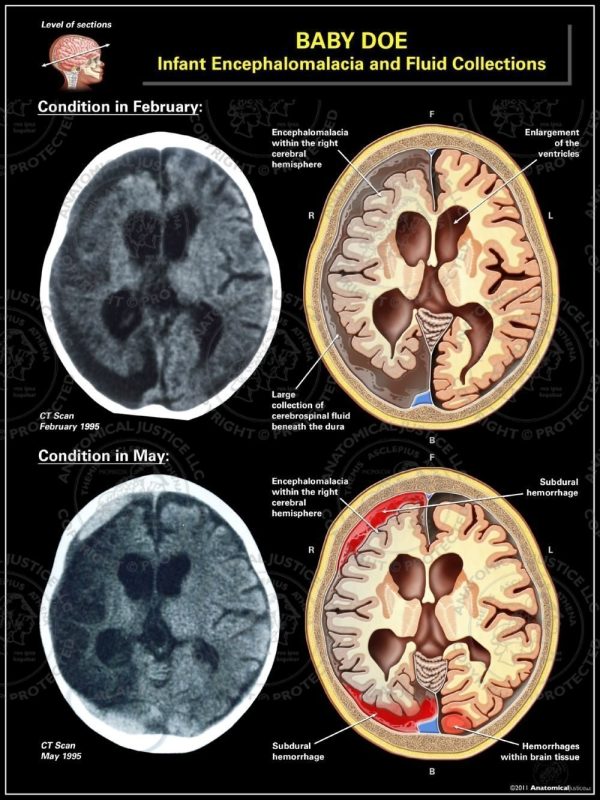
Infant Encephalomalacia and Fluid Collections
Namun, penyebab encephalomalacia yang paling sering adalah stroke atau cedera kepala serius, karena kedua kondisi tersebut berpotensi menyebabkan pendarahan (hemoragik) ke dalam otak. Pelunakan otak biasanya terjadi di area dengan akumulasi darah yang abnormal. Stroke juga menyebabkan gangguan aliran darah, sehingga otak tidak bisa mendapatkan.

Encephalomalacia Causes Symptoms And Treatment Nursa
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is a brain disorder likely caused by repeated head injuries. It causes the death of nerve cells in the brain, known as degeneration. CTE gets worse over time. The only way to definitively diagnosis CTE is after death during an autopsy of the brain. CTE is a rare disorder that is not yet well understood.
Encephalomalacia (softened Brain Tissue) Definition, Symptoms, Treatment
Encephalomalacia is the softening or loss of brain tissue after cerebral infarction, cerebral ischemia, infection, craniocerebral trauma, or other injury. The term is usually used during gross pathologic inspection to describe blurred cortical margins and decreased consistency of brain tissue after.
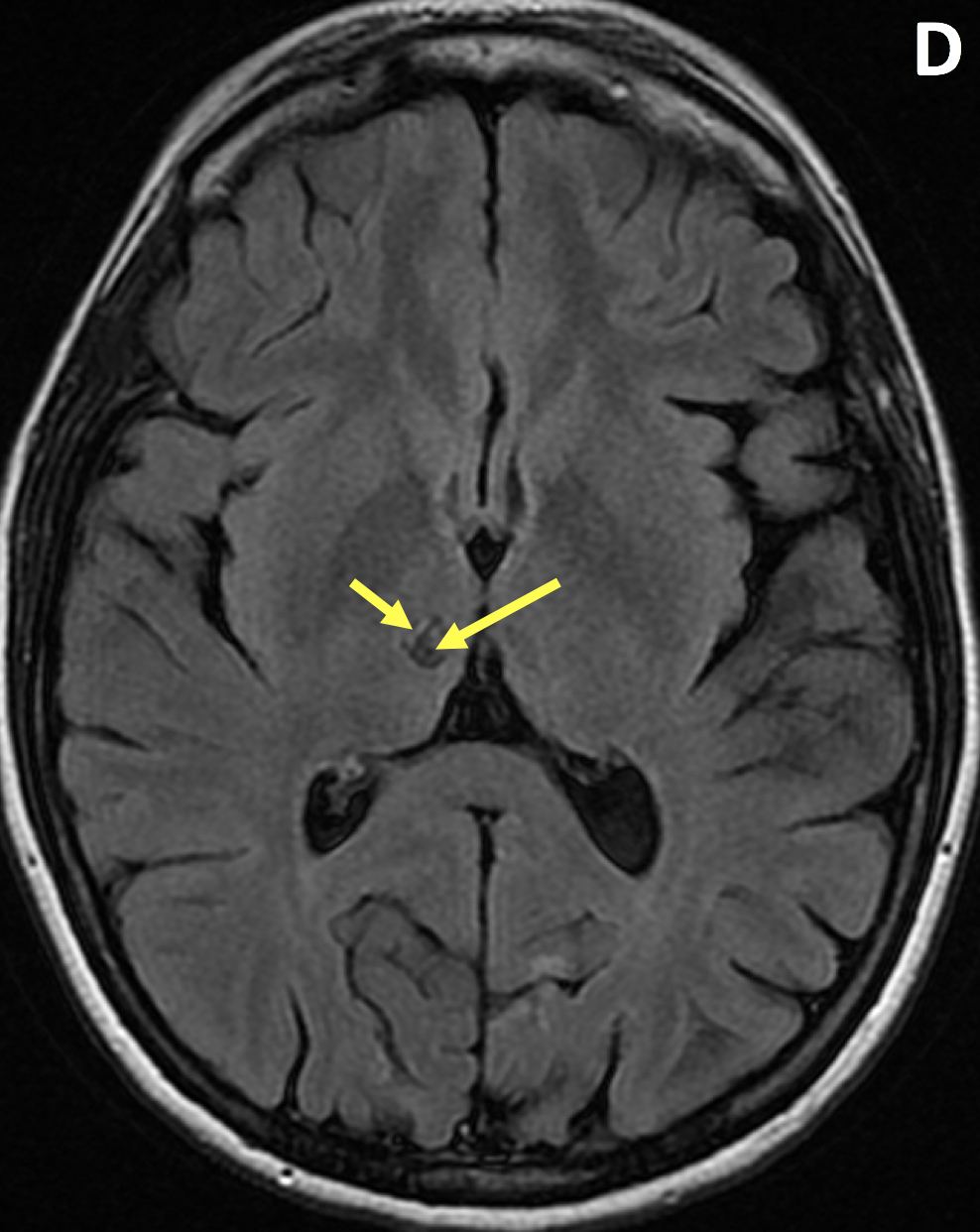
Encephalomalacia Diagnosis MRI Online
Encephalitis is brain inflammation (swelling). Causes include viral infections, infections from insect bites or an autoimmune reaction that affects your brain. It can be life-threatening or cause long-term complications. Treatment varies, but most people require hospitalization so they can receive intensive treatment, including life support.
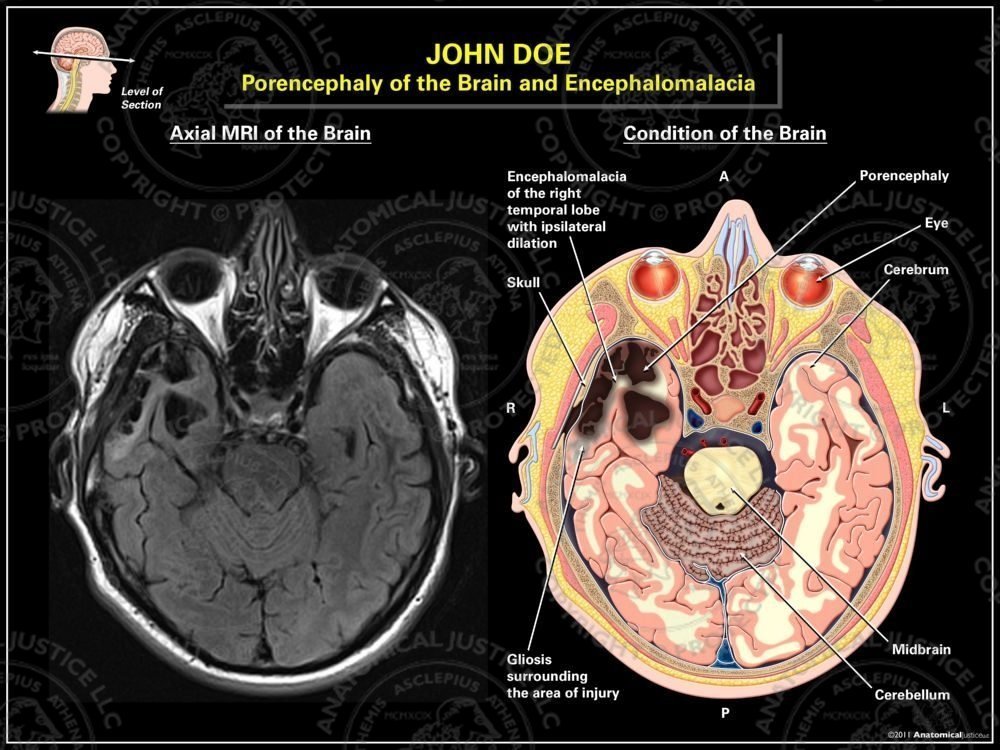
Porencephaly of the Brain and Encephalomalacia
BACKGROUND. Automated software-based Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) on unenhanced CT is associated with clinical outcomes after acute stroke. However, encephalomalacia or white matter hyperintensities (WMH) may result in a falsely low automated ASPECTS if such findings are interpreted as early ischemia. OBJECTIVE. The purpose of this study was to assess the impact of.

Encephalomalacia Causes, Types, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, Complications and Prevention
Encephalomalacia (literally, "softening of the brain") is a nonspecific term for the end result of liquefactive necrosis of brain parenchyma; it can be focal or diffuse, and can be seen in adults, children and even in utero. Encephalomalacia can occur anywhere in the brain; after trauma, characteristic locations are anteroinferior frontal.

Encephalomalacia Radiology Case
Encephalomalacia adalah suatu kondisi yang ditandai dengan pelunakan lokal pada jaringan otak akibat peradangan atau pendarahan. Kondisi ini terkadang juga dikenal dengan pelunakan otak. Pelunakan dapat terjadi di satu bagian otak tertentu atau mungkin lebih luas lagi.

Encephalomalacia Image
Symptoms. Bulging fontanel Enlarge image. Encephalitis may cause many different symptoms including confusion, personality changes, seizures or problems with movement. Encephalitis also may cause changes in sight or hearing. Most people with infectious encephalitis have flu-like symptoms, such as:
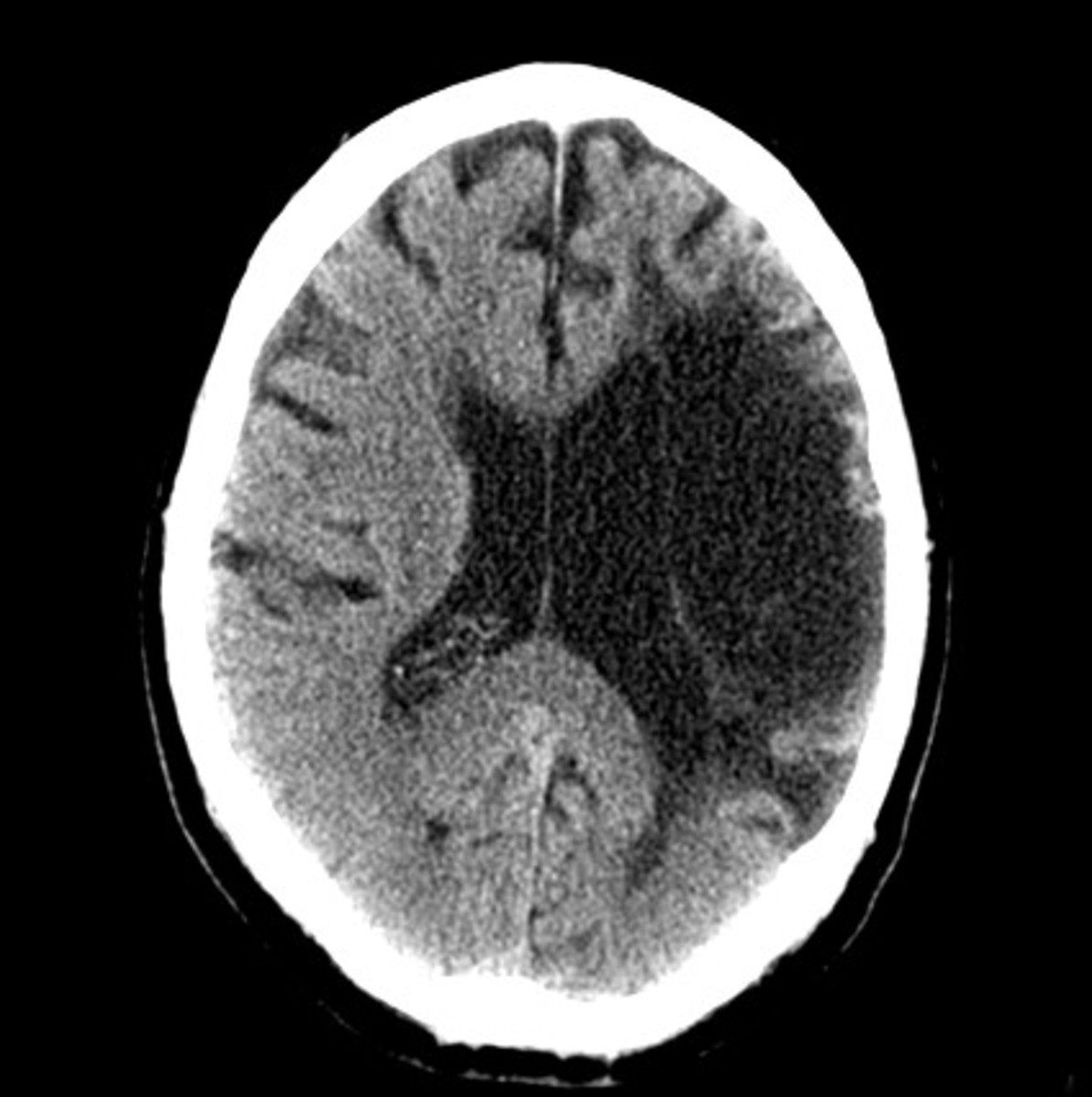
Encephalomalacia Symptoms, Prognosis, Treatment, Causes, Diagnosis HubPages
Pengertian Encephalomalacia. Encephalomalacia atau pelunakan otak adalah kondisi yang disebabkan oleh peradangan atau perdarahan di area tertentu. Pelunakan otak ini biasanya terjadi pada bagian leukoencephalomalacia atau materi putih otak dan polioencephalomalacia atau materi abu-abu otak.

Encephalomalacia Radiology Case
9 Citing Articles. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) 1,2 is an acute or subacute cerebral syndrome, the main manifestations of which are headache, encephalopathy, seizures, or.
Multicystic encephalomalacia Download Scientific Diagram
Pelunakan otak, begitulah encephalomalacia disebut, adalah kondisi kerusakan otak yang serius, karena mengakibatkan lunak atau menghilangnya jaringan yang berada di otak. Kerusakan ini bisa terjadi di bagian otak mana saja, termasuk lobus frontal, temporal, parietal, hingga oksipital dengan disertai defisit sensorik dan motorik.

Encephalomalacia Causes Symptoms And Treatment Nursa
Encephalomalacia is the softening or loss of brain tissue after cerebral infarction, cerebral ischemia, infection, craniocerebral trauma, or other injury.[] In the imaging classification of traumatic brain injury, encephalomalacia is a type of chronic condition secondary to injury of the brain.[] Cerebral softening leads to the brain changes which can have varied clinical manifestations.
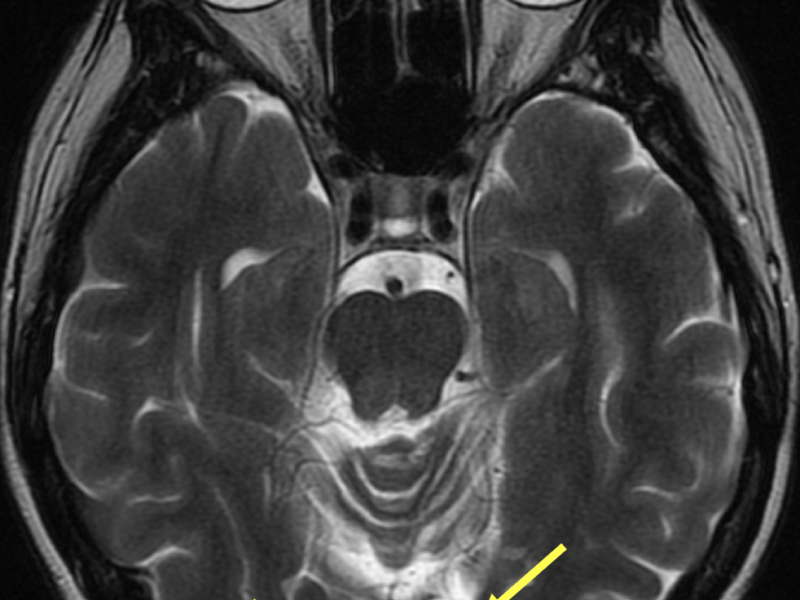
Encephalomalacia MRI Online
Cerebral softening. Cerebral softening, also known as encephalomalacia, is a localized softening of the substance of the brain, due to bleeding or inflammation. Three varieties, distinguished by their color and representing different stages of the disease progress, are known respectively as red, yellow, and white softening.

Figure 1 from Right frontal lobe encephalomalacia in an adult propionic acidemia patient with
Encephalomalacia (EM) on non-contrast cranial CT (NCCT) may be a better alternative to stroke history. The NCCT was used as a pretreatment screening modality for almost all the thrombectomy candidates. This approach can identify EM that occurs before the acute index stroke which could provide an objective indicator of a previous brain injury.
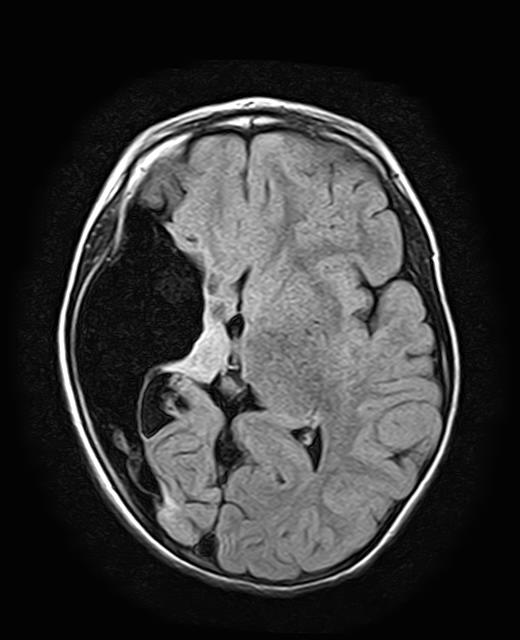
Encephalomalacia Image
Encephalomalacia is a serious condition that causes softening of tissue in the brain. It's also known as cerebral softening or brain softening. Fortunately, cases of Encephalomalacia are somewhat rare, although the ailment can affect patients of all age groups and ethnicities. Most people will never hear about Encephalomalacia. Thousands of people do live with this condition or deal with it.

Head CT showing encephalomalacia in the right frontal lobe. Download Scientific Diagram
Encephalomalacia is the end result of liquefactive necrosis of brain parenchyma following insult, usually occurring after cerebral ischemia, cerebral infection, hemorrhage, traumatic brain injury, surgery or other insults. It is often surrounded by an area of gliosis, which is the proliferation of glial cells in response to injury.