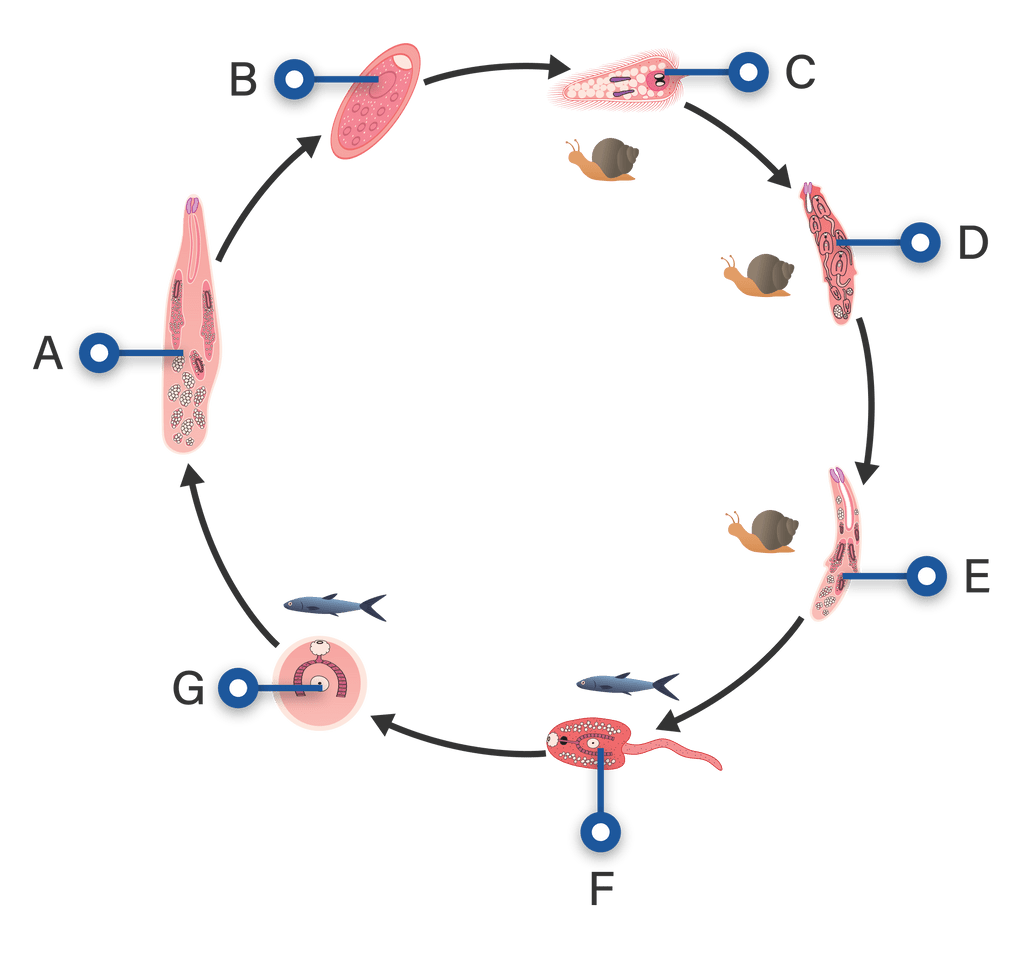
Perhatikan gambar daur hidup ( Clonorchis sinensis...
Clonorchis sinensis requires two intermediate hosts for completion of its life cycle. The first is a snail and the second is cyprinoid fish (although at least eight families of fish may serve as intermediate hosts for C. sinensis).Among the snails, over 100 species in several general may serve as the primary intermediate host.

Clonorchis sinensis eggs in the bile sediment blue arrowhead indicates... Download Scientific
Clonorchiasis is an infectious disease caused by the Chinese liver fluke (Clonorchis sinensis) and two related species.Clonorchiasis is a known risk factor for the development of cholangiocarcinoma, a neoplasm of the biliary system. [citation needed]Symptoms of opisthorchiasis caused by Opisthorchis viverrini and by O. felineus are indistinguishable from clonorchiasis caused by Clonorchis.

Clonorchis sinensis Trends in Parasitology
Clonorchis sinensis, the Chinese liver fluke, is a liver fluke belonging to the class Trematoda, phylum Platyhelminthes.It infects fish-eating mammals, including humans. In humans, it infects the common bile duct and gall bladder, feeding on bile.It was discovered by British physician James McConnell at the Medical College Hospital in Calcutta (Kolkata) in 1874.

Clonorchis sinensis life cycle YouTube
Clonorchiasis, caused by Clonorchis sinensis (C. sinensis), is an important food-borne parasitic disease and one of the most common zoonoses. Currently, it is estimated that more than 200 million people are at risk of C. sinensis infection, and over 15 million are infected worldwide. C. sinensis infection is closely related to cholangiocarcinoma

Clonorchis sinensis Wikiwand
Clonorchis sinensis adults are flattened, lance shaped, and measure approximately 10 to 25 mm long by 3 to 5 mm wide. The oral and ventral suckers (acetabulum) are relatively small. Like other flukes, they are hermaphroditic. The two testes are located posterior to the ovary, and are highly branched-a feature which separates it from the related Opisthorchis spp. (rounded testes).

Clonorchis sinensis egg and adult morphology (clear explanation) YouTube
Ciri-ciri biologi. kebetulan hati cina (Clonorchis sinensis) terkenal kerana menjadi trematode khunsa, iaitu, cacing dewasa yang mempunyai keupayaan untuk pendebungaan sendiri, kerana kedua-dua organ seks berada di dalam individu yang sama, walaupun kadang-kadang silang biasanya berlaku.

"Clonorchis sinensis" by circa24 Redbubble
The epidemiological profiles and determinants of C. sinensis infection, knowledge, practice and attitude related to clonorchiasis were demonstrated in Hengxian county, Guangxi, China. The overall prevalence of C. sinensis was 60.3%, which was higher in male than in female and in elder population compared to children.

Life cycle of Clonorchis sinensis. Download Scientific Diagram
Authors' summary Currently 13 snail species are reported as first intermediate hosts of Clonorchis sinensis, including two species of the Thiaridae, Melanoides tuberculata and Tarebia granifera. Both snail species have wide distributions in tropical and subtropical waters across the World, while the distribution of C. sinensis is much narrower and only occurs in endemic areas of East Asia.

PPT Clonorchis sinensis PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1158357
Resources for Health Professionals. Infection with Clonorchis liver flukes arises from the ingestion of raw or poorly cooked fish contaminated by these parasites. After ingestion, these liver flukes grow to adulthood inside the human biliary duct system. Infections are not known to persist beyond 25-30 years, the lifespan of the parasite.
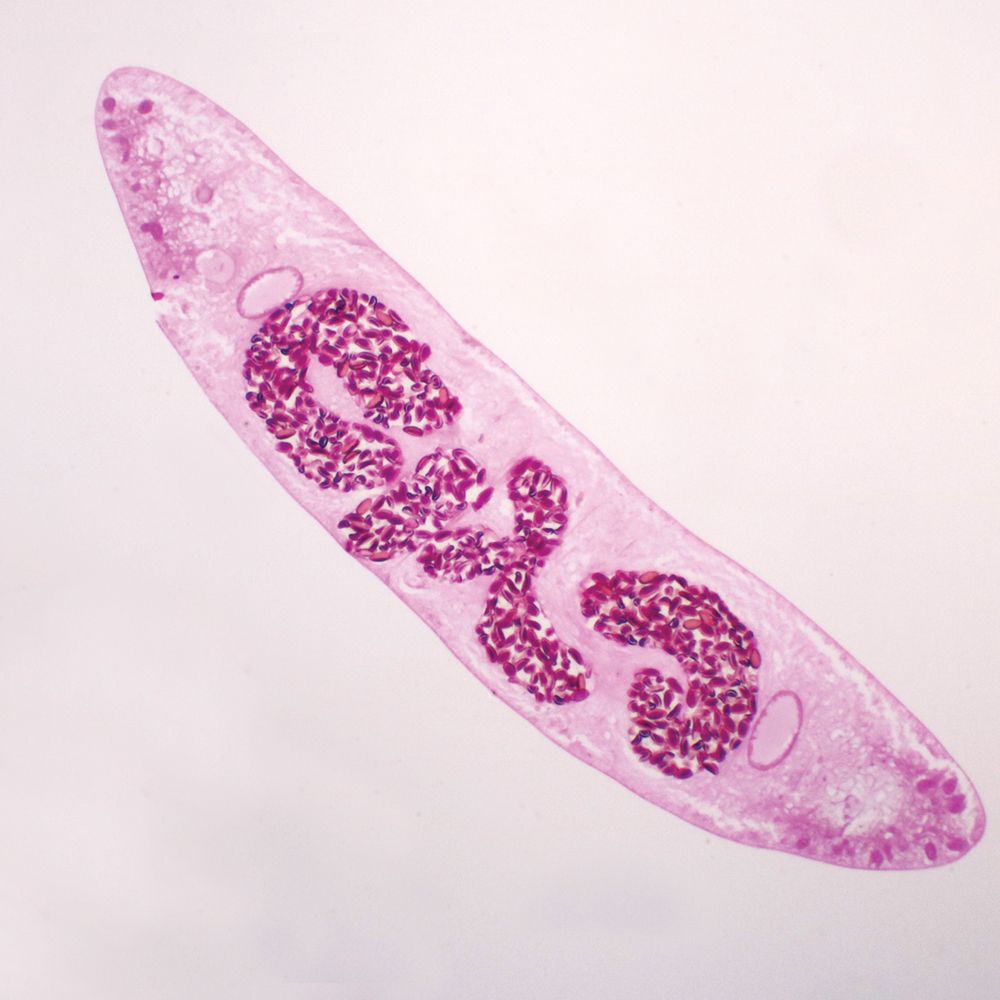
Clonorchis sinensis, c.s. Microscope Slide
Clonorchiasis, caused by Clonorchis sinensis (C. sinensis), is an important food-borne parasitic disease and one of the most common zoonoses. Currently, it is estimated that more than 200 million people are at risk of C. sinensis infection, and over 15 million are infected worldwide. C. sinensis infection is closely related to cholangiocarcinoma (CCA), fibrosis and other human hepatobiliary.

Parasitic Platyhelminthes Clonorchis sinensis Diagram Quizlet
Pengertian Clonorchis sinensis. Clonorchis sinensis adalah salah satu trematoda hati yang bersifat hermaprodit yang dapat menimbulkan penyakit clonorchiasis. Nama lain parasit ini adalah Opisthorchis sinensis atau The chinese liver fluke. Hospes definitif : kucing, anjing, manusia. Hospes intermedier 1 : keong air.
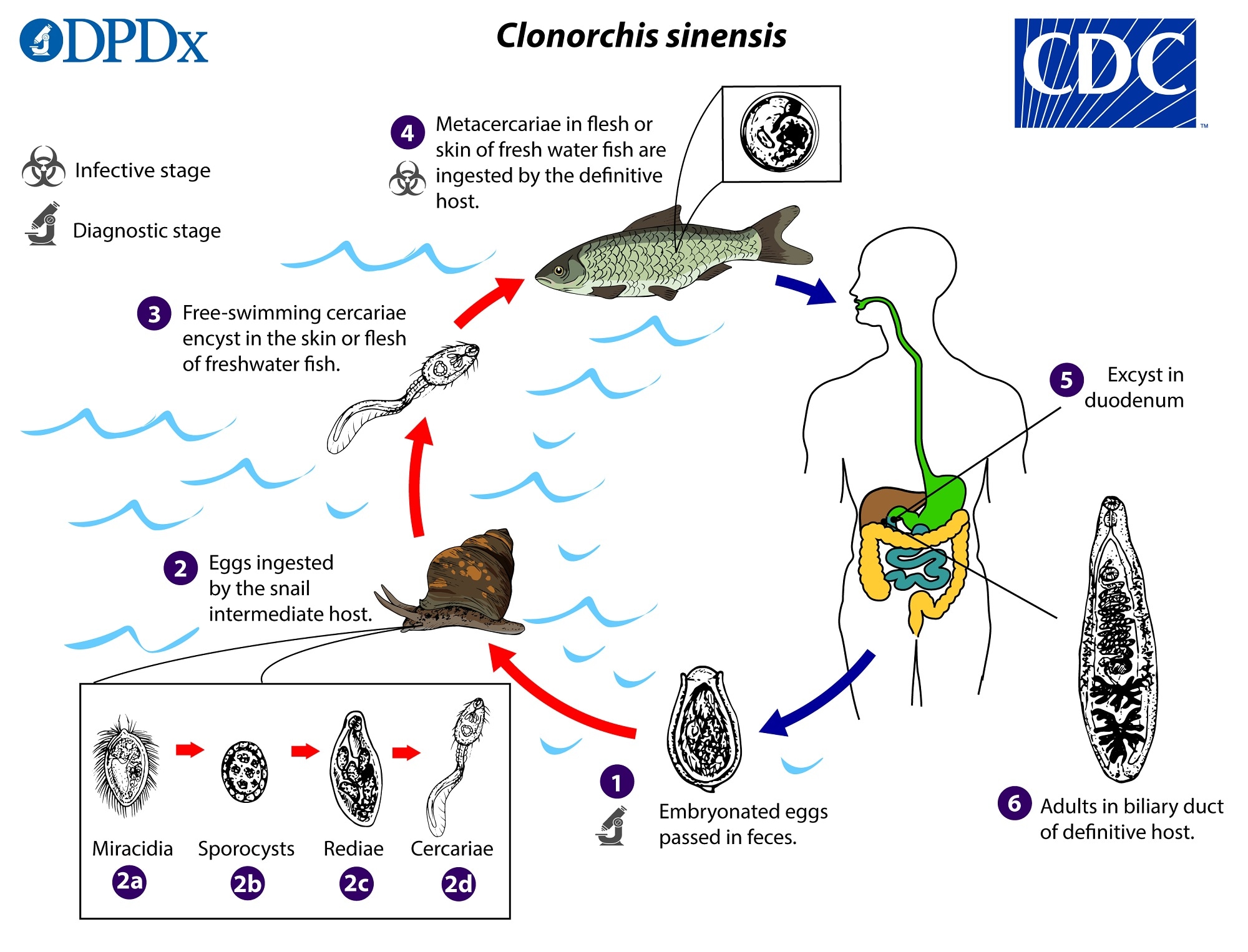
CDC DPDx Clonorchiasis
Clonorchis is endemic in East Asia (China, South Korea, northern Vietnam, Taiwan, and parts of Russia), and infection occurs elsewhere among immigrants and people eating raw or undercooked fish, or sometimes shrimp, from endemic areas. The number of people infected with C. sinensis is growing, from an estimated 7 million in the 1990s to 15 to 20 million worldwide in the 2010s (1 References.

Oriental or Chinese liver fluke egg (Clonorchis sinensis) revealed in the micrograph film, 1986
Infections caused by Clonorchis sinensis remain a significant public health challenge for both humans and animals, causing pyogenic cholangitis, cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, biliary fibrosis, and even cholangiocarcinoma. However, the strategies used by the parasite and the immunological mechanisms used by the host have not yet been fully understood. With the advances in technologies and the.
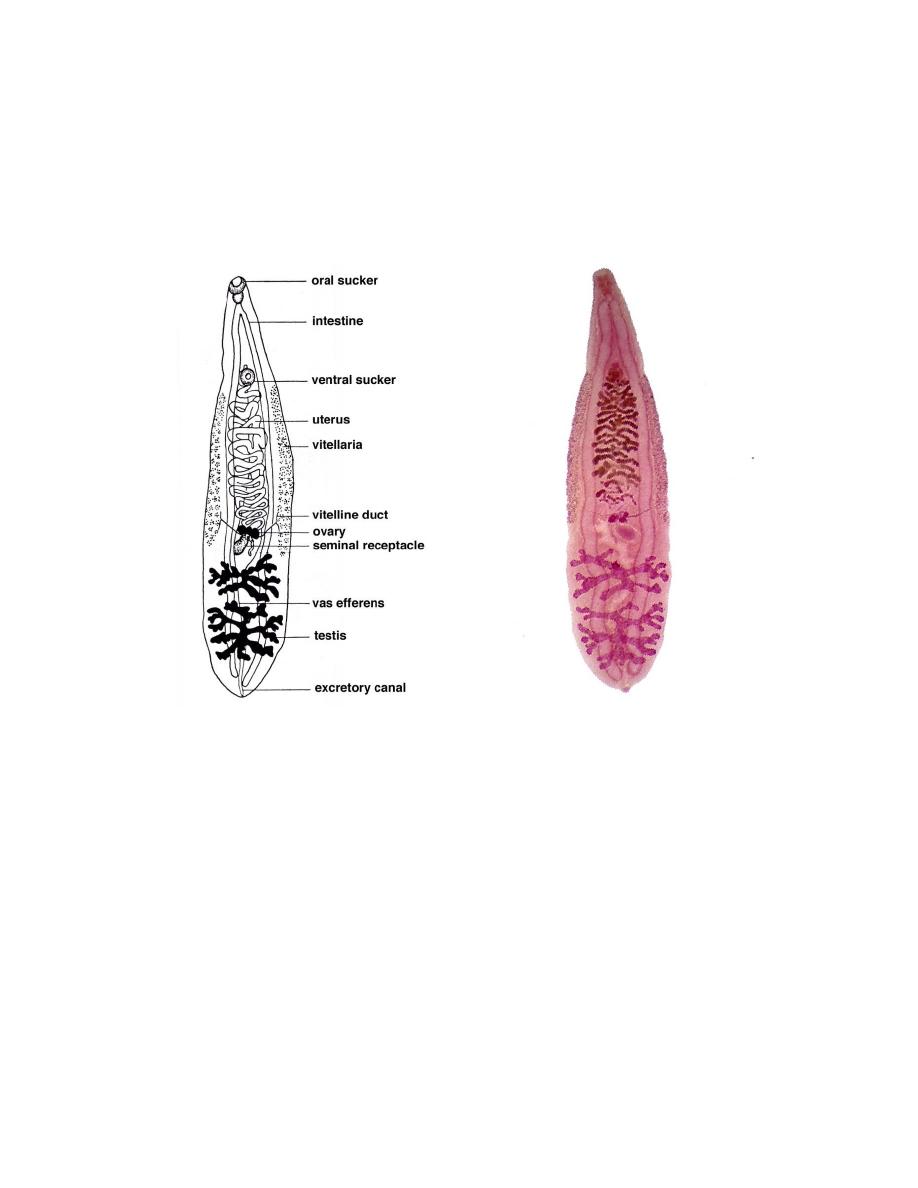
Clonorchis sinensis pdf D. Khalid Muhadharaty
Clonorchis is a liver fluke parasite that humans can get by eating raw or undercooked fish from areas where the parasite is found. Found across parts of Asia, Clonorchis is also known as the Chinese or oriental liver fluke. Liver flukes infect the liver, gallbladder, and bile duct in humans. While most infected persons do not show any symptoms, infections that last a long time can result in.

Clonorchis sinensis; opisthorchis sinensis
Cook fish adequately (to an internal temperature of at least 145° F [~63° C]). At -31°F (-35°C) or below until solid, and storing at -31°F (-35°C) or below for a least 15 hours; or. At -31°F (-35°C) or below until solid and storing at -4°F (-20°C) or below for at least 24 hours. Frequently asked questions about clonorchis.

Clonorchis sinensis Oswaldo Valencia uDocz
Clonorchiasis is an important yet neglected foodborne parasitic disease in East Asian countries, including China, South Korea, Vietnam and parts of Russia. The disease is caused by a trematode known as Clonorchis sinensis (C. sinensis) [1-3]. A high morbidity can occur including disorders and carcinogenesis in the liver and biliary system [1, 4