Pathway Efusi Pleura PDF
However, the exact molecular pathways that promote the infiltration of the pleura are unknown. The majority of RA-associated effusions will resolve spontaneously or with the initiation of specific RA treatment and thus do not necessitate additional management strategies. In cases of breathlessness and chest pain, thoracocentesis is recommended.

Pleural Effusion (DETAILED) (pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, treatment) Medical News Alley
A thorough chest examination should be performed, with particular attention to dullness to percussion because it is sensitive and specific for diagnosing effusion. 17 Figure 1 outlines an approach.

Pleural effusion Video, Anatomy, Definition & Function Osmosis
thickened pleura) and liquid components of a pleural process. It is useful in detecting abnor-malities that are subpulmonic (under the lung) or subphrenic (below the diaphragm) and in differentiating them.9-11 A major use of ultrasonography is to guide thoracentesis in small or loculated pleural effusions, thereby increasing the yield and

Pathway Efusi Pleura
A pleural effusion, ie, an excessive accumulation of fluid in the pleural space, indicates an imbalance between pleural fluid formation and removal. Accumulation of pleural fluid is not a specific disease, but rather a reflection of underlying pathology. Pleural effusions accompany a wide variety of disorders of the lung, pleura, and systemic.

PATHWAY EFUSI PLEURA Teguh Subianto
Pleural effusion is the accumulation of fluid in between the parietal and visceral pleura, called the pleural cavity. It can occur by itself or can be the result of surrounding parenchymal disease like infection, malignancy, or inflammatory conditions. Pleural effusion is one of the major causes of pulmonary mortality and morbidity.[1][2][3]

8 Pathway Efusi Pleura PDF
the diagnostic pathway •Indwelling pleural catheters can now allow many patients with recurrent effusions to be managed at home • Link to this article online for CPD/CME credits SOURCES AND SELECTION CRITERIA We searched through PubMed, Embase, Medline, and the Cochrane database of systematic reviews from inception to

Efusi Pleura Pathway PDF
A pleural effusion is an abnormal collection of fluid in the pleural space resulting from excess fluid production or decreased absorption or both. It is the most common manifestation of pleural disease, with etiologies ranging from cardiopulmonary disorders to symptomatic inflammatory or malignant diseases requiring urgent evaluation and trea.

Pathway Efusi Pleura PDF
Terminology. "Pleural effusion" is commonly used as a catch-all term to describe any abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity. The lack of specificity is mainly due to the limitations of the imaging modality. Given that most effusions are detected by x-ray, which generally cannot distinguish between fluid types, the fluid in.

pleuraleffusionspathogenesisandanteriorposteriorchestxrayfindings Calgary Guide
Pleurodesis involves the administration of a drug or material in the pleural space to cause adhesions between the parietal and visceral pleura, and prevention of fluid reaccumulation. Talc is the most widely used pleurodesis agent, and has been shown in previous meta-analysis ( 33 ) and a head-to-head RCT ( 45 ) to be the most effective.

Efusi Pleura Pathway PDF
Exudative stage, in which there is an accumulation of fluid in the pleural space due to increased capillary permeability that results from proinflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin 8 (IL-8) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-a). The pleural fluid in this early stage is usually clear exudative fluid with a predominance of neutrophils. Pleural fluid in this stage is simple parapneumonic.

Pathway Efusi Pleura PDF
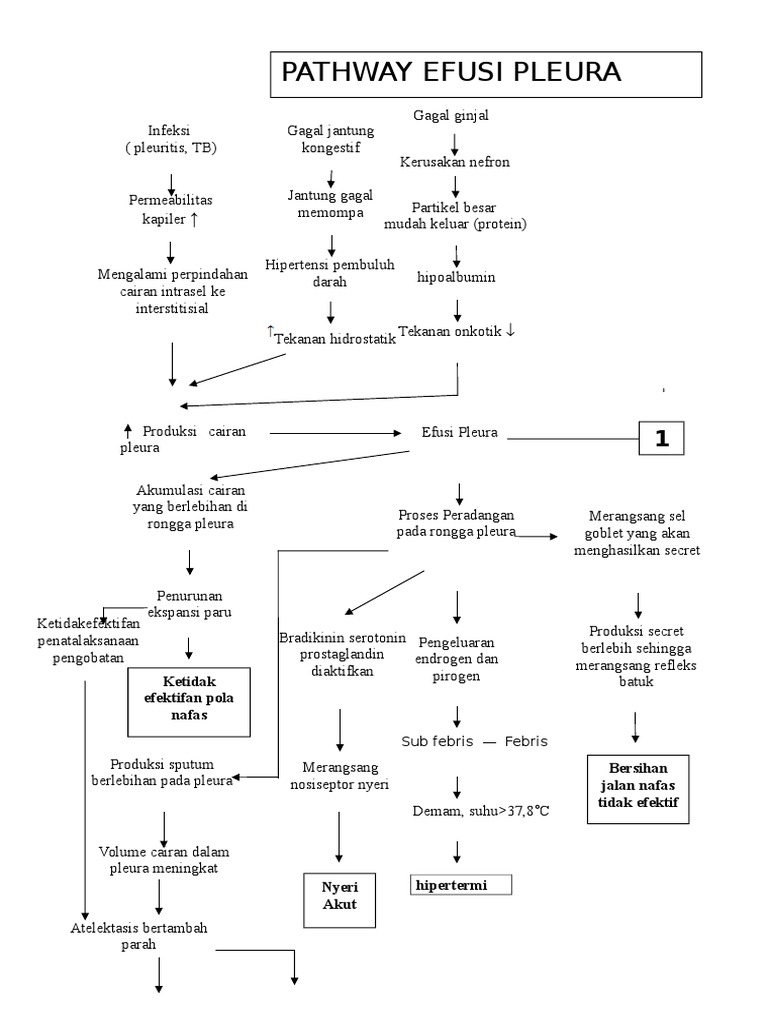
Gambar 2.1 Pathway Efusi Pleura (sudoyo, 2009:2330). 2.1.5 Klasifikasi Efusi Pleura Transudat adalah cairan pleura dalam keadaan normal yang jumlahnya sedikit. Transudat terjadi apabila hubungan normal antara tekanan kapiler hidrostatik dan koloid osmotik menjadi terganggu, sehingga terbentuknya cairan pada satu sisi pleura akan melebihi.

(DOC) 8 Pathway Efusi Pleura DOKUMEN.TIPS
Pleural effusion has a wide differential diagnosis. Its most common causes are congestive heart failure, cancer, pneumonia, and pulmonary embolism. A delayed etiological diagnosis can be associated with markedly higher morbidity and mortality, e.g., if the patient develops a pulmonary empyema on the basis of a parapneumonic effusion.

Pleural Effusion Nursing Care Plan & Management RNpedia
Results: The most common causes of pleural effusion are congestive heart failure, cancer, pneumonia, and pulmonary embolism. Pleural fluid puncture (pleural tap) enables the differentiation of a transudate from an exudate, which remains, at present, the foundation of the further diagnostic work-up. When a pleural effusion arises in the setting.

Pathway Efusi Pleura. PDF
The parietal pleura has a more significant role in pleural fluid homeostasis. Its vessels are closer to the pleural space compared with its visceral counterpart; it contains lymphatic stomata, absent on visceral pleura, which are responsible for a bulk clearance of fluid. The diagnosis and successful treatment of pleural effusions requires a.

Pathway Efusi Pleura PDF
A pleural effusion is a condition affecting the lining of the lung (pleura). Your pleura is a large, thin sheet of tissue that wraps around your lungs and lines the inside of your chest wall. Between the two layers is a very thin space that is normally filled with a small amount of fluid. Occasionally this pleural space can fill with air, fluid.

Pathway Efusi Pleura PDF
Considerations in the differential diagnosis of transudative pleural effusion include the following: Congestive heart failure (most common) Cirrhosis with hepatic hydrothorax. Nephrotic syndrome. Peritoneal dialysis/continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Hypoproteinemia. Glomerulonephritis. Superior vena cava obstruction.