
Dobereiner`s law of triads stock illustration. Illustration of periodic 250967359
Johann Wolfgang Dobereiner. As the number of elements increased, chemists inevitably began to find patterns in their properties.. that the atomic weight of the middle element in each triad is about equal to the average of the atomic weights of the first and third elements. The atomic weight of sodium (22.99 g/mol), for example, is remarkably.

DOBEREINER LAW OF TRIADS.. "Periodic classification" Lecture 1 YouTube
By 1829, Döbereiner had found other groups of three elements (hence "triads") whose physical properties were similarly related. He also noted that some quantifiable properties of elements (e.g. atomic weight and density) in a triad followed a trend whereby the value of the middle element in the triad would be exactly or nearly predicted by taking the arithmetic mean of values for that.

Periodic Classification of Elements part 1 Dobereiner's Triads, Newland law of Octaves YouTube
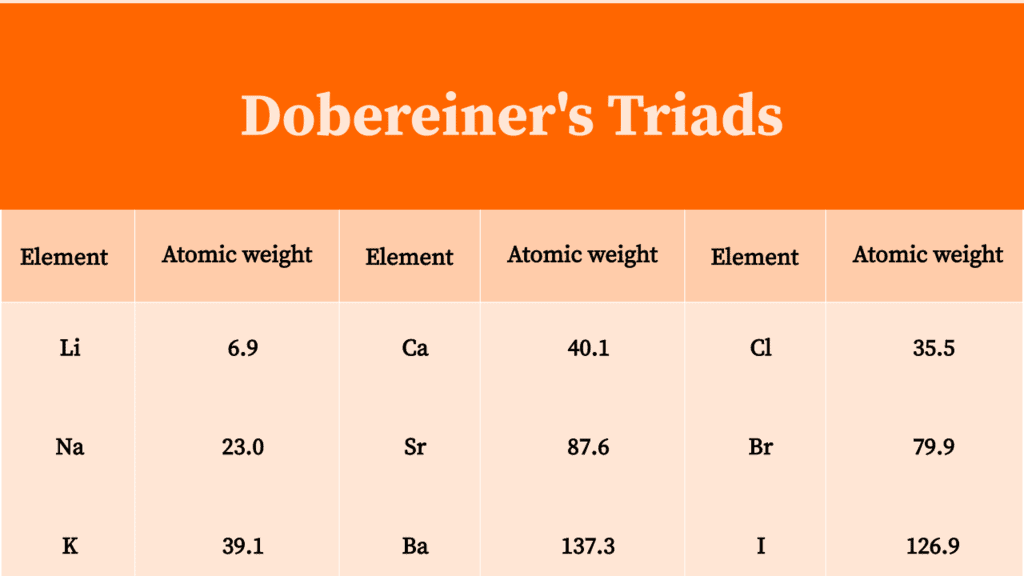
According to the law of Dobereiner's triads, the atomic mass of the middle element is approximately equal to the mean of the atomic masses of the first and last elements. Calcium-strontium-barium, Chlorine-bromine-iodine, and Sulphur-selenium-tellurium are examples of Dobereiner's triads. Only 5 of Dobereiner's triads have been identified yet.

Döbereiner's Triads School Of Elements Part 2 YouTube
One of the most famous examples of a Dobereiner Triad is the alkali metal triad: lithium (Li), sodium (Na), and potassium (K). These elements share similar chemical properties, and their atomic weights form a clear pattern: the atomic weight of sodium is approximately the mean of lithium and potassium. This kind of relationship was also evident.

Trick to learn Doberenier Triad / dobereiner's law of triads / NEET chemistry video lecturer
Elements X , Y , and Z belong to Dobereiner's triad. The atomic masses of X and Z are as follows. The atomic mass of the element Y is roughly equal to . Stuck? Use a hint. Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the.

ChemistryDobereiner triads and example of Dobereiner triads YouTube
Hence they form Dobereiner's triad. Question 6: State the alkaline earth metal Dobereiner's triad. Answer: The alkaline earth metals that are a part of the Dobereiner triads are calcium, strontium and barium. Question 7: Verify the law of triads for the alkali metals triad. Answer: The alkali metals triad consists of Lithium. Sodium and.
Dobereiner's Triads, Newlands Octaves and Mendeleev's Periodic Table Class 11 Notes EduRev
A triad is a grouping of three elements in order of atomic mass. Dobereiner's Law of Triads deals with putting three elements in order of atomic weight. The average of the first and third elements.
¿Qué es Triadas de Dobereiner? » Su Definición y Significado [2022]
furfural. magnesium. triad. Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner (born Dec. 13, 1780, Hof an der Saale [Germany]—died March 24, 1849, Jena) was a German chemist whose observation of similarities among certain elements anticipated the development of the periodic system of elements. As a coachman's son, Döbereiner had little opportunity for formal.

Dobereiner's Triads Classification, Chemistry Lecture Sabaq.pk YouTube
In 1817, the first Dobereiner's triad was discovered. Calcium, strontium, and barium are alkaline earth metals that make up this compound. Three more triads were identified later on. Let's take a closer look at these triads. The following are five of Dobereiner's triads: Triad 1: The alkali metals lithium, sodium, and potassium made up.

Dobereiner's Triads & Newlands Law of Octave Periodic classification of elements SSC Board
In the history of the periodic table, Döbereiner's triads were an early attempt to sort the elements into some logical order by their physical properties. In 1829, the German chemist Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner noted that there were groups of three elements (hence "triads") which had similar physical properties. He also noted that some quantifiable properties of elements (e.g. atomic weight.

Dobereiner's Triads Class 10 Chemistry Periodic Classification of Elements YouTube
The Dobereiner's triad's examples: Lithium- 6.94. Sodium- 22.99. Potassium- 39.1. Thus the atomic masses give the arithmetic means that corresponds to 23.02 and are also similar to the atomic mass of sodium. Triad 2: Calcium, strontium, and barium are some strong examples of the Law of triads. Barium- 137.3,

Dobereiner's Triads Periodic table Chemistry Class 11 YouTube
The first of Dobereiner's triads was identified in the year 1817 and was constituted by the alkaline earth metals calcium, strontium and barium. Three more triads were identified by the year 1829. These triads are tabulated below. Triad 1. This triad was made up of the alkali metals lithium, sodium and potassium.

Na=Li+K/2=7+39/2=46/2=23 What is dobereiners law of triads explain with the help of one example
Johann Wolfgang Dobereiner, who attempted to sort the elements in an order which consisted of triads. In the history of the periodic table, Dobereiner's triads were an early attempt to sort the elements into some logical order by their physical properties. In 1817, a letter reported Johann Wolfgang Dobereiner's observations of the alkaline.

Dobereiner's Triads Chemistry YouTube
Dobereiner's Triad. Dobereiner arranged the element in increasing order of atomic masses. He found that the atomic mass of the middle element was approximately equal to the arithmetic mean (average) of the atomic masses of the other two elements of that triad when they are arranged in their increasing order of atomic mass, e.g., Li, Na, K.

Dobereiner's Triads 02 YouTube
This was known as the Dobereiner's law of triads. The law states that when elements are placed in the ascending order of atomic masses, groups of three elements having similar properties are obtained. The atomic mass of the middle element of the triad is equal to the mean of the atomic masses of the other two elements of the triad.

Dobereiner's Law Of Triads In Just 4 Minutes Chemistry Calibre Tutorial YouTube
Hello Friends, Checkout our Video on Explanation Video Dobereiner's Triads0:00 Introduction0:10 Dobereiner's Triads1:05 Dobereiner's law of Traids 1:53 1.