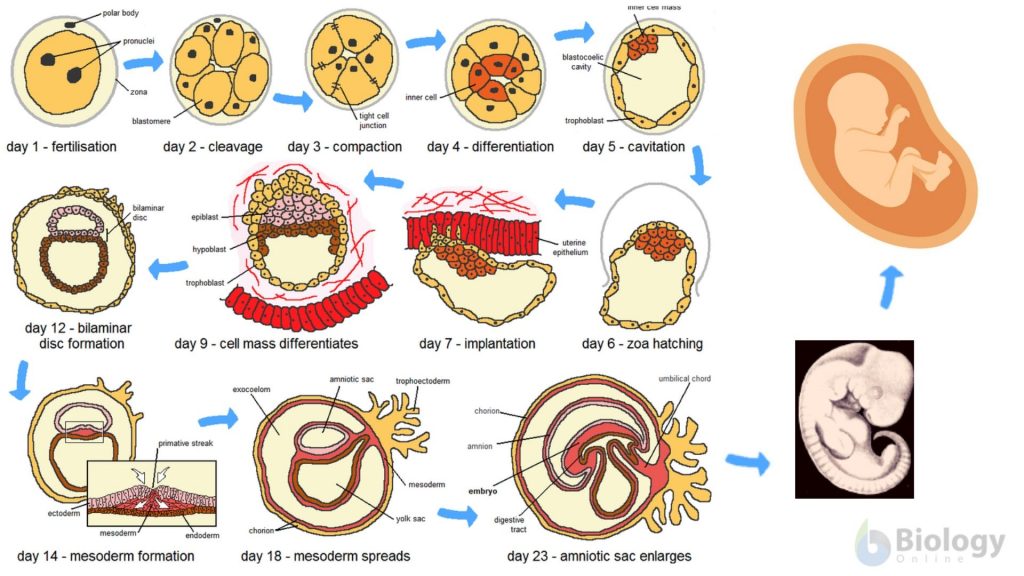
Cell differentiation Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
This week your baby's face is broad, the eyes widely separated, the eyelids fused and the ears low set. Buds for future teeth appear. Red blood cells are beginning to form in your baby's liver. By the end of this week, your baby's external genitalia will start developing into a penis or a clitoris and labia majora.

Zygote Embryo Fetus How Gestational Age is Measured? YouTube
Key Facts: The study identifies the OBOX gene family as crucial in awakening the genome of a newly fertilized egg cell (zygote). The OBOX genes guide the enzyme RNA polymerase II to start transcribing the correct genes for the embryo's development. The redundancy of these genes' functions is likely an evolutionary response to ensure the.
/fertilization-zygote-155301406-58a70e1f3df78c345b67eedc.jpg)
Zygote, Embryo, Fetus Learn the Differences New Baby Time
When the egg and sperm come together (a process called fertilization), they form a zygote. This is essentially a fertilized egg, says Spencer Richlin, M.D., a board-certified fertility specialist.
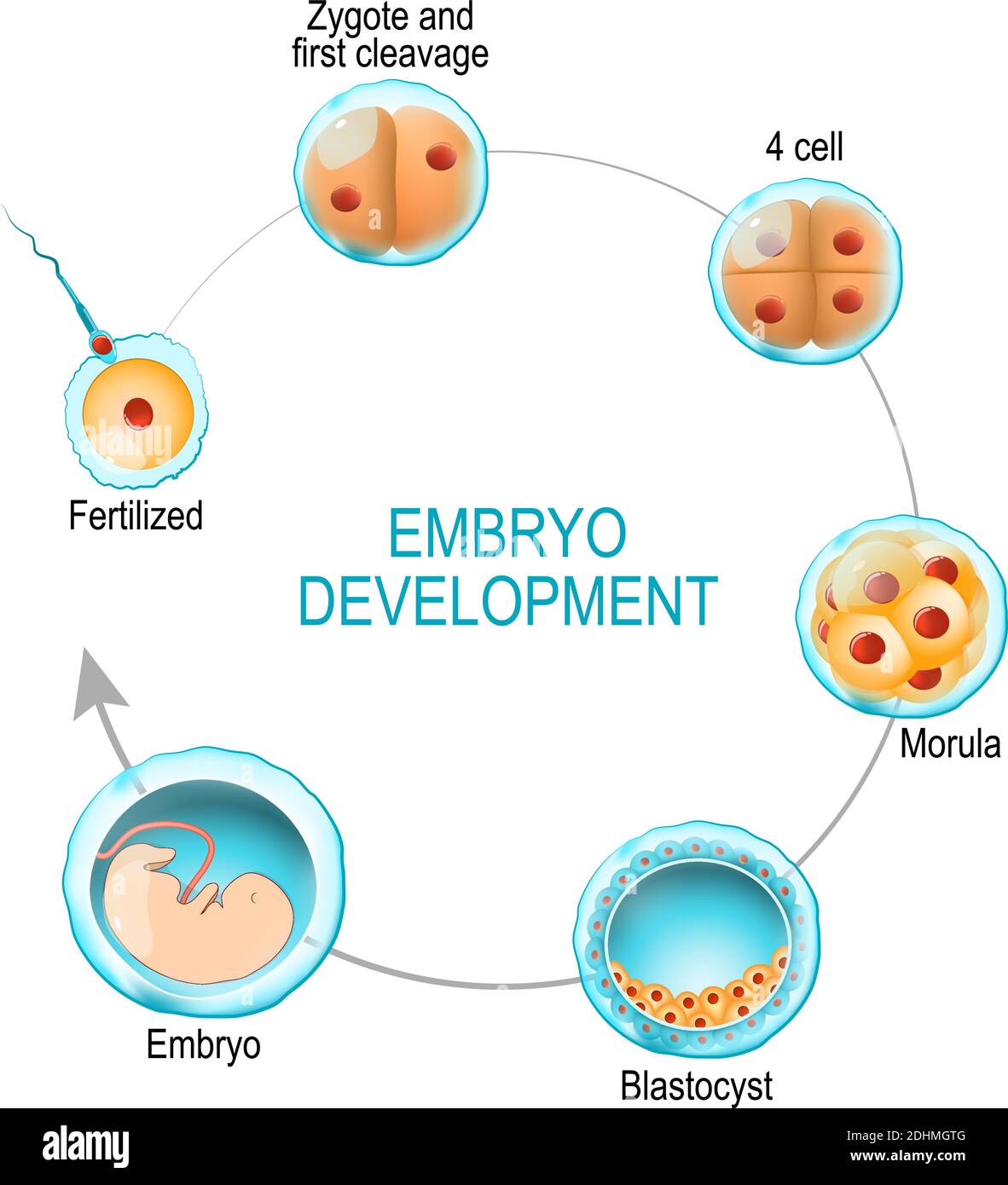
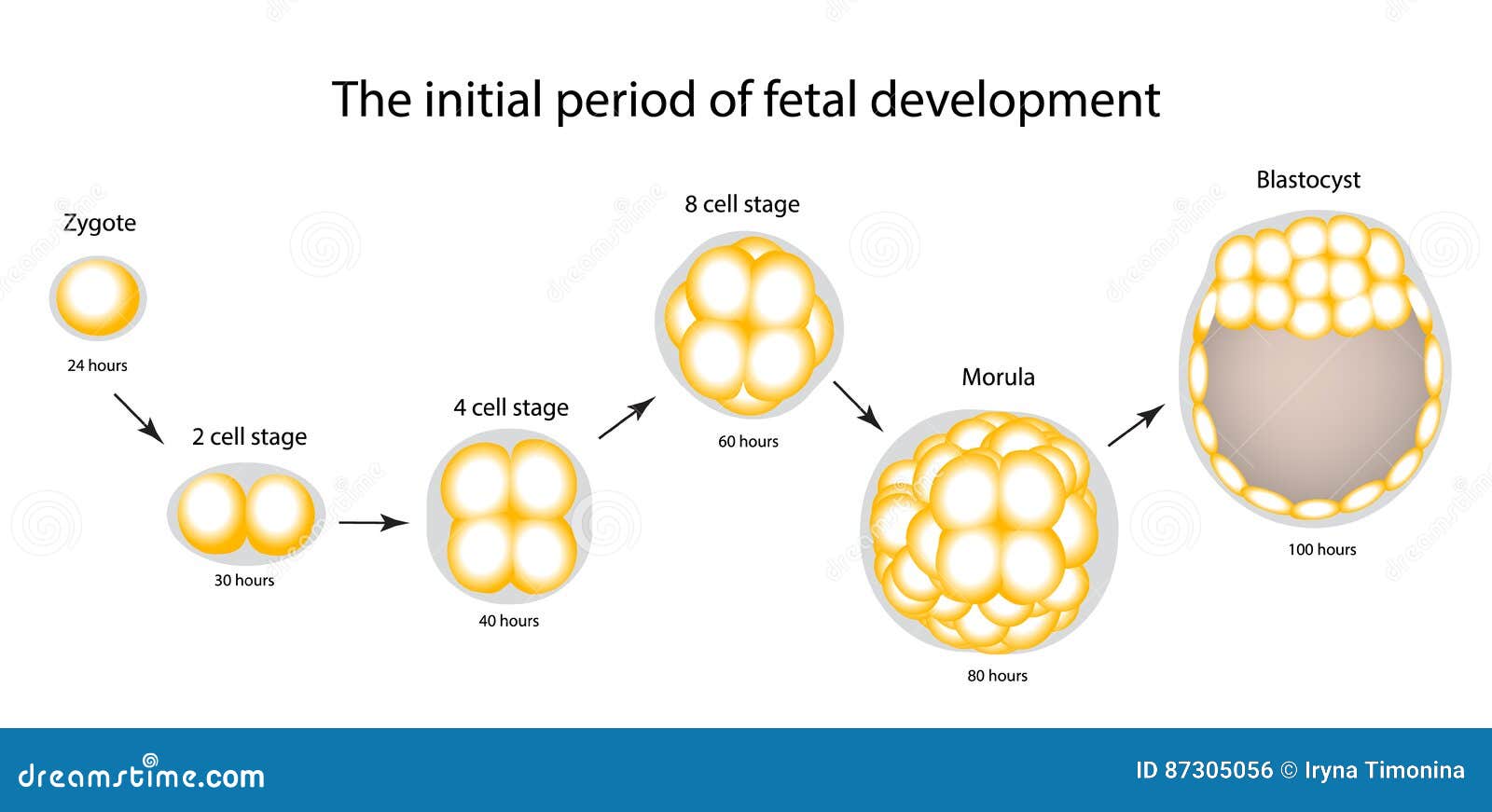
embryo development. from fertilization to zygote, morula and Blastocyst. vector diagram for
Conclusion. The union of the sperm cell and the egg cell includes a zygote. Often known as a fertilized ovum, in the days following fertilization, the zygote starts as a single cell but divides rapidly. Eventually, the zygote becomes an embryo after this two-week cycle of cell division. The egg becomes a fetus if all goes well.
Proses Zigot Terbentuk Menjadi Embrio pada Tahap Pembuahan
Abstract. Zygote, the first cell of the sporophytic generation, is a product of fertilization, the fusion of a female (egg cell) and male (sperm) gamete. After fertilization the zygote starts its characteristic type of development (embryogenesis) which, if continues undisturbed by external and inner factors, secures normal germination and post.

Zygote définition et explications
A zygote is a fertilized egg. It's created when sperm meets an egg in one of the fallopian tubes. When the sperm enters the egg, you conceive and the result is the zygote. It contains all the genetic information (DNA) that's required to create a little human being. Half of that comes from the egg, and the other half comes from the sperm.
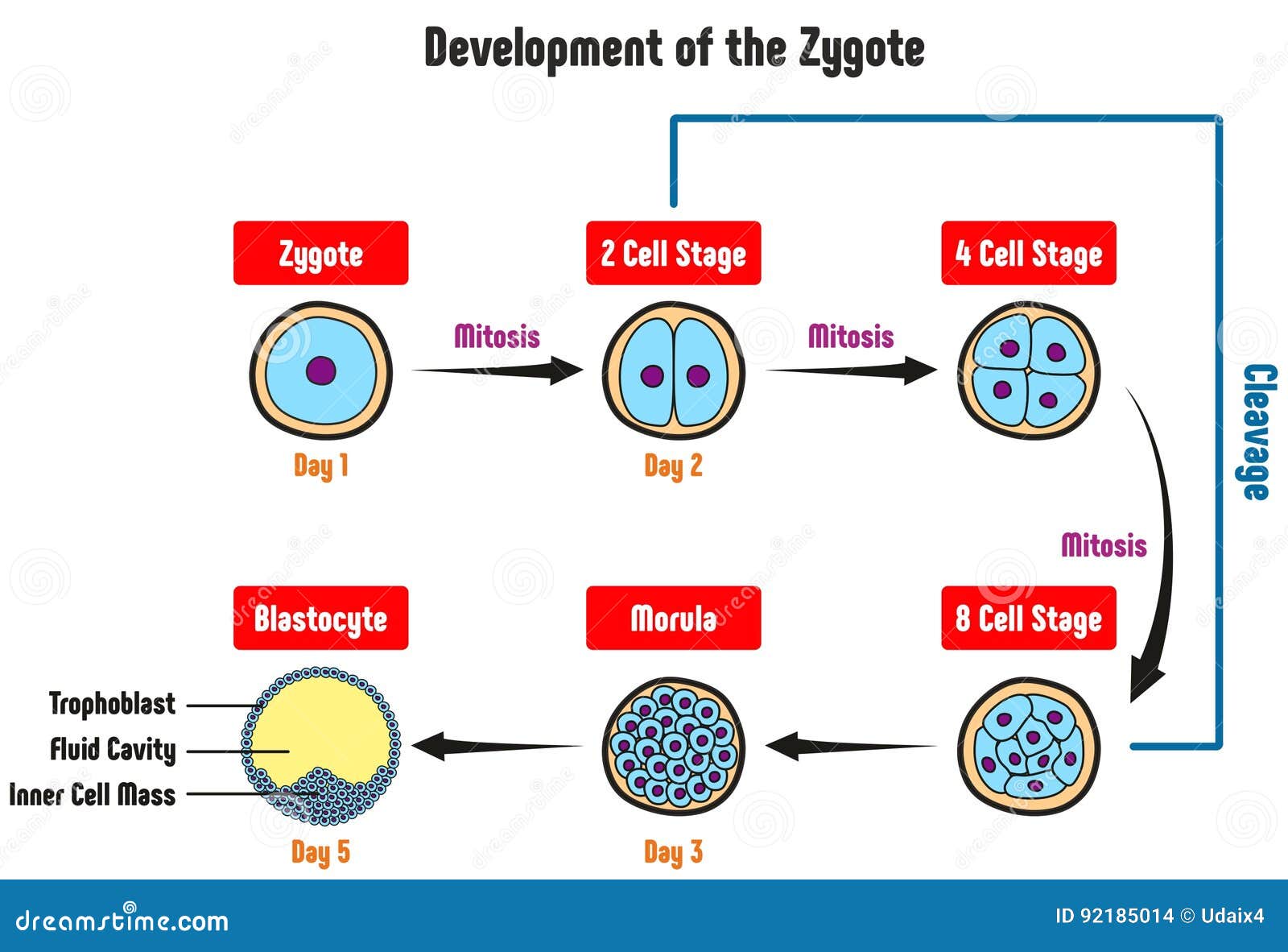
Development of the Zygote Diagram Stock Vector Illustration of blastocyte, biological 92185014
In females, egg; in males, sperm. Fertilization. The process in sexual reproduction in which a female gamete and male gamete fuse to form a new cell. Zygote. Cell resulting from fertilization. Diploid (2n) Cell that contains two sets of homologous chromosomes. Haploid (n) Cell that contains only a single set of genes.

The zygote first stage of embryo development after fertilization
A zygote is a fertilized egg that can eventually become an embryo. A zygote, also known as a fertilized ovum or fertilized egg, is the union of a sperm cell and an egg cell. The zygote begins as a single cell but divides rapidly in the days following fertilization. The zygote's single cell contains all of the 46 necessary chromosomes, getting.
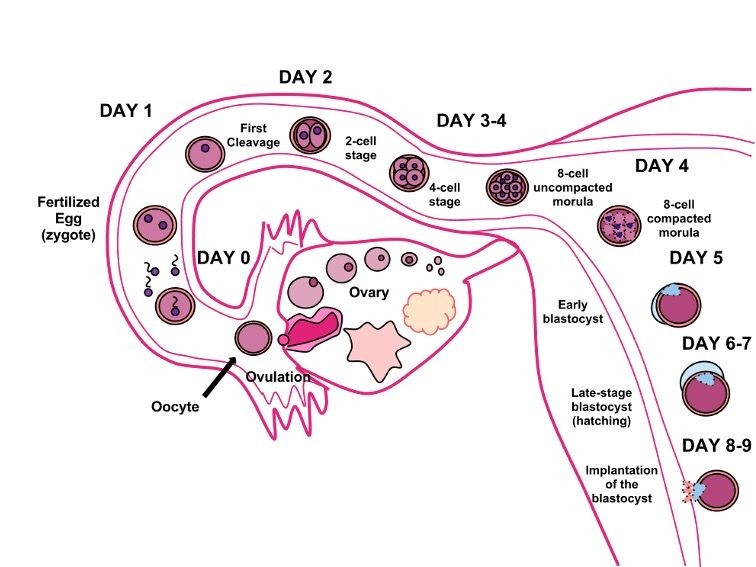
Stages Of Zygote Development
Embryo vs. fetus. In human pregnancies, a baby-to-be isn't considered a fetus until the 9th week after conception, or week 11 after your last menstrual period (LMP). The embryonic period is all.

Zygote, Embryo, Fetus Learn the Differences New Baby Time
By the end of the 3rd week of pregnancy (when counting from the last period), the embryo is receiving nutrients from the pregnant person's blood supply (2). The embryo (and later the fetus) is reliant on the pregnant person's blood (which carry oxygen and nutrients) through the placenta. The placenta is an organ specially formed from the.

Fertilisation, zygote, embryo, germination How do organisms reproduce Biology Khan Academy
Within the world of Reproductive Biology, we can find many terms and concepts that people without specific health knowledge may confuse. This is the case of the words zygote, embryo and fetus, which definition and main differences will be explained hereunder.. It should be noted that these terms are used during the early stages of human development, known as Carnegie stages, which are based on.

Embryo Development A Development process of Fetus Week by Week
zygote, fertilized egg cell that results from the union of a female gamete (egg, or ovum) with a male gamete ( sperm ). In the embryonic development of humans and other animals, the zygote stage is brief and is followed by cleavage, when the single cell becomes subdivided into smaller cells. The zygote represents the first stage in the.

Differences between human 'zygote', 'embryo' and 'fetus'
The zygote is the first diploid cell that forms following fertilization by fusion of the haploid oocyte (egg) and spermatozoa (sperm) resulting in the combination of their separate genomes. The zygote will therefore form the conceptus, the embryonic (embryo, fetus) and extra-embryonic (fetal membranes, fetal component of the placenta) cellular.