
Chain promises in Fetch JavaScript The freeCodeCamp Forum
Here we are fetching a JSON file across the network, parsing it, and printing the data to the console. The simplest use of fetch() takes one argument — the path to the resource you want to fetch — and does not directly return the JSON response body but instead returns a promise that resolves with a Response object.. The Response object, in turn, does not directly contain the actual JSON.
GitHub shansatech/FetchAPIandPromises
But in order for a promise to exist in the first place, it must first be built. So it must be created in the case of the fetch API, it's the fetch function that builds the promise and returns it.

How to make HTTP requests using Fetch API and Promises by Armando
JavaScript Promises and all their glory! This is episode 12 in a 10 part series I'm calling 10 things Javascript Developers Should Know But Probably Don't.Ja.

Fetch with Promise.all and async / await DEV Community
Here we are: calling the fetch() API, and assigning the return value to the fetchPromise variable; immediately after, logging the fetchPromise variable. This should output something like: Promise {

[Solved] Promises/Fetch in JavaScript how to extract 9to5Answer
Fetch returns a promise, and you can chain multiple promises, and use the result of the 1st request in the 2nd request, and so on. This example uses the SpaceX API to get the info of the latest launch, find the rocket's id, and fetch the rocket's info.
Understanding Asynchronous operation, Promise & Fetch Call in
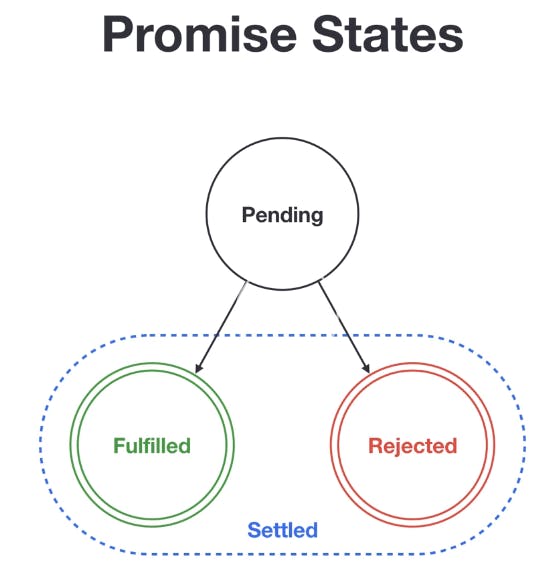
Promise.then. fetch is an asynchronous function. What this function returns is a Promise object. This kind of object has three possible states: pending, fullfilled and rejected. It always starts.

Javascript Fetch (Promises and Async/Await) YouTube
In this video I'll teach you the very basics of Promise and Fetch. I use both of them on a daily basis and I is veery helpful if you understand how they work.

Fetch Requests, Promises, and Asynchronous Code DEV Community
ES6 - A beginners guide (12 Part Series) This time I am going to cover ES6's introduction of Promise and Fetch as native JavaScript functionality in the browser. A lot of dev's will use 3rd party libraries such as Axios, SuperAgent, or jQuery although it might not always be necessary to do so and it may just add bloat to your projects.

NodeJS Using Promises & Fetch Part 11 Programming Stream 0602
Check out the Fetch API demo.. Summary. The Fetch API allows you to asynchronously request a resource. Use the fetch() method to return a promise that resolves into a Response object. To get the actual data, you call one of the methods of the Response object e.g., text() or json().These methods resolve into the actual data.

JavaScript Promises & Fetch API YouTube
Once the promise has been resolved, the results from the fetch method can now be assigned to the response variable. The same thing happens on line 3. The .json method returns a promise, and we can use await still to delay the assigning until the promise is resolved. To Block Code or Not to Block Code

Promises and the Fetch API The JavaScript
In the ever-evolving landscape of web development, mastering advanced JavaScript concepts is essential for creating efficient and responsive applications. Among these concepts, Promises, async/await, and the fetch API stand out as powerful tools for handling asynchronous operations, managing network requests, and improving code readability.

Promises An example with fetch 18 YouTube
The fetch call returns a Promise object which will help us with this uncertainty. Promises. Turn asynchronous code into re-usable synchronous "objects" that can be (eventually) resolved or rejected while letting the program continue working. Much easier to manage asynchronous and synchronous tasks without "callback hell".

Build a website using API E7 JavaScript promises promise all and
Fetch () allows you to make network requests similar to XMLHttpRequest (XHR). The main difference is that the Fetch API uses Promises, which enables a simpler and cleaner API, avoiding callback hell and having to remember the complex API of XMLHttpRequest. Here is an example of the fetch api. 01. 02.
[Solved] Promises/Fetch in JavaScript how to extract 9to5Answer
JavaScript promises and fetch () As developers, we often need to gather data from external sources for use in our own programs. Doing this in JavaScript used to require clunky code or the use of outside libraries, but fortunately the Fetch API has in recent years made retrieving, adding, editing, and removing data from external databases easier.

Combining fetch and the Promise all Method YouTube
The Fetch API is a replacement for jQuery's AJAX function. AJAX allows you to send a GET or POST request to another URL and consume the response. It's useful in my opinion, but I'm about moving into the future; jQuery represents the past. Plus, I prefer dealing with vanilla JS over any libraries. Fetch API leverages Promises.
How to Learn JavaScript Promises and Async/Await in 20 Minutes
Fetch () allows you to make network requests similar to XMLHttpRequest (XHR). The main difference is that the Fetch API uses Promises, which enables a simpler and cleaner API, avoiding callback.