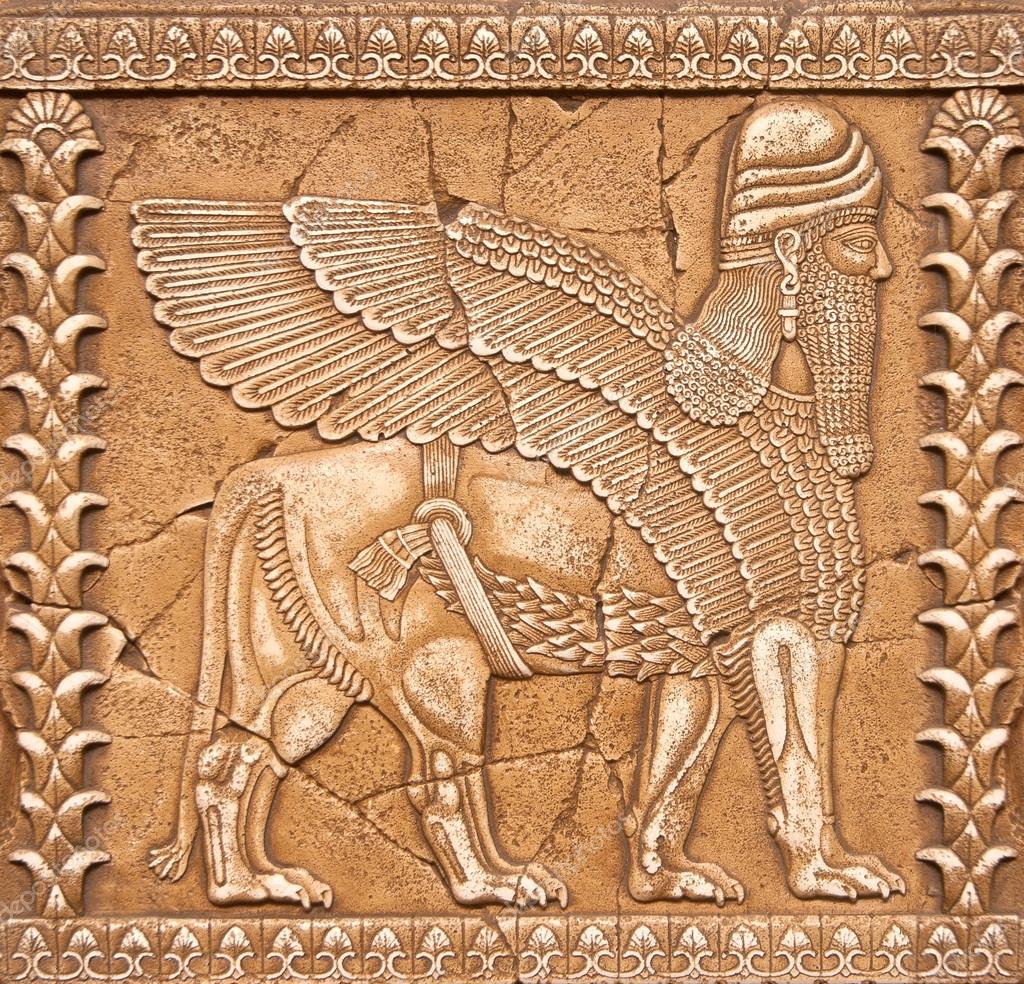

Piedra tallada Lamassu o Shedu en Mesopotamia mitología fotografía de stock © Kasza 18386857
history of Mesopotamia, history of the region in southwestern Asia where the world's earliest civilization developed. The name comes from a Greek word meaning "between rivers," referring to the land between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, but the region can be broadly defined to include the area that is now eastern Syria, southeastern Turkey, and most of Iraq.

DIOSES DE MESOPOTAMIA HISTORIA Y CARACTERISTICAS
Mesopotamian mythology refers to the myths, religious texts, and other literature that comes from the region of ancient Mesopotamia which is a historical region of Western Asia, situated within the Tigris-Euphrates river system that occupies the area of present-day Iraq. In particular the societies of Sumer, Akkad, and Assyria, all of which.
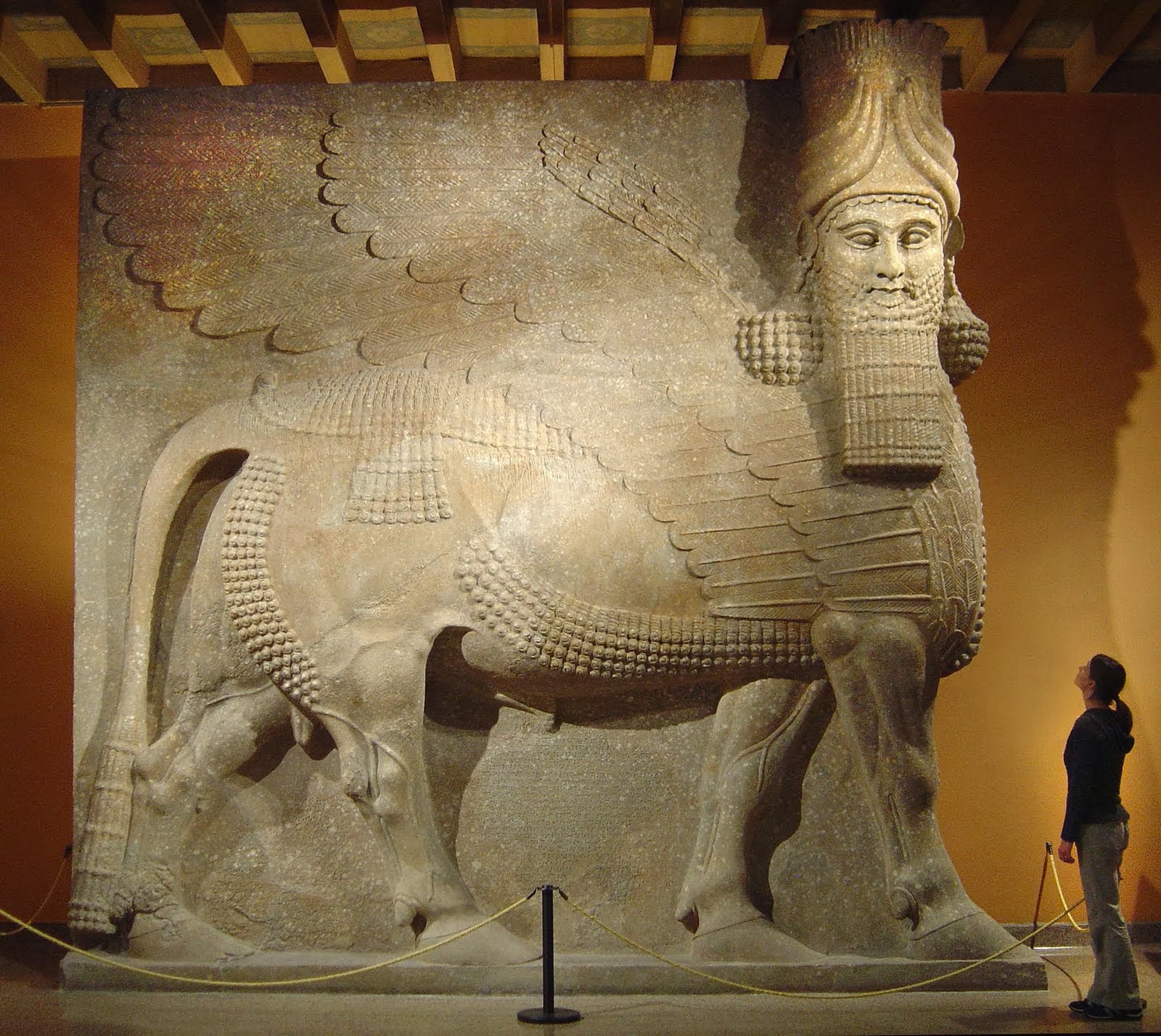

Historia Universal MESOPOTAMIA, Cuna de la civilización.
Mesopotamian mythology, the myths, epics, hymns, lamentations, penitential psalms, incantations, wisdom literature, and handbooks dealing with rituals and omens of ancient Mesopotamia.. A brief treatment of Mesopotamian mythology follows. For full treatment, see Mesopotamian religion. The literature that has survived from Mesopotamia was written primarily on stone or clay tablets.

Lammasu/ Shedu (Divinidad Protectora de las puertas de ciudades y palacios/ mitología
Mesopotamian Religion was central to the people's lives. Humans were created as co-laborers with their gods to hold off the forces of chaos and to keep the world running smoothly. As in ancient Egypt, the gods were honored daily for providing humanity with life and sustenance, and people were expected to give back through works that honored the.

Lamassu Mythological Creature Sumerian Assyrian Babylonian for him Art Drawing Mesopotamian Luck
Pre-Pottery Neolithic period Overview of Göbekli Tepe with modern roof to protect the site against the weather. The early Neolithic human occupation of Mesopotamia is, like the previous Epipaleolithic period, confined to the foothill zones of the Taurus and Zagros Mountains and the upper reaches of the Tigris and Euphrates valleys. The Pre-Pottery Neolithic A (PPNA) period (10,000-8,700 BC.

Mesopotamian Mythology
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris-Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent.Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and Iran, In the broader sense, the historical region of Mesopotamia included parts of present-day Kuwait, Syria, and Turkey.. The Sumerians and Akkadians (including Assyrians and Babylonians), each.
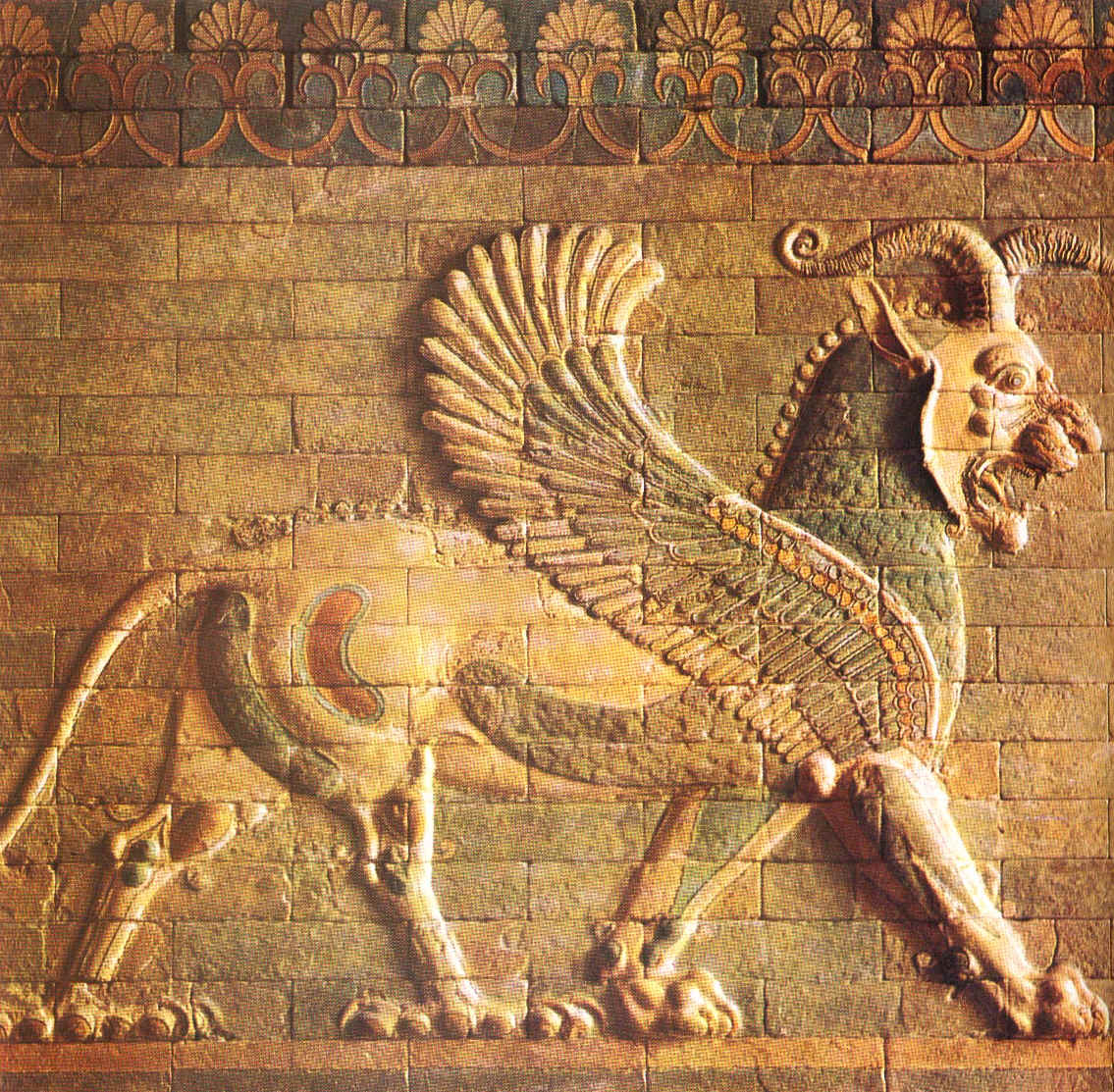

mesopotamia MESOPOTAMIA
Akin también celebra la temporada de siembra y corte de cebada en la Mesopotamia Antigua. Lugares sagrados de la mitología Mesopotámica Nippur. Fue una de las ciudades sumerias más antiguas y uno de los centros religiosos más importantes de Mesopotamia. Algunos investigadores datan la creación de la ciudad alrededor del año 5000 a.C.
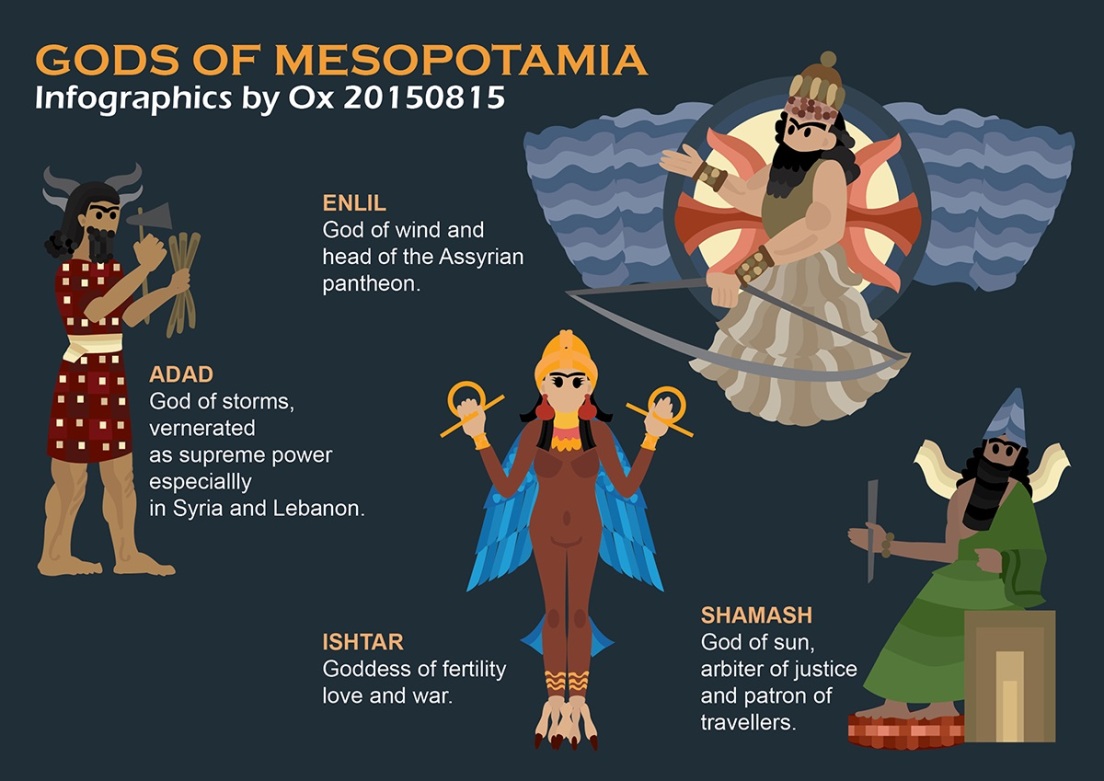
Infographics Gods of Mesopotamia
Early civilizations began to form around the time of the Neolithic Revolution—12000 BCE. Some of the major Mesopotamian civilizations include the Sumerian, Assyrian, Akkadian, and Babylonian civilizations. Evidence shows extensive use of technology, literature, legal codes, philosophy, religion, and architecture in these societies.
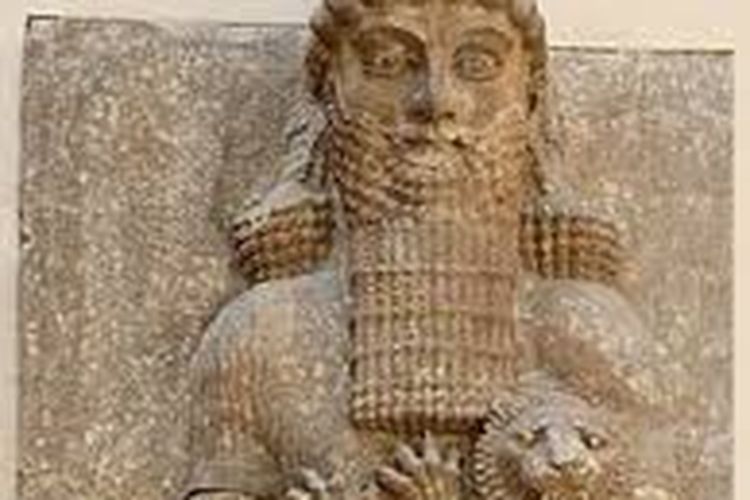

Gilgamesh, Sosok Dua Per Tiga Dewa dari Mesopotamia Kuno
Mesopotamian religion, beliefs and practices of the Sumerians and Akkadians, and their successors, the Babylonians and Assyrians, who inhabited ancient Mesopotamia (now in Iraq) in the millennia before the Christian era.These religious beliefs and practices form a single stream of tradition. Sumerian in origin, Mesopotamian religion was added to and subtly modified by the Akkadians (Semites.

DESCUBRE LOS MÁS IMPORTANTES DIOSES DE MESOPOTAMIA
Mesopotamia adalah peradaban kuno yang terletak di antara Sungai Tigris dan Sungai Efrat. Hari ini, daerah ini dikenal sebagai Irak. Mitologi inti Mesopotamia adalah campuran sihir dan hiburan, dengan kata-kata bijak, pujian untuk pahlawan atau raja individu , dan kisah magis. Para ahli percaya bahwa tulisan pertama mitos dan epos Mesopotamia adalah alat bantu mnemonik untuk membantu pembaca.

DIOSES DE MESOPOTAMIA HISTORIA Y CARACTERISTICAS
History. Archaeology. Ancient Egypt. Ruins. More. Mohenjo-Daro was one of two prominent cities of the ancient Indus Valley civilization. The citadel, a center of activity at the city's peak, towers over the.

12 de los dioses antiguos más poderosos de Mesopotamia Ancient Code
Ide akan Mesopotamia telah memabukkan Barat selama berabad-abad. Alastair Sooke melihat peradaban yang menjadi sumber terbentuknya budaya modern.
Anunnaki DewaDewi Yang Mencipta Manusia Moden Dalam Mitologi Mesopotamia The Patriots
Mesopotamia is thought to be one of the places where early civilization developed. It is a historic region of West Asia within the Tigris-Euphrates river system. In fact, the word Mesopotamia means "between rivers" in Greek. Home to the ancient civilizations of Sumer, Assyria, and Babylonia these peoples are credited with influencing mathematics and astronomy.

DIOSES DE MESOPOTAMIA HISTORIA Y CARACTERISTICAS
Mesopotamia is a region of southwest Asia in the Tigris and Euphrates river system that benefitted from the area's climate and geography to host the beginnings of human civilization. Its history.

Los 14 dioses de Mesopotamia más importantes YouTube
Mitologi Mesopotamia adalah mitologi Sumeria, Akkadia, Assyria dan Babilonia dari wilayah antara sungai Tigris dan Efrat di Irak.. Banyak kisah dalam mitologi Sumeria yang muncul dalam agama Timur Tengah lainnya.. Pranala luar. alt.mythology Sumerian Mythology FAQ; The Sumerians and Akkadians Diarsipkan 2007-11-01 di Wayback Machine

DIOSES DE MESOPOTAMIA HISTORIA Y CARACTERISTICAS
The god Marduk and his dragon Mušḫuššu. Mesopotamian religion was the original religious beliefs and practices of the civilizations of ancient Mesopotamia, particularly Sumer, Akkad, Assyria and Babylonia between circa 6000 BC and 400 AD. The religious development of Mesopotamia and Mesopotamian culture in general, especially in the south, were not particularly influenced by the movements.