
Cross Product for Calculus Everything You Need to Know
The cross product and the volume of a parallelepiped. The volume of the parallelepiped determined by u, v, and w is | (u × v) ⋅ w |. As a dot product of two vectors, the quantity (u × v) ⋅ w is a scalar and is called the triple scalar product. Activity 9.4.4. Suppose u = 3, 5, − 1 and v = 2, − 2, 1 .
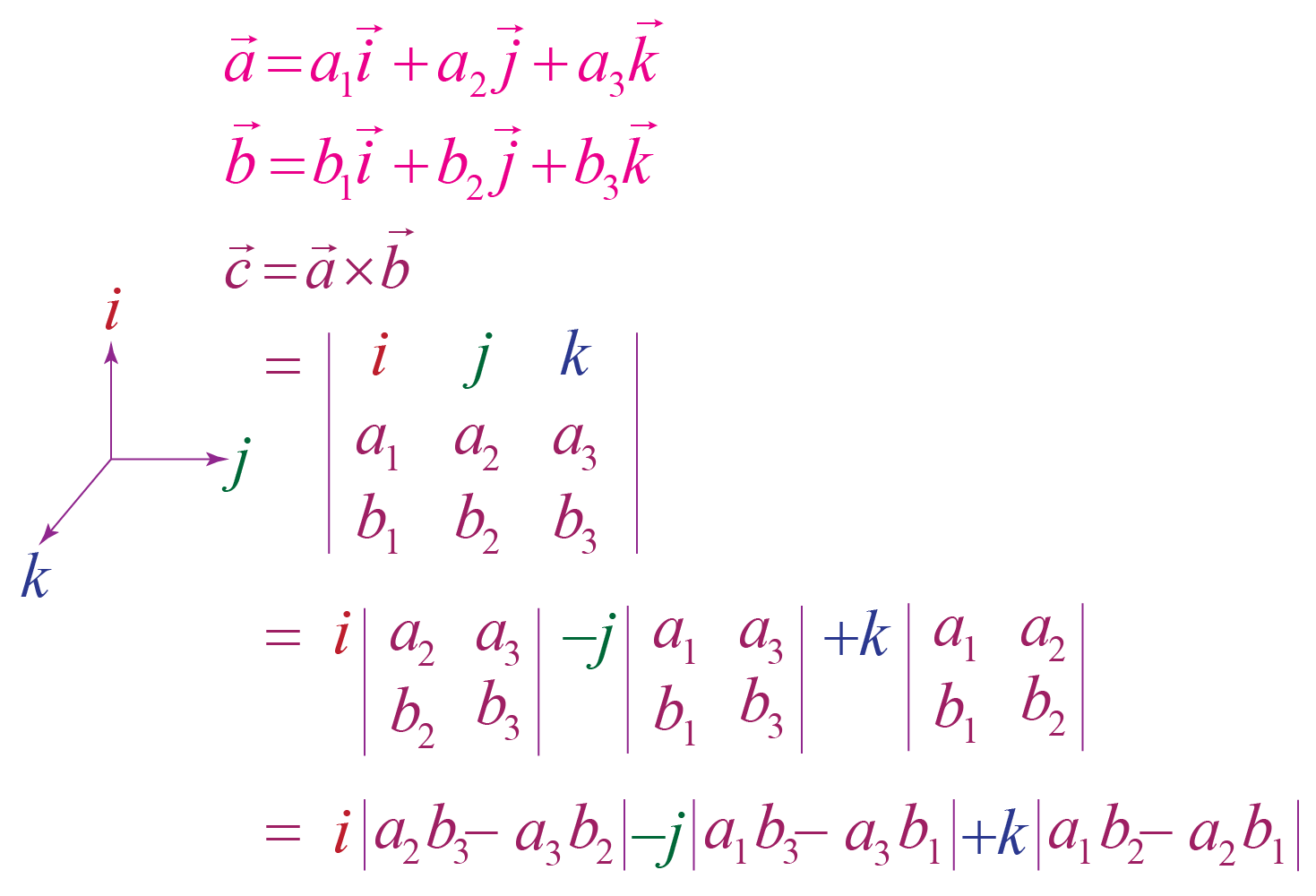
Cross Product Cuemath
The cross product may be used to determine the vector, which is perpendicular to vectors x 1 = (x 1, y 1, z 1) and x 2 = (x 2, y 2, z 2). Additionally, magnitude of the cross product, namely | a × b | equals the area of a parallelogram with a and b as adjacent sides. Properties of the Cross Product:
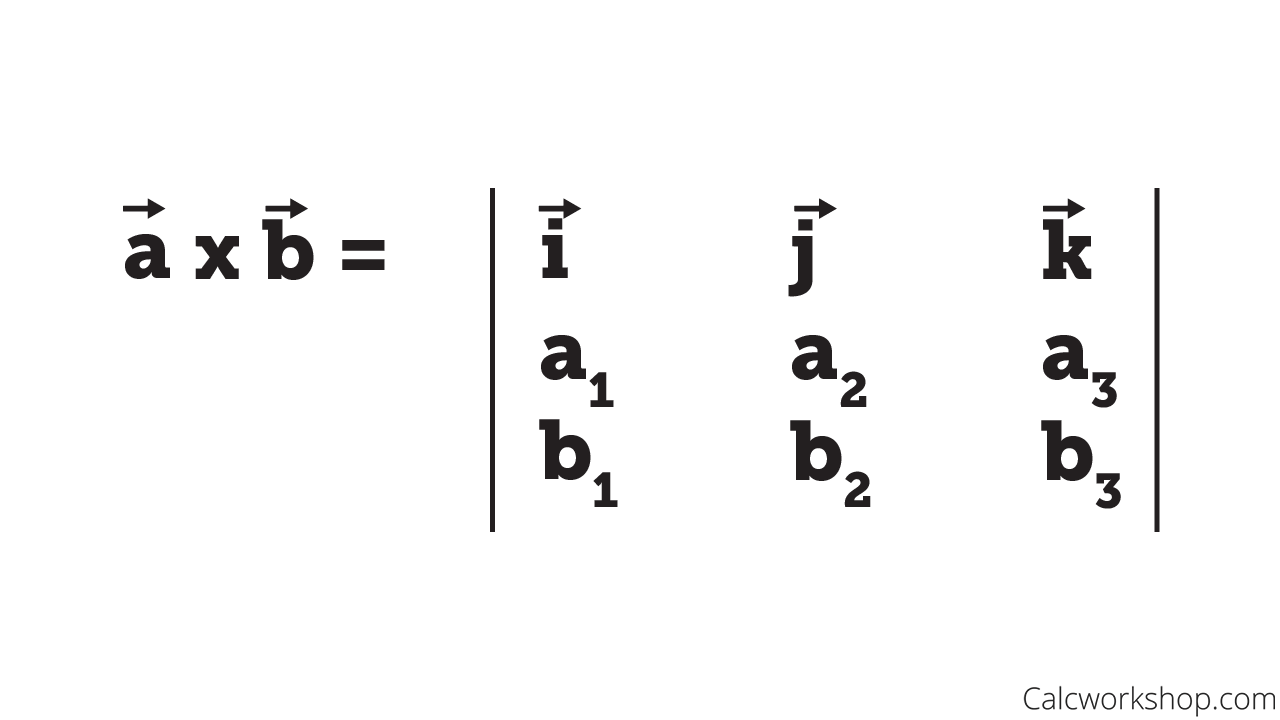
Cross Product for Calculus Everything You Need to Know
Cross product. The cross product is a binary operation, involving two vectors, that results in a third vector that is orthogonal to both vectors. The figure below shows two vectors, u and v, and their cross product w. Notice that u and v share the same plane, while their cross product lies in an orthogonal plane. This will always be the case.

Perkalian Dot Dan Cross Umi Soal
Cross product is a form of vector multiplication, performed between two vectors of different nature or kinds. A vector has both magnitude and direction. We can multiply two or more vectors by cross product and dot product.When two vectors are multiplied with each other and the product of the vectors is also a vector quantity, then the resultant vector is called the cross product of two vectors.
PPT Cross Product PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2849156
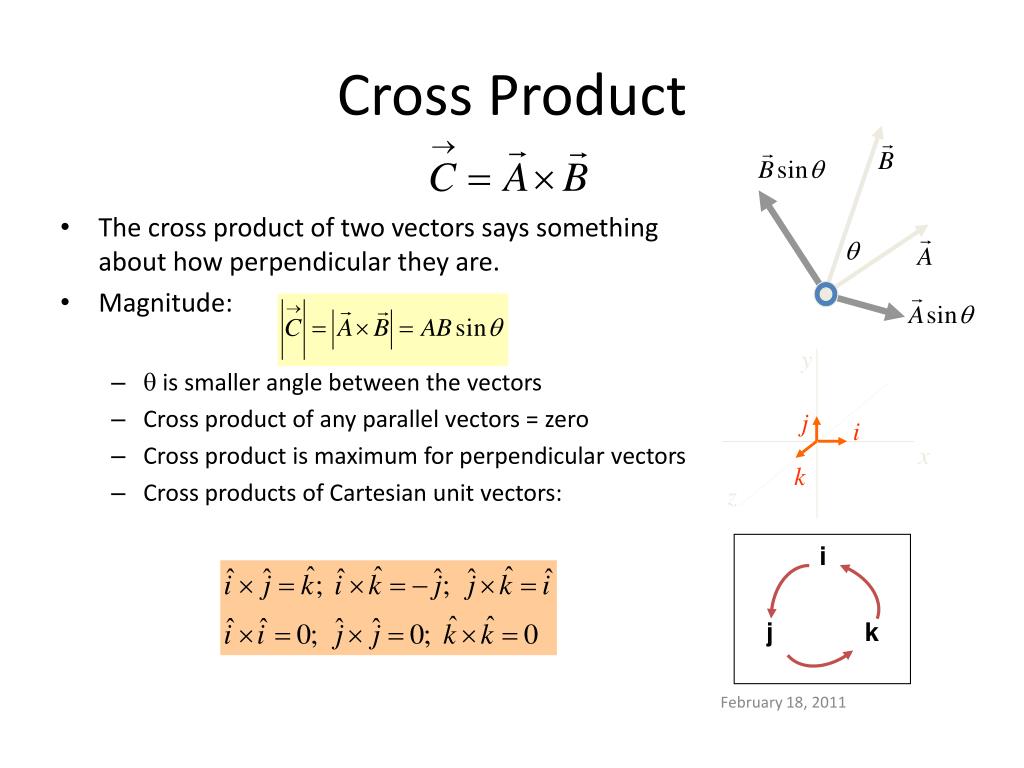
We have just shown that the cross product of parallel vectors is \(\vec 0\). This hints at something deeper. Theorem 86 related the angle between two vectors and their dot product; there is a similar relationship relating the cross product of two vectors and the angle between them, given by the following theorem.

Rumus Dan Sifat Perkalian Silang Cross Product 2 Vektor Beserta Pola Riset
Properties of the cross product. We write the cross product between two vectors as a → × b → (pronounced "a cross b"). Unlike the dot product, which returns a number, the result of a cross product is another vector. Let's say that a → × b → = c → . This new vector c → has a two special properties. First, it is perpendicular to.

Perkalian Silang Dua Vektor (Cross Product) YouTube
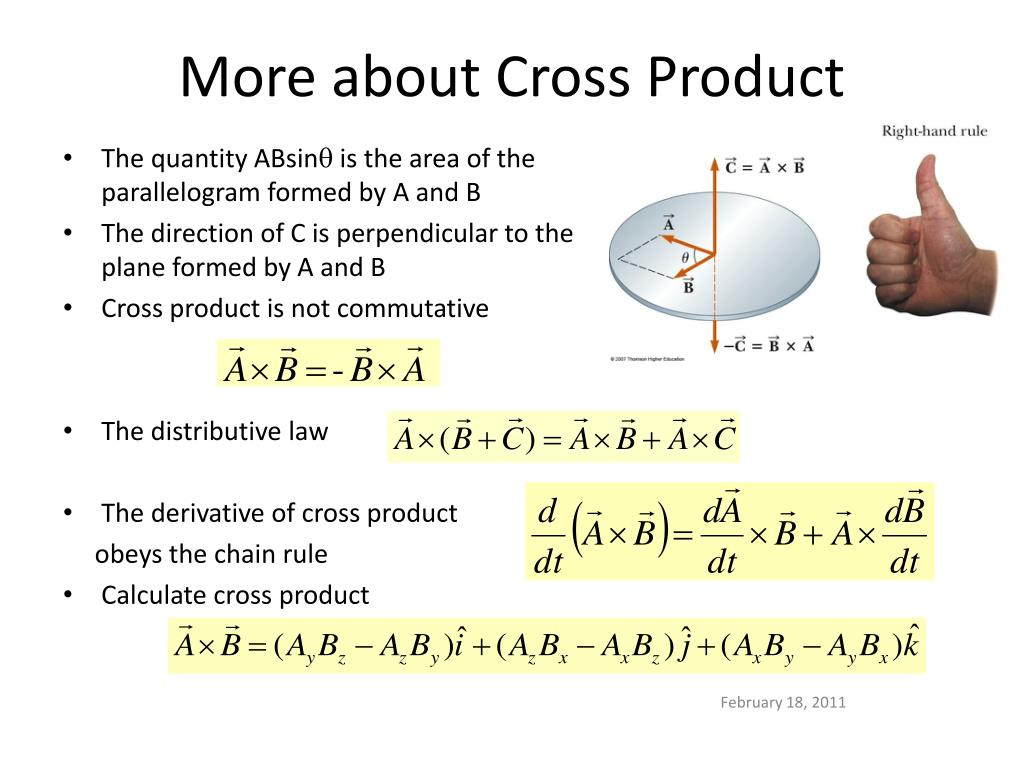
The first step is to redraw the vectors →A and →B so that the tails are touching. Then draw an arc starting from the vector →A and finishing on the vector →B . Curl your right fingers the same way as the arc. Your right thumb points in the direction of the vector product →A × →B (Figure 3.28). Figure 3.28: Right-Hand Rule.

Contoh Soal Cross Product LEMBAR EDU
A vector has magnitude (how long it is) and direction:. Two vectors can be multiplied using the "Cross Product" (also see Dot Product). The Cross Product a × b of two vectors is another vector that is at right angles to both:. And it all happens in 3 dimensions! The magnitude (length) of the cross product equals the area of a parallelogram with vectors a and b for sides:

How to Find the Cross Product of Two Vectors YouTube
Dari persamaan perkalian silang di atas, dapat disimpulkan bahwa hasil perkalian silang dua buah vektor adalah sebuah vektor baru yang arahnya tegak lurus pada bidang yang dibentuk oleh dua vektor tersebut. Simbol dari perkalian silang adalah " × " (baca: cross). Karena hasil perkalian silang adalah vektor maka perkalian silang atau cross product disebut juga dengan perkalian vektor atau.
Cross Product Of Vectors 2d slide share
Latihan Soal Perkalian Silang Cross Product Dua Vektor (Sukar) Pertanyaan ke 1 dari 5. Jika A = 2i − 6j − 3k dan B = 4i + 3j − k, maka vektor satuan yang tegak lurus terhadap kedua vektor tersebut adalah…. 1. 1 7i + 2 3j − 2 3k. 1 7 i + 2 3 j − 2 3 k. 2.

Perkalian Vektor ǀ Dot Product dan Cross Product, Pengertian & Contohnya Aisyah Nestria
The Cross Product Calculator is an online tool that allows you to calculate the cross product (also known as the vector product) of two vectors. The cross product is a vector operation that returns a new vector that is orthogonal (perpendicular) to the two input vectors in three-dimensional space. Our vector cross product calculator is the.
The Cross Product YouTube
The proof can be given using the distributive property of the cross product and the fact that c(v × w) = (cv) × w = v × (cw) for vectors v and w and a scalar c : A × B = (Axˆi + Ayˆj + Azˆk) × (Bxˆi + Byˆj + Bzˆk) = AxBx(ˆi × ˆi) + AxBy(ˆi × ˆj) + AxBz(ˆi × ˆk) + AyBx(ˆj × ˆi) + AyBy(ˆj × ˆj) + AyBz(ˆj × ˆk) + AzBx.
Cross Product and its Properties Math, Calculus, Cross products ShowMe
Learning Objectives. 2.4.1 Calculate the cross product of two given vectors.; 2.4.2 Use determinants to calculate a cross product.; 2.4.3 Find a vector orthogonal to two given vectors.; 2.4.4 Determine areas and volumes by using the cross product.; 2.4.5 Calculate the torque of a given force and position vector.

What is the CROSS PRODUCT and how to find the cross product of two vectors YouTube
The Cross Product and Its Properties. The dot product is a multiplication of two vectors that results in a scalar. In this section, we introduce a product of two vectors that generates a third vector orthogonal to the first two. Consider how we might find such a vector. Let [latex]\mathbf {u} =\langle u_1, u_2, u_3 \rangle [/latex] and [latex.

Perkalian Vektor ǀ Dot Product dan Cross Product, Pengertian & Contohnya Aisyah Nestria
Cross product is a binary operation on two vectors in three-dimensional space. It results in a vector that is perpendicular to both vectors. The Vector product of two vectors, a and b, is denoted by a × b. Its resultant vector is perpendicular to a and b. Vector products are also called cross products.
Lecture 3 Cross Products, Equations of Planes
The cross product (purple) is always perpendicular to both vectors, and has magnitude zero when the vectors are parallel and maximum magnitude ‖ ⇀ a‖‖ ⇀ b‖ when they are perpendicular. (Public Domain; LucasVB ). Example 12.4.1: Finding a Cross Product. Let ⇀ p = − 1, 2, 5 and ⇀ q = 4, 0, − 3 (Figure 12.4.1 ).