
Foot Anatomy and Function पाद pāda Elliot's WebSite
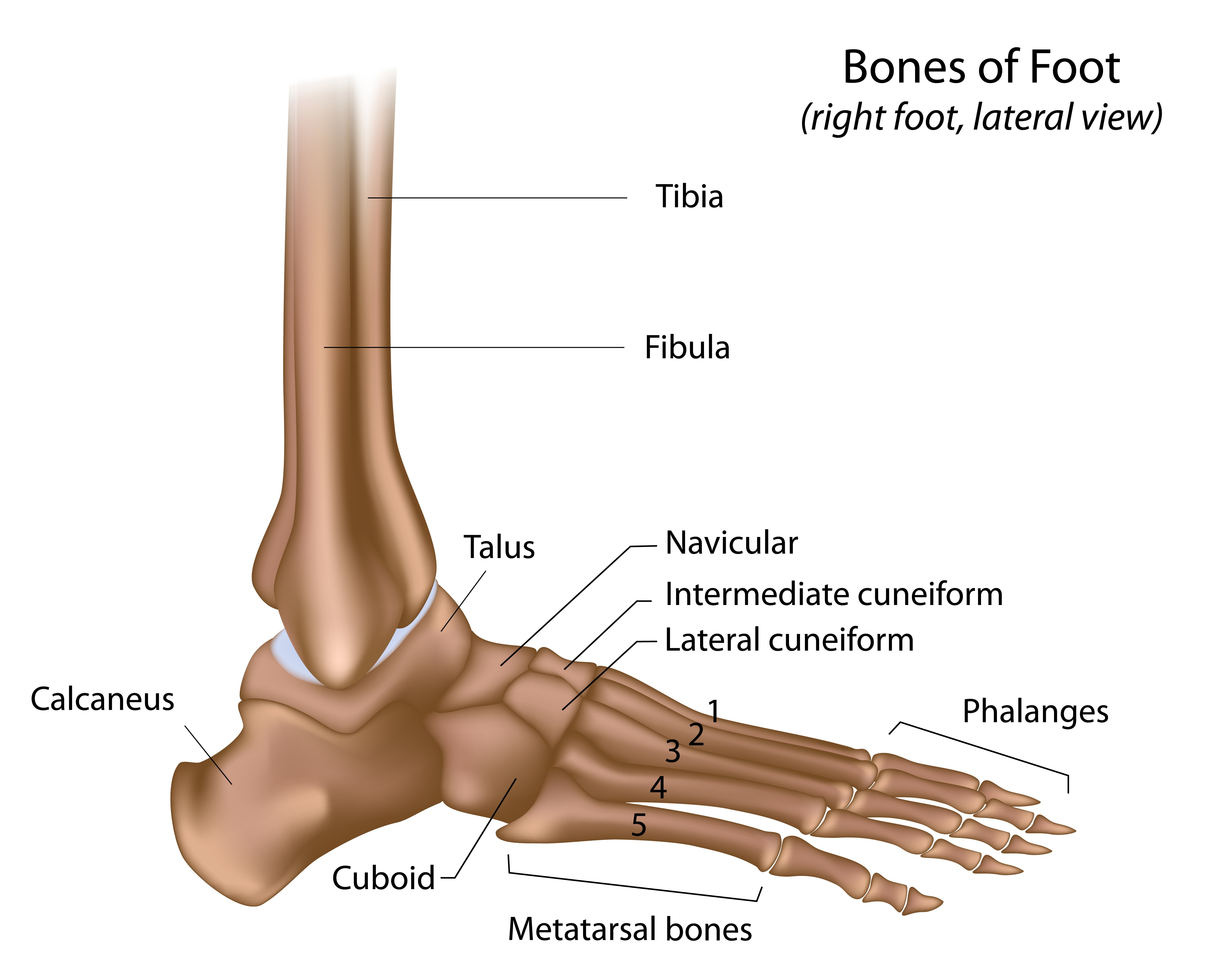
These bones are arranged in two rows, proximal and distal. The bones in the proximal row form the hindfoot, while those in the distal row from the midfoot. Hindfoot. Talus. Calcaneus. The talus connects the foot to the rest of the leg and body through articulations with the tibia and fibula, the two long bones in the lower leg. Midfoot. Navicular.

Loading... Human anatomy chart, Foot anatomy, Nerve anatomy
Cuboid: This multi-faceted bone sits on the outside of the foot near the fifth phalanx (little toe). Cuneiforms: These three small bones are closest to the five metatarsal bones. They sit in a row.

Foot Anatomy and Function पाद pāda Elliots World
Dr. Ebraheim's educational animated video describes anatomical structures of the foot and ankle, The Bony Anatomy, The Joints, Ligaments, and the Compartment.
Ankle and Foot Pain Massage Therapy Connections
The anatomy of the foot. The foot contains a lot of moving parts - 26 bones, 33 joints and over 100 ligaments. The foot is divided into three sections - the forefoot, the midfoot and the hindfoot. The forefoot. This consists of five long bones (metatarsal bones) and five shorter bones that form the base of the toes (phalanges).

Diagram Of A Human Foot Human Foot Diagram Anatomy Organ Anatomy
The foot is the region of the body distal to the leg that is involved in weight bearing and locomotion. It consists of 28 bones, which can be divided functionally into three groups, referred to as the tarsus, metatarsus and phalanges. The foot is not only complicated in terms of the number and structure of bones, but also in terms of its joints.

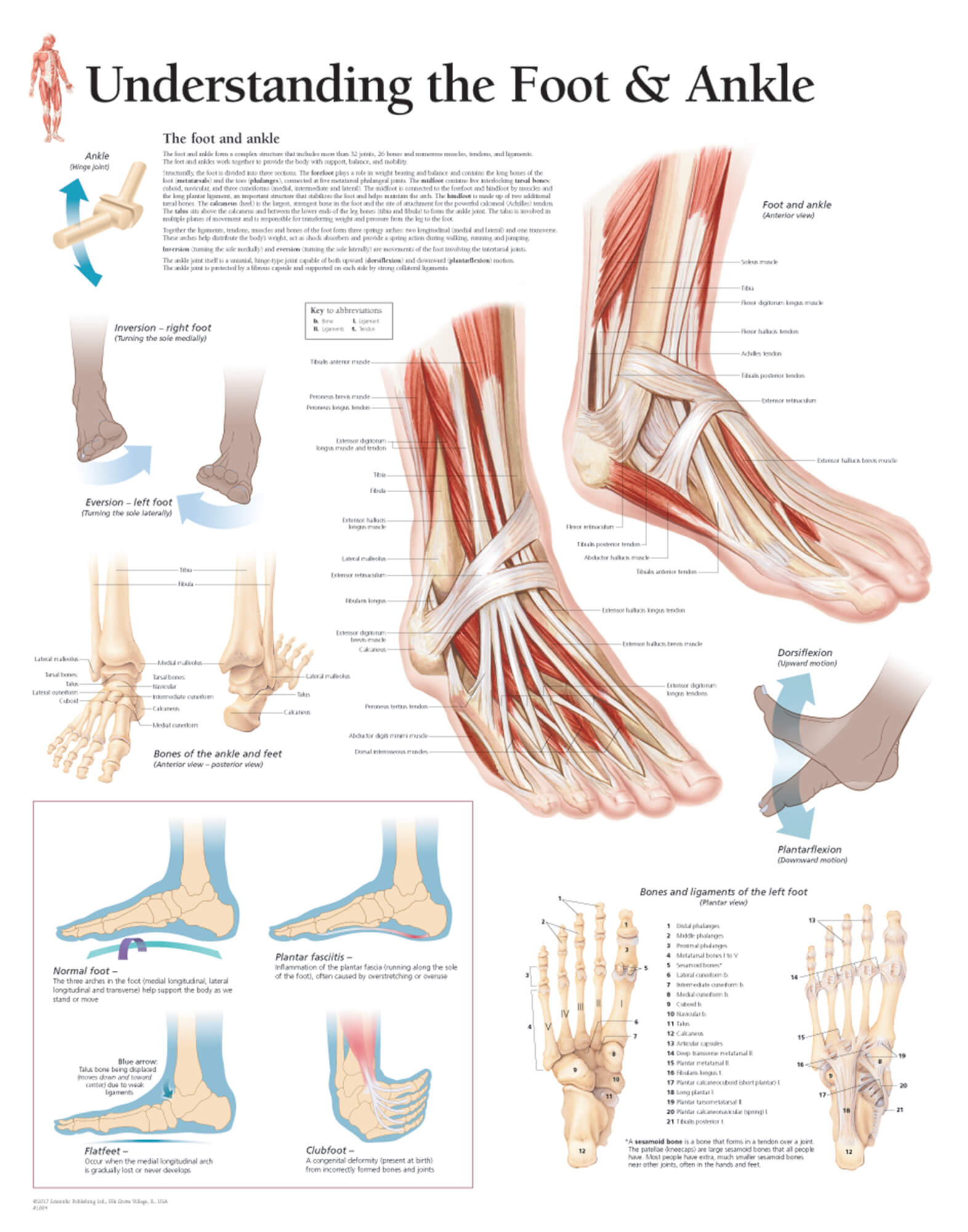
Foot and Ankle Anatomical Chart Anatomy Models and Anatomical Charts
Gastrocnemius (calf muscle): One of the large muscles of the leg, it connects to the heel. It flexes and extends the foot, ankle, and knee. Plantaris: This small, thin muscle is absent in about.
Understanding the Foot & Ankle Scientific Publishing
A solid understanding of anatomy is essential to effectively diagnose and treat patients with foot and ankle problems. Anatomy is a road map. Most structures in the foot are fairly superficial and can be easily palpated. Anatomical structures (tendons, bones, joints, etc) tend to hurt exactly where they are injured or inflamed.

Know Your Foot American Foot & Ankle
The foot is a part of vertebrate anatomy which serves the purpose of supporting the animal's weight and allowing for locomotion on land. In humans, the foot is one of the most complex structures in the body. It is made up of over 100 moving parts - bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments designed to allow the foot to balance the body's.
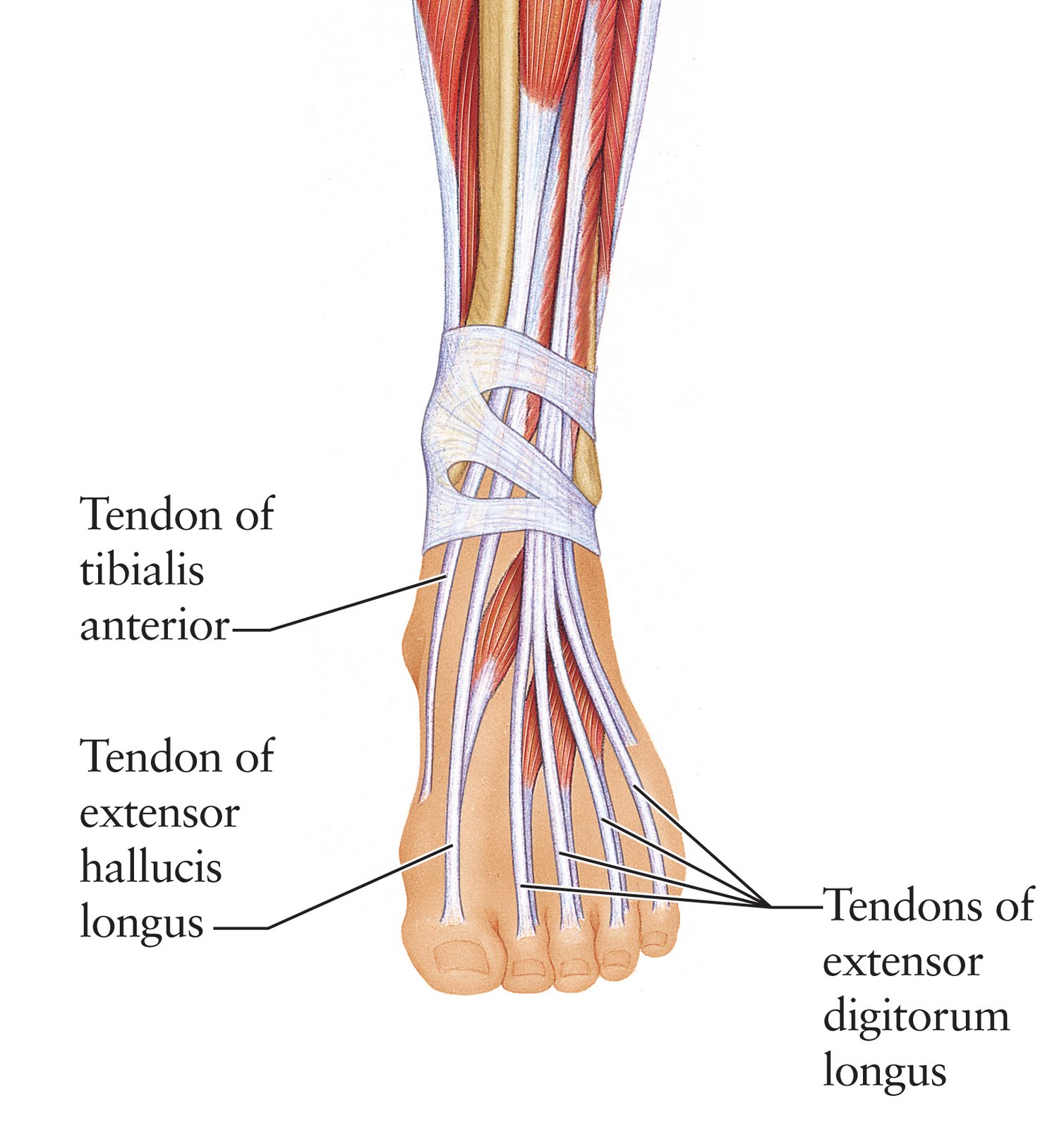
Human Anatomy for the Artist The Dorsal Foot How Do I Love Thee? Let
Morton's neuroma is a common foot problem where compression on a nerve in the ball of the foot causes burning, tingling, and pain near the third and fourth toes. It can make you feel like you have a pebble in your shoe or on a fold in your sock. Wearing high heels is a common cause of Morton's neuroma.

hand bone and tendon chart Artist The Dorsal Foot How Do I Love
The Anatomy of Feet: Bones and Structure. The foot is composed of 26 bones, making up about one-quarter of all the bones in the human body. These bones are divided into three main regions: the hindfoot, midfoot, and forefoot. The hind foot consists of the talus and calcaneus bones, which form the ankle joint and provide stability for weight.

Tendon Diagram Leg muscles leg tendons hamstrings diagram
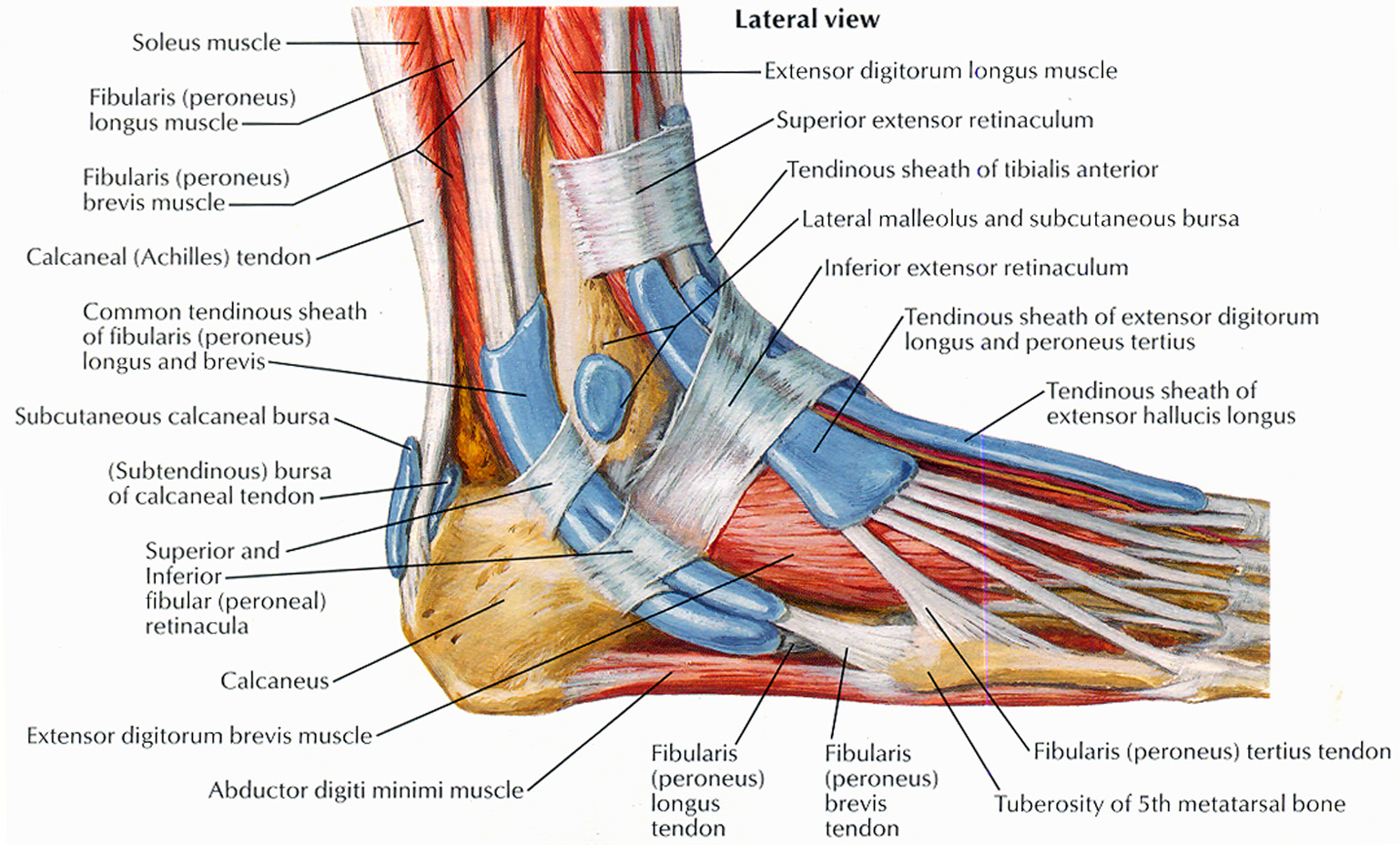
Ankle anatomy. The ankle joint, also known as the talocrural joint, allows dorsiflexion and plantar flexion of the foot. It is made up of three joints: upper ankle joint (tibiotarsal), talocalcaneonavicular, and subtalar joints.The last two together are called the lower ankle joint. The upper ankle joint is formed by the inferior surfaces of tibia and fibula, and the superior surface of talus.

Toe Dislocation JOI Jacksonville Orthopaedic Institute
The foot (pl.: feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates.It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion.In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate [clarification needed] organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws and/or nails.
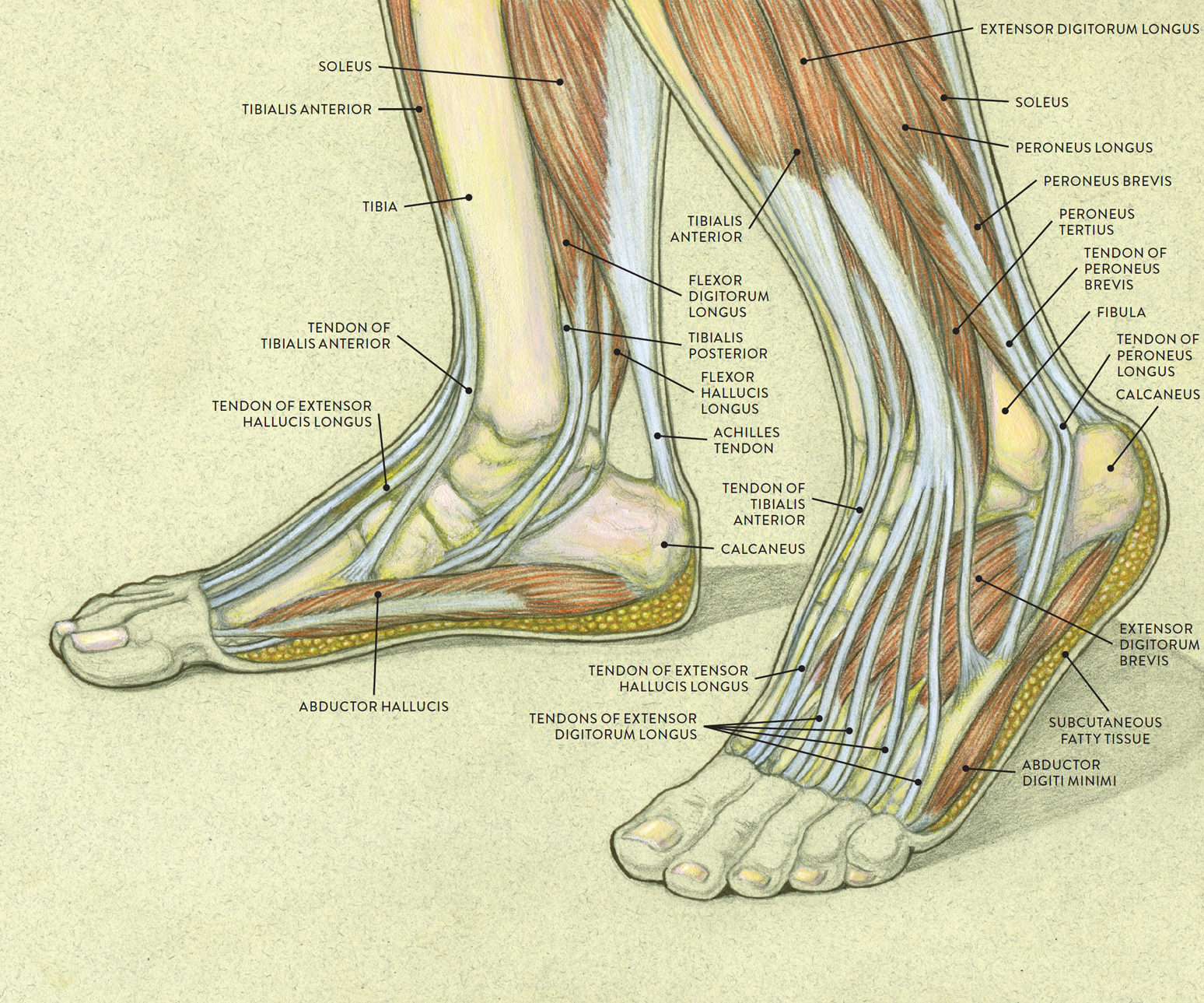
Muscles of the Leg and Foot Classic Human Anatomy in Motion The
Bones of foot. The 26 bones of the foot consist of eight distinct types, including the tarsals, metatarsals, phalanges, cuneiforms, talus, navicular, and cuboid bones. The skeletal structure of.
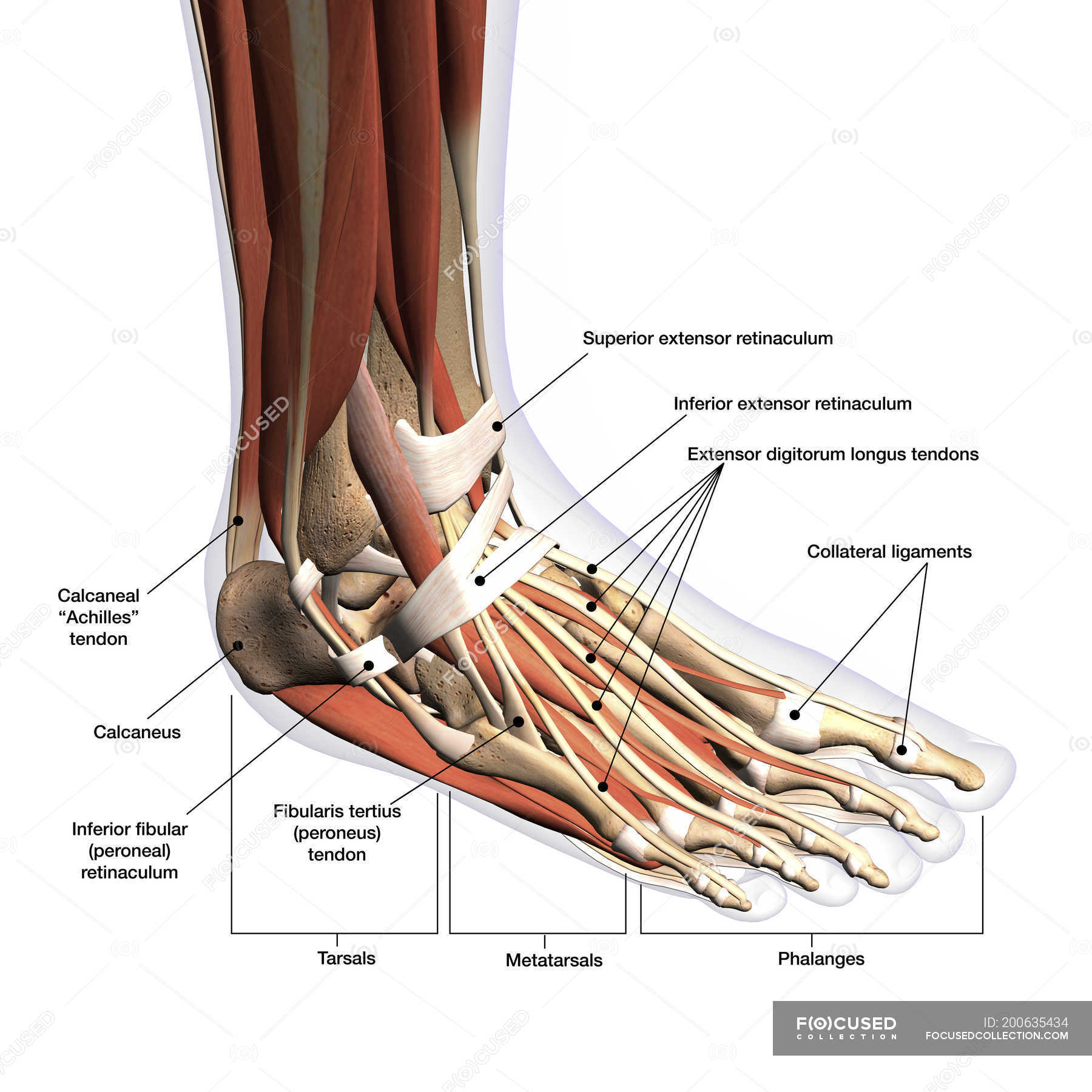
Anatomy of human foot with labels on white background — ankle, leg
The feet support the human body when standing, walking, running, and more. They are complex structures with 26 bones. Learn more about foot bones and foot anatomy here.
Foot Anatomy Bones, Muscles, Tendons & Ligaments
Foot. The foot is the lowermost point of the human leg. The foot's shape, along with the body's natural balance-keeping systems, make humans capable of not only walking, but also running.

Foot Anatomy Muscles Foot Archives Anatomy Human Body Foot anatomy
Foot and ankle anatomy consists of 33 bones, 26 joints and over a hundred muscles, ligaments and tendons. This complex network of structures fit and work together to bear weight, allow movement and provide a stable base for us to stand and move on. The foot needs to be strong and stable to support us, yet flexible to allow all sorts of complex.