
Normal CT of the neck Image
pemeriksaan CT-Scan kepala klinis cephalgia menggunakan slice thickness 5 mm dengan scan area dari angulus mandibula sampai dengan vertex (Al-nabhani et al., 2014). Sedangkan, pada penelitian yang dilakukan oleh Sarjani pemeriksaan CT-Scan kepala menggunakan pengaturan scan area dari sinus maxillaris hingga

PPT MELAPORKAN HASIL CT SCAN KEPALA PADA PASIEN STROKE PowerPoint Presentation ID2325407
Pada CT scan kepala dapat dilakukan untuk mendiagnosis stroke tumor, infeksi, atau perdarahan di dalam kepala, ataupun fraktur kepala. Pada hasil CT scan kepala tentunya perlu dilihat dari keluhan yang dialami dan dikonfirmasi. Pada hasil yang normal didapatkan otak, pembuluh darah, tengkorak, dan wajah mempunyai ukuran, bentuk dan posisi yang.
CT Head Normal Anatomy
CT Head by Robert Michael Barnes; MSK Anatomy by Derek Smith UQ Med Yr 1 GAF/Radiographic Anatomy - Head and neck by Craig Hacking CT Head by Robert Michael Barnes; HS teaching by Jonathan Bong; JA Neuro RMS by Jonathan Adlam; UQ Radiologic Anatomy 2. Head & Neck 2.02 Facial Bones by Craig Hacking Neuro Anatomy by Laura Jorgenson

Image
this is a CT of the Abdomen and Pelvis, Enterography protocol. this is a higher quality study than a standard CT. It is performed with a higher radiation dose and larger dose of IV contrast, which helps to evaluate subtle areas of bowel inflammation. the slice thickness is 2.5 mm. This provides an excellent look at the large and small bowel.
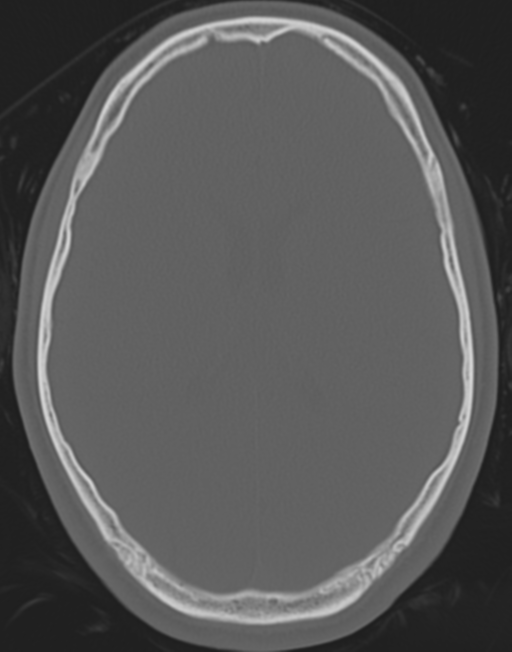
Normal CT head (cerebral and bone windows) Image
Dalam pemeriksaan CT scan kepala, pasien harus telentang dengan kepala ke arah gantry atau rumah tabung sinar-X. Pasien harus tepat di garis tengah pemindai. Operator bisa menggunakan tali pengikat khusus untuk mempertahankan posisi kepala. Pasien juga harus sedikit menundukkan dagu ke arah dada. Bisa pula operator mengarahkan gantry agar.
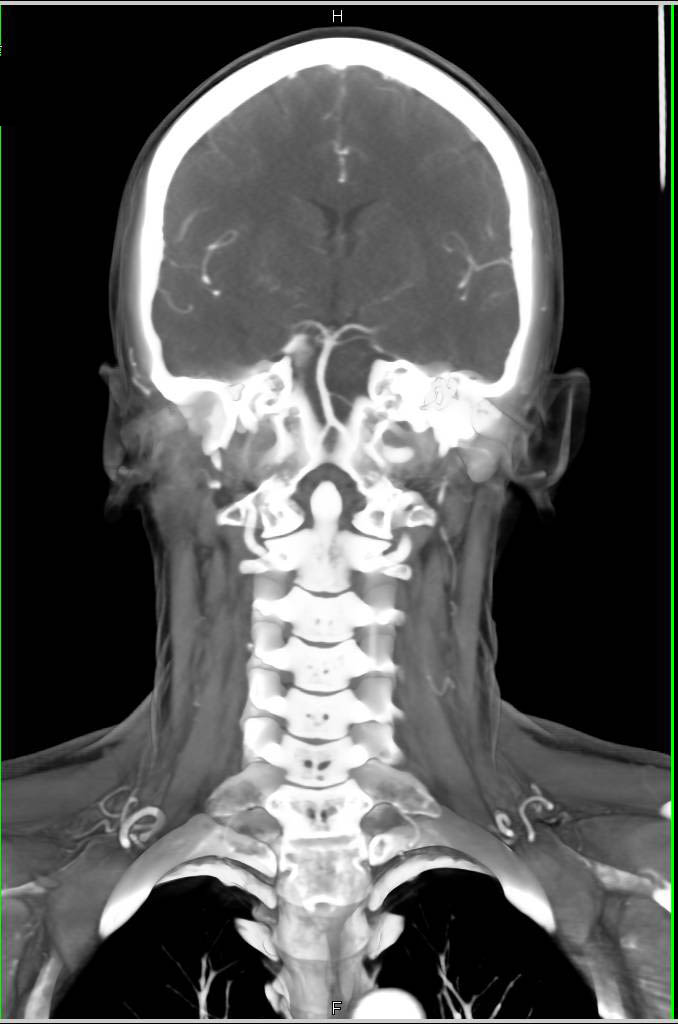
Normal CTA of the Head and Neck Neuro Case Studies CTisus CT Scanning
Normal Anatomy of Brain (CT) by Kyaing Yi Mon Thin; 111 Normal anatomy by Mohamed shweel; braın by HMB * CT Brain by Gourab Mitro Plaban; CT head by Mohit Kumar; Dr Abid cases by Abid Hussain; illustrations annotated images by Mini Singhal; CT Head Tutorial RadSIG by Alexander Troyer; NIMA by Miguel F Andrade Egues; 07 juillet by Amar Hadj; 07.
Kepala Normal Pada Ct Scan Foto Stok Unduh Gambar Sekarang Cat scan, Hidung, Jaringan iStock
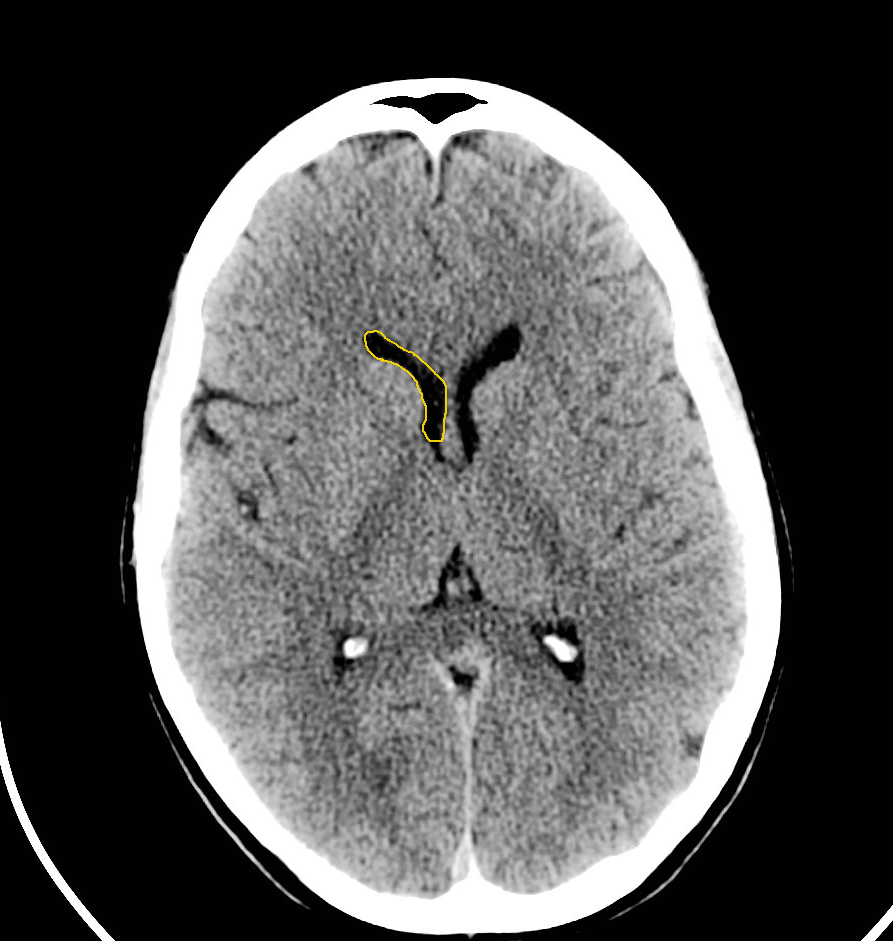
Examine the brain for: Symmetry - make sure sulci and gyri appear the same on both sides. (easiest when patient not rotated in the scanner) Grey-white differentiation - the earliest sign of a CVA on CT scan is the loss of the grey-white interface on CT scan. Compare side to side. Shift - the falx should be in the midline with ventricles the same on both sides.
:strip_icc():format(webp)/article/EuImghXRiPgzNRBHu02Rl/original/1670044476-Proses Prosedur CT Scan Kepala.jpg)
SerbaSerbi CT Scan Kepala yang Perlu Kamu Tahu KlikDokter
CT scan kepala merupakan salah satu pemeriksaan yang dilakukan untuk mengetahui kondisi atau penyakit di dalam kepala, yang terdiri dari tulang tengkorak, pembuluh darah, cairan otak, otak, dan batang otak. Biaya CT scan kepala di daerah kabupaten kisaran Rp 600.000-800.000, sedangkan di daerah di kota besar bisa mencapai Rp 800.000-1.200.000.
CT Scan Kepala Prosedur, Resiko, Hasil Tes • Hello Sehat
CT head (sometimes termed CT brain ), refers to a computed tomography examination of the brain and surrounding cranial structures. It is most commonly performed as a non-contrast study, but the addition of a contrast-enhanced phase is performed for some indications. This article covers non-contrast and delayed post-contrast imaging.

Normal head, CT scan Stock Image C001/8701 Science Photo Library
The CT head scan is one of the most common imaging studies you can be faced with and the most frequently requested by the emergency department. This article will cover some of the underlying principles of CT head studies and discuss a method for their interpretation.. On a normal CT head scan, the grey and white matter should be clearly.

CT Scan untuk Melihat Kepala hingga Ujung Kaki OTC Digest
A combined PET/CT exam fuses images from a PET and CT scan together to provide detail on both the anatomy (from the CT scan) and function (from the PET scan) of organs and tissues. A PET/CT scan can help differentiate Alzheimer's disease from other types of dementia. Another nuclear medicine test called a single-photon emission computed.

CT Scan Kepala Fungsi, Prosedur dan Efek Samping IDN Medis
CT Brain. Brainstem and cerebellum without evidence of focal lesions. Lateral ventricles of normal volume. Third and fourth ventricles in midline. Basal subarachnoid cisterns normal configuration. Focal abnormalities are not observed in the brain parenchyma. Adequate gray matter-white matter differentiation.
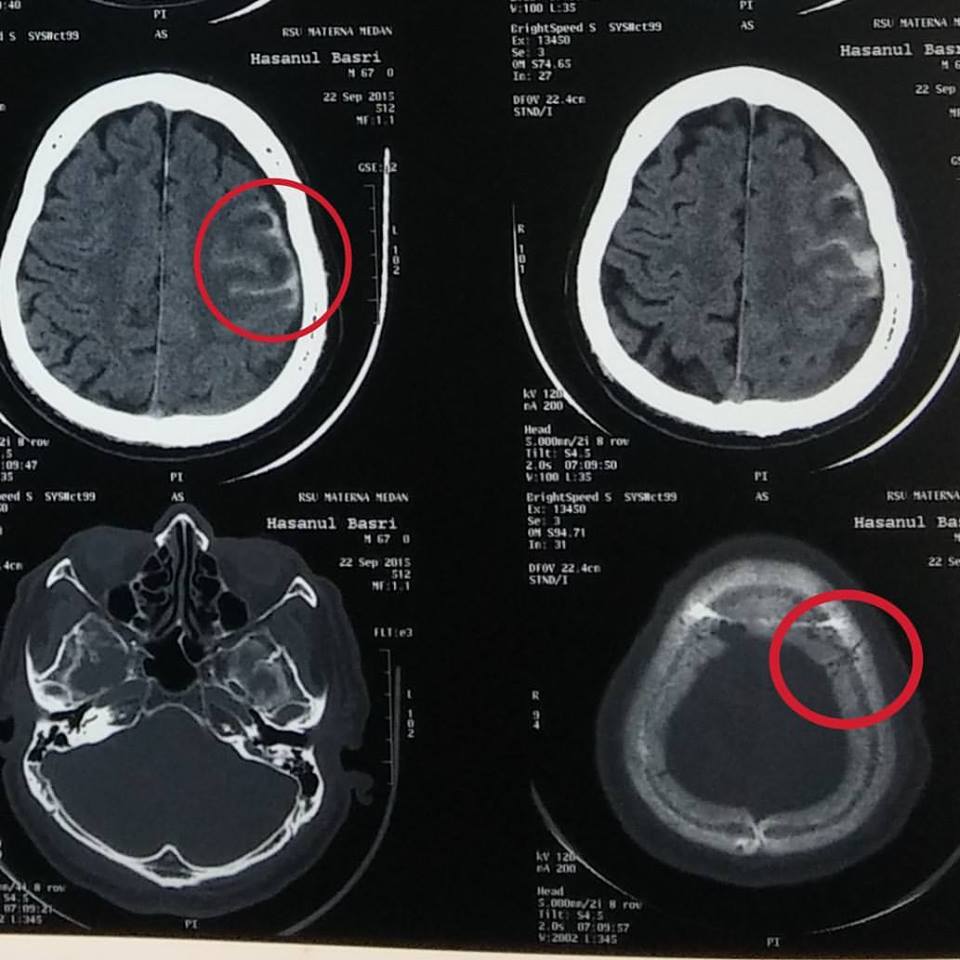
Dari RS Materna, Berikut Hasil CT Scan Bagian Kepala Abu Mudi Dayah MUDI Mesra
IMAIOS and selected third parties, use cookies or similar technologies, in particular for audience measurement. Cookies allow us to analyze and store information such as the characteristics of your device as well as certain personal data (e.g., IP addresses, navigation, usage or geolocation data, unique identifiers).

Teknik Pemeriksaan CT Scan Kepala YouTube
Normal cranial CT Scan of the head: brain, bones of cranium, sinuses of the face. Fully annotated brain CT - Normal anatomy of the head on a cross-sectional cranial CT Scan (axial, sagittal and coronal): brain, bones of skull, paranasal sinuses, vasculary territories, cranial base.
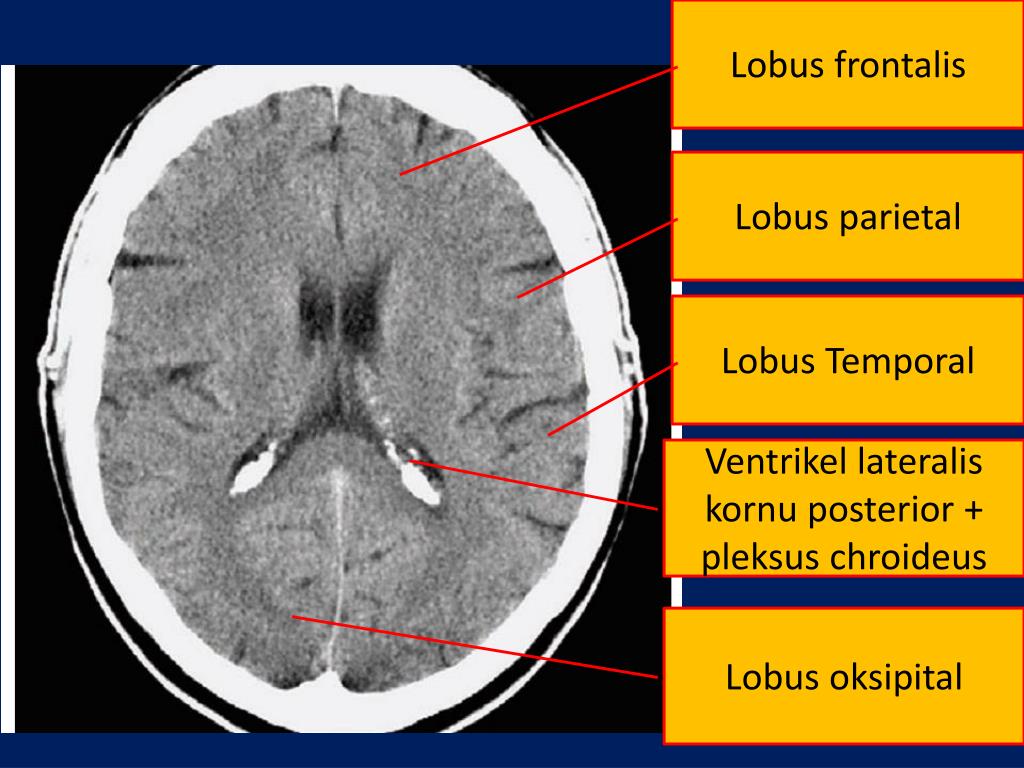
PPT MELAPORKAN HASIL CT SCAN KEPALA PADA PASIEN STROKE PowerPoint Presentation ID3712083
Pemeriksaan CT scan kepala dapat dilakukan dengan atau tanpa kontras, sesuai dengan indikasi klinis masing-masing pasien. [1,2] CT scan kepala menggunakan teknologi komputer berbasis sinar X untuk melihat komponen intrakranial. CT scan kepala menghasilkan gambar penampang otak pada beberapa level, serta dapat memberikan gambaran tiga dimensi.

MRI of head showing normal brain structures Stock Photo Dissolve
A computed tomography (CT) scan, commonly referred to as a CT, is a radiological imaging study. The machine was developed by physicist Allan MacLeod Cormack and electrical engineer Godfrey Hounsfield.[1][2][3] Their development awarded them the Nobel prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1979.[4] The first scanners were installed in 1974. Since then, technological advances and math have allowed.