
Homeostasis (Anatomy & Physiology l ) My Biology Notebook
Homeostasis is actually the process of maintaining a stable internal environment despite changes in the external environment. There are mechanisms in organisms that regulate pH and this regulation is an example of homeostasis. For example, if you have learned about buffers, then it may help to know that essentially all organisms use buffers.
What Is Homeostasis? Meaning, Definition And Examples
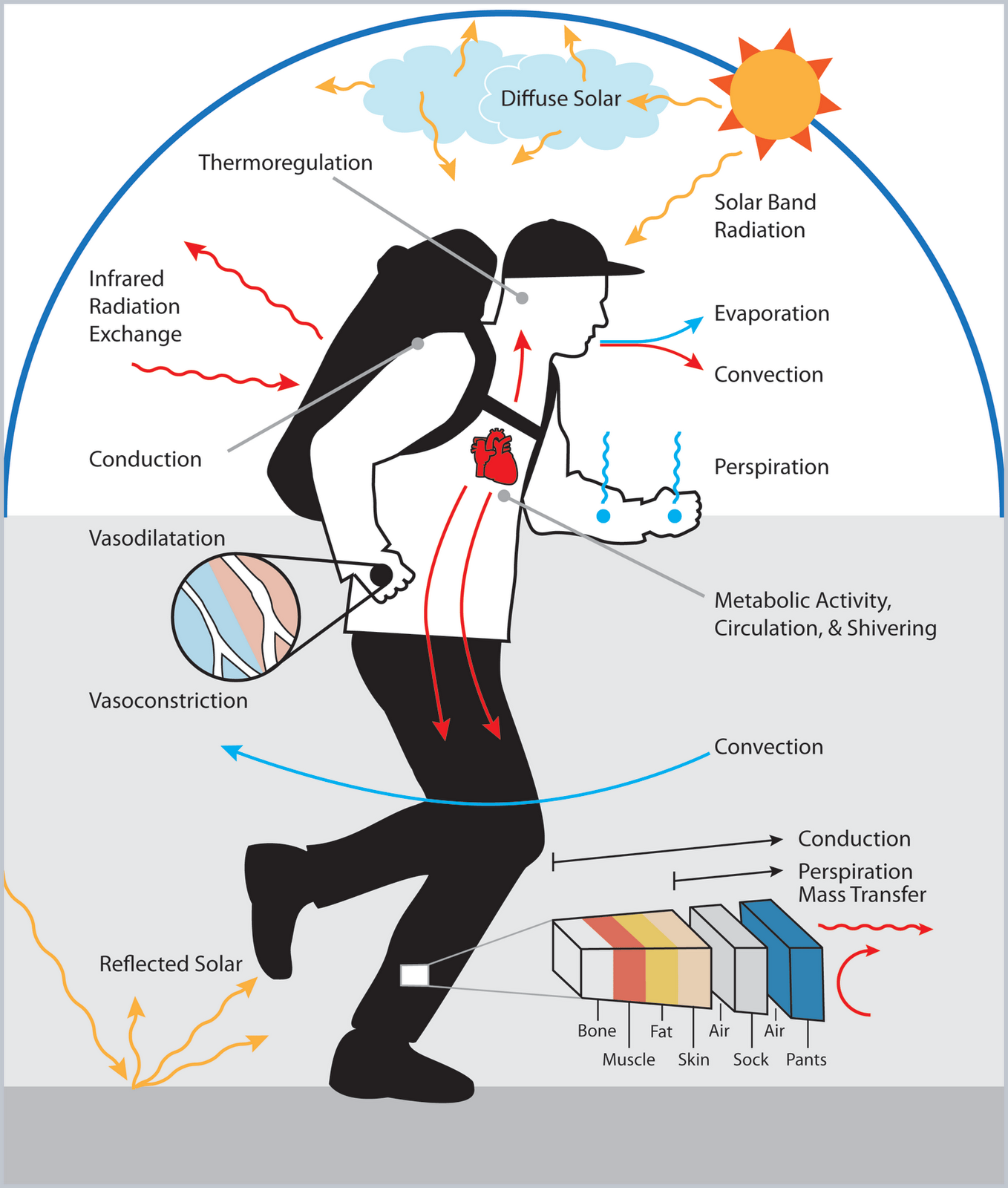
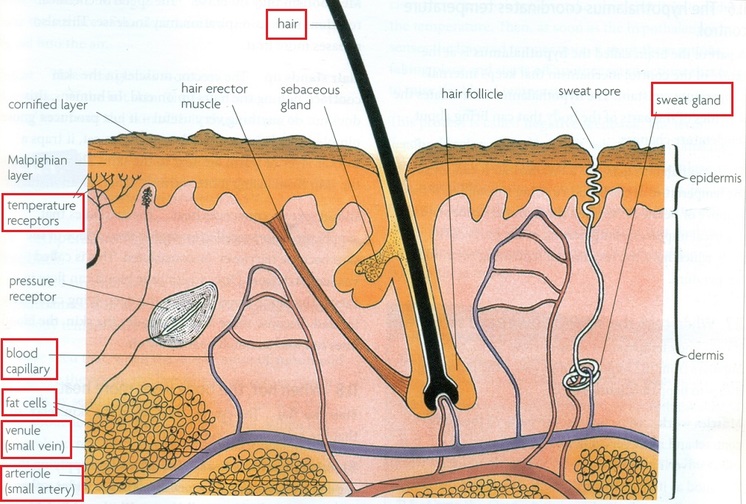
The nervous system is important to thermoregulation, as illustrated in Figure 14.23. The processes of homeostasis and temperature control are centered in the hypothalamus of the advanced animal brain. Figure 14.23. The body is able to regulate temperature in response to signals from the nervous system.
homeostasis Thermoregulation
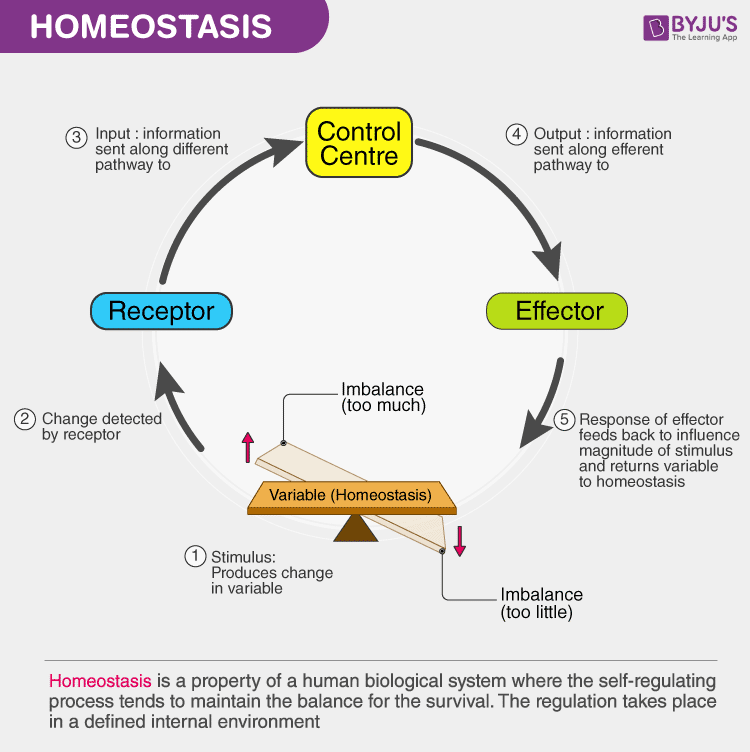
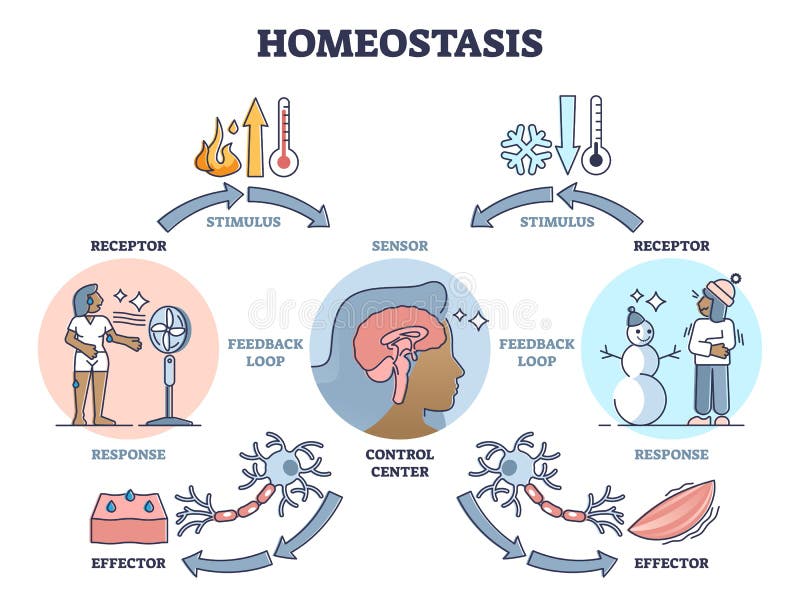
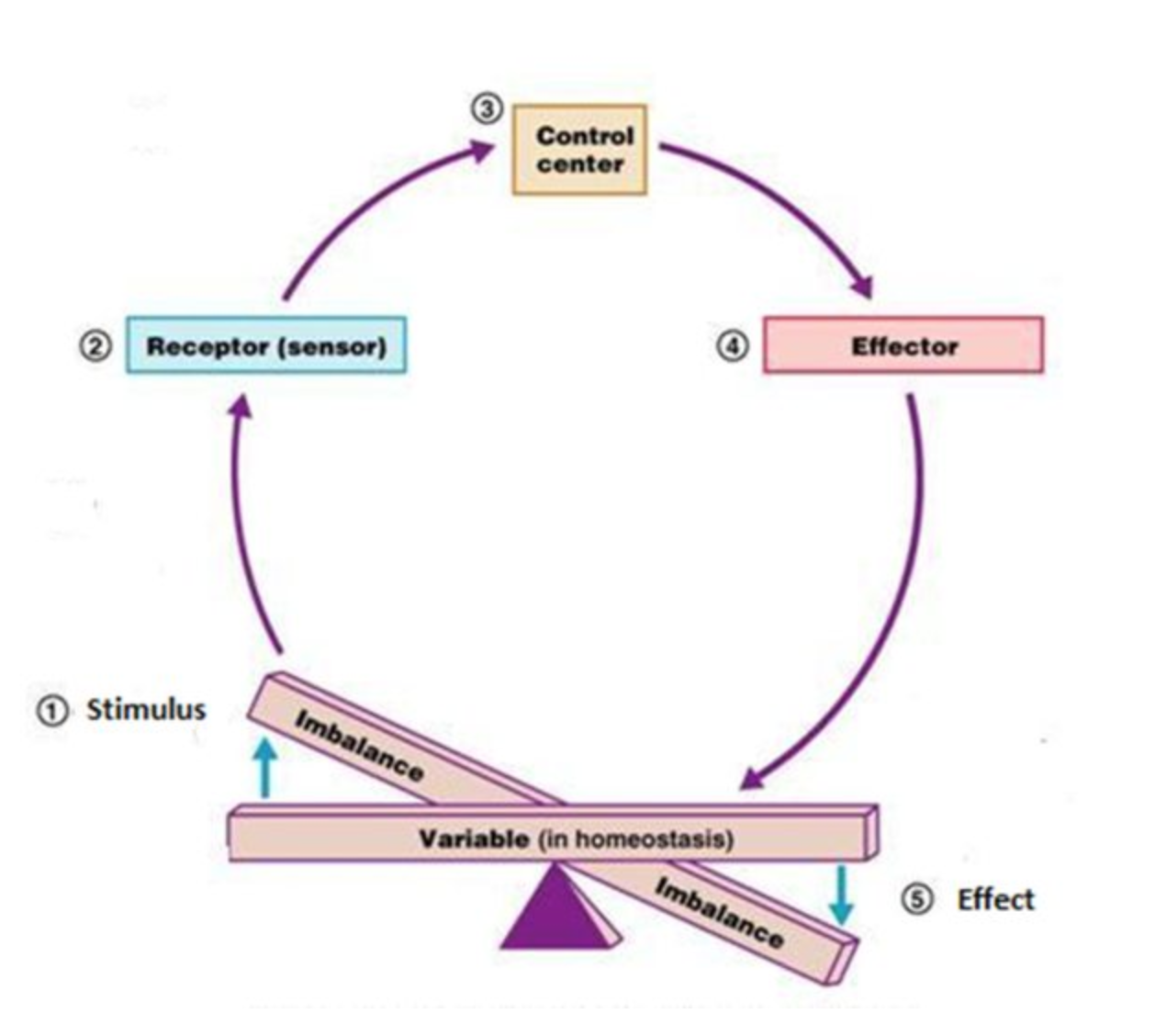
Figure 1.10 Negative Feedback Loop In a negative feedback loop, a stimulus—a deviation from a set point—is resisted through a physiological process that returns the body to homeostasis. (a) A negative feedback loop has four basic parts. (b) Body temperature is regulated by negative feedback. In order to set the system in motion, a stimulus.
ADH Diagram, Homeostasis Biology Lecture Slides Docsity
Each of these components is illustrated in Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\). The diagram on the left is a general model showing how the components interact to maintain homeostasis. The stimulus activates the sensor. The sensor activates the control system that regulates the effector. The diagram on the right shows the example of body temperature.

Homeostasis Biology I
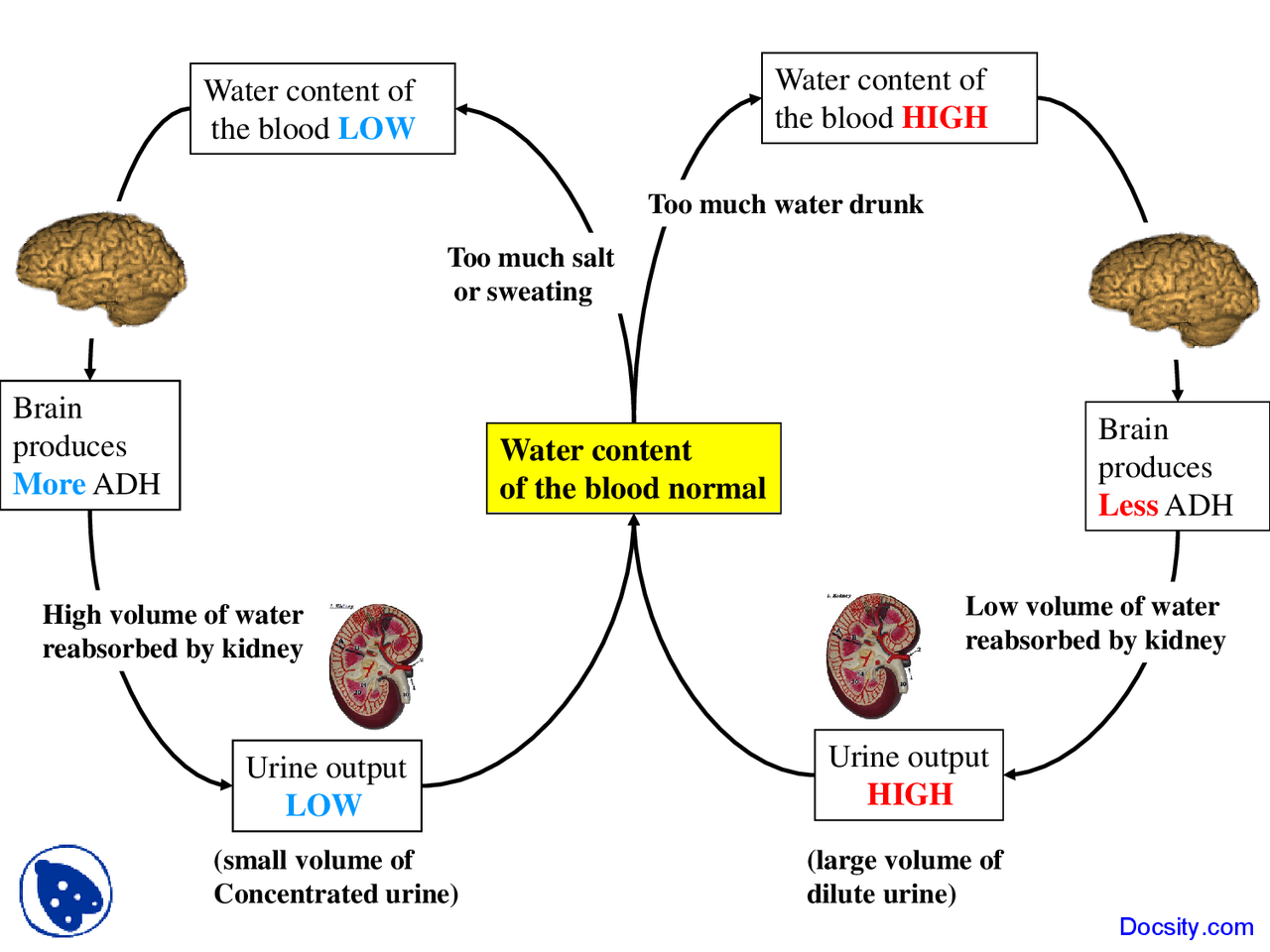
Osmoregulation. Osmoregulation is the process of maintaining salt and water balance (osmotic balance) across membranes within the body. The fluids inside and surrounding cells are composed of water, electrolytes, and nonelectrolytes. An electrolyte is a compound that dissociates into ions when dissolved in water.

CH103 Chapter 8 Homeostasis and Cellular Function Chemistry
The diagram on the left is a general model showing how the components interact to maintain homeostasis. The diagram on the right shows the example of body temperature. From the diagrams, you can see that maintaining homeostasis involves feedback, which is data that feeds back to control a response. Feedback may be negative (as in the example.
Human Biology Online Lab / lab three Homeostasis
Meaning. Homeostasis. The tendency to resist change in order to maintain a stable, relatively constant internal environment. Negative feedback loop. Feedback loop that acts to oppose the triggering stimulus. Positive feedback loop. Feedback loop that amplifies the starting signal. Cell. Smallest unit of life.
Process of homeostasis as human body temperature regulation outline
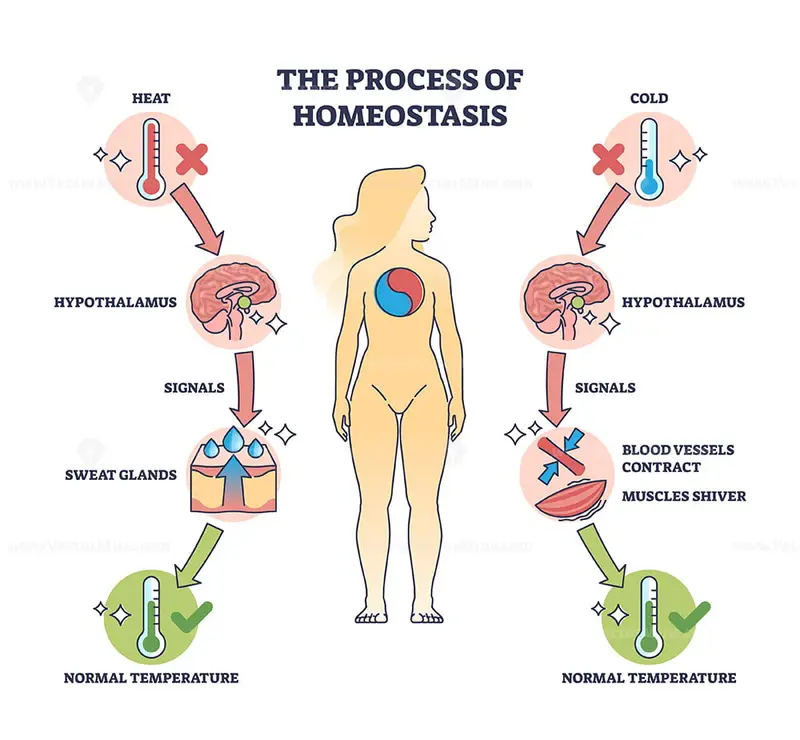
Homeostasis (homeo- = "like, resembling, of the same kind"; stasis = "standing still") means to maintain body functions within limits that are compatible with life. To cope with internal and external changes, the organism continuously adjusts its physiology so that its functions remain within normal limits.. Draw a diagram that.
pianista erupt Insoddisfatto body temperature regulation diagram liscio
Homeostasis is controlled by the nervous and endocrine system of mammals. Negative Feedback Mechanisms. Any homeostatic process that changes the direction of the stimulus is a negative feedback loop. It may either increase or decrease the stimulus, but the stimulus is not allowed to continue as it did before the receptor sensed it. In other.
Physiological Homeostasis Biology Online Tutorial
anatomy and physiology of homeostasis. Homeostasis comprises the dynamic processes that enable optimum conditions to be maintained for cells, in spite of continual changes taking place internally and externally (Clancy and McVicar, 1995). All the systems of the human body are involved, with particular contributions by the endocrine,

Maintain Stable Internal Environment (Homeostasis) Expii
Homeostasis is a term that was first coined by physiologist Walter Cannon in 1926, clarifying the 'milieu intérieur' that fellow physiologist Claude Bernard had spoken of in 1865.[1] 'Homeo,' Latinized from the Greek word 'homio,' means 'similar to,' and when combined with the Greek word 'stasis,' meaning 'standing still' gives us the term that is a cornerstone of physiology.
Homeostasis Biology Notes for IGCSE 2014
Homeostasis is a term derived from the Greek words "homeo" (meaning similar to) and "stasis" (meaning standing still). In the 1920s, an American physiologist named Walter B. Cannon invented the word "homeostasis." Cannon described homeostasis as "coordinated physiological processes" that maintain "steady states" in a living organism.

How the Process of Homeostasis Works Supedium
The process of blood coagulation (hemostasis) is a cascading positive feedback loop. When the body is damaged inside or outside, the damaged tissues release factors that cause platelets to adhere to the tissue (the effector) at the site of the wound. The platelets release granules that activate and attract more platelets and cause them to bind.
CuriouSTEM Homeostasis
Many important systems involved in homeostasis involve negative feedback loops. This is because the body wants to maintain balance and will attempt to reverse most changes.. Shown is a diagram of respiratory regulation of blood pH. Two processes are shown- acidosis and alkalosis. In acidosis, blood pH is too low.

[LS13] Feedback Mechanisms and Homeostasis Biology Dictionary
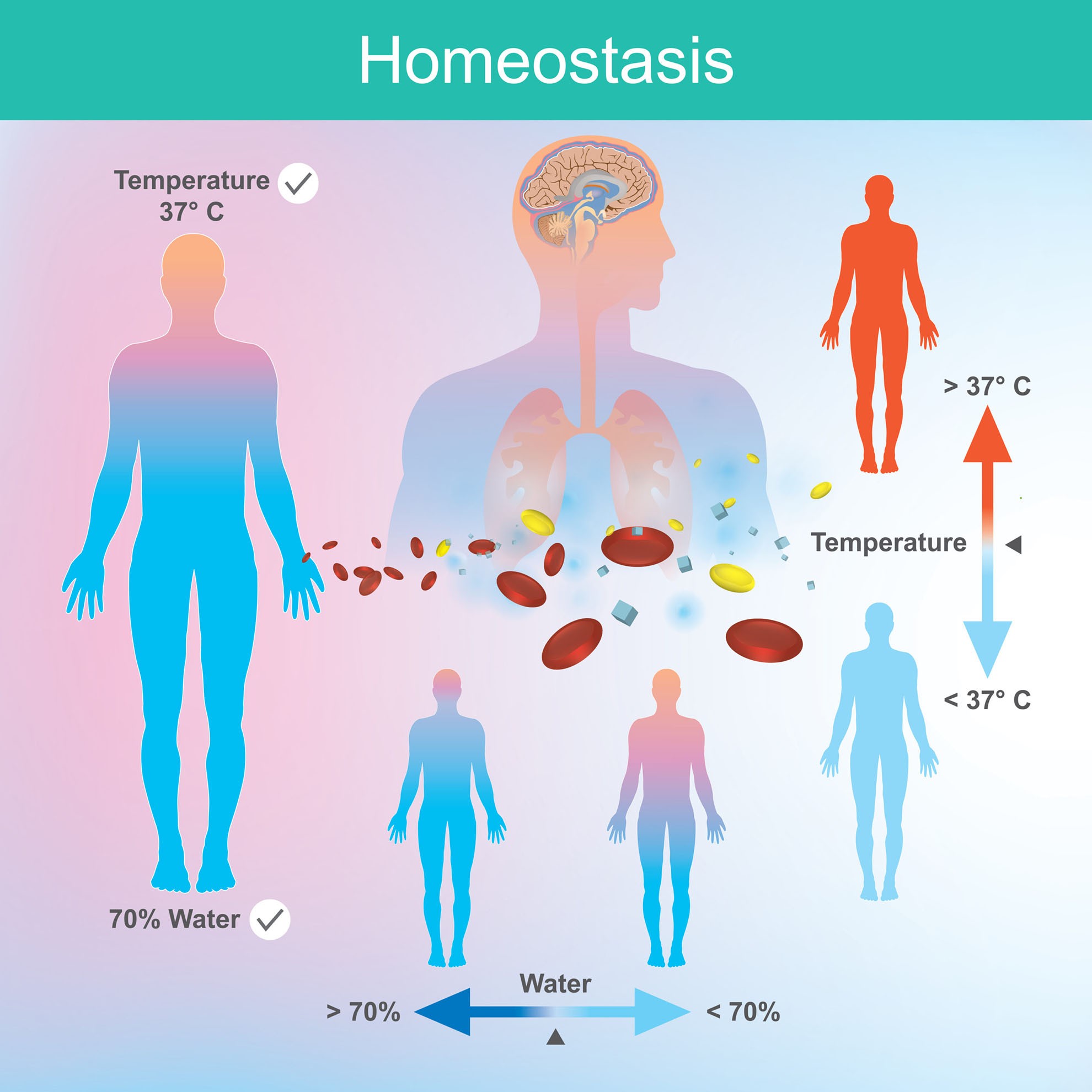
Homeostasis (homeo- = "like, resembling, of the same kind"; stasis = "standing still") means to maintain body functions within specific livable ranges, adjusting to internal and external changes. Temperature, nutrient concentration, acidity, water, sodium, calcium, oxygen, as well as blood pressure, heart rate, and respiratory rate are some of the internal body variables that must remain.

Cell Membrane Homeostasis Functions Functions and Diagram
Homeostasis. Maintaining homeostasis requires that the body continuously monitor its internal conditions. From body temperature to blood pressure to levels of certain nutrients, each physiological condition has a particular set point. A set point is the physiological value around which the normal range fluctuates.