
RiT radiology When to Obtain Ankle Radiographs
There are three main sets of ligaments: Medial: deltoid ligament Lateral: posterior talofibular, anterior talofibular and calcaneofibular ligaments Syndesmotic ligament From Radiology Masterclass Ankle views An x-ray of the ankle will have three views - AP, mortise, and lateral.

Ankle xrays Don't the Bubbles
Routine Radiographs These include a series of ankle and foot X-rays. ♦ Ankle series X-rays • Anteroposterior (AP) ( Fig. 2.1A) Fig. 2.1 (A and B) (A) Anteroposterior (AP) and (B) Lateral (LAT) views of ankle. • Lateral (LAT) ( Fig. 2.1B)

normal right foot x ray Google Search Foot x ray Pinterest Foot pain
Stress view. Positioning. patient. manual stress = supine + knee extended + ankle inverted/everted. gravity stress = supine + hip ER + knee flexed + ankle placed on bump. beam. aim at tibiotalar joint. Uses. joint stability = < 5° difference between ipsilateral + contralateral ankles.
Ankle Fracture FootEducation
A standard ankle x-ray series consists of the AP, lateral and a 15 degree internal oblique (aka Mortise View) [2]. Figure 1: Example of a normal ankle series. Case courtesy of Andrew Murphy, Radiopaedia.org

Normal Foot X Ray Normal foot series Image Check you have the right
Correct side (right vs. left) Views In the United Kingdom, two views of the ankle joint are routinely performed: Mortise view: this is a modified anteroposterior (AP) view of the ankle in 10-20° internal rotation so that the medial and lateral malleoli are in the same horizontal plane and joint visualisation is optimised Lateral view

Normal foot xray ownnipod
Ankle Fracture Mechanism and Radiography. Robin Smithuis. Radiology Department of the Rijnland Hospital, Leiderdorp, the Netherlands. The ankle is the most frequently injured joint. Management decisions are based on the interpretation of the AP and lateral X-rays. In this article we will focus on:
NORMAL FOOT 7
X-ray technology is used to examine many parts of the body. Bones and teeth. Fractures and infections. In most cases, fractures and infections in bones and teeth show up clearly on X-rays. Arthritis. X-rays of your joints can reveal evidence of arthritis. X-rays taken over the years can help your doctor determine if your arthritis is worsening.
NORMAL FOOT 5
If questionable osseous findings noted on x-ray, consider CT to evaluate further. If x-rays are negative, consider MRI to search for occult osseous, ligament, or tendon injuries.. Note the normal fat density anterior to the ankle joint on the lateral view of the normal ankle ( Figure 11-1 C ).

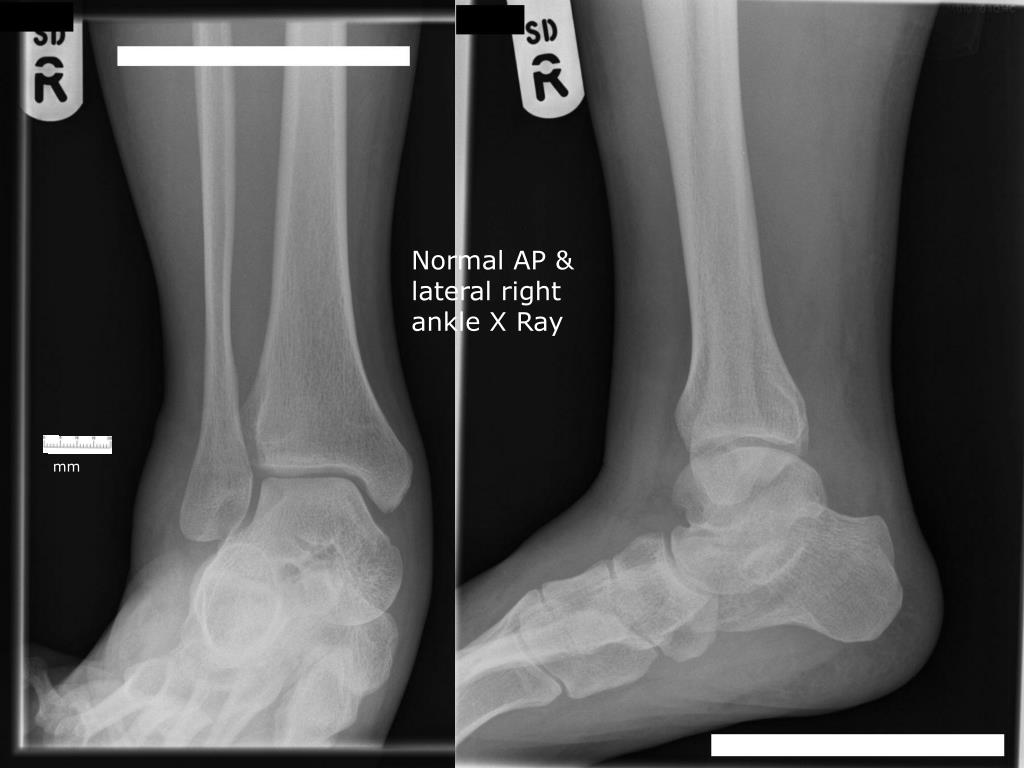
Normal ankle series Image
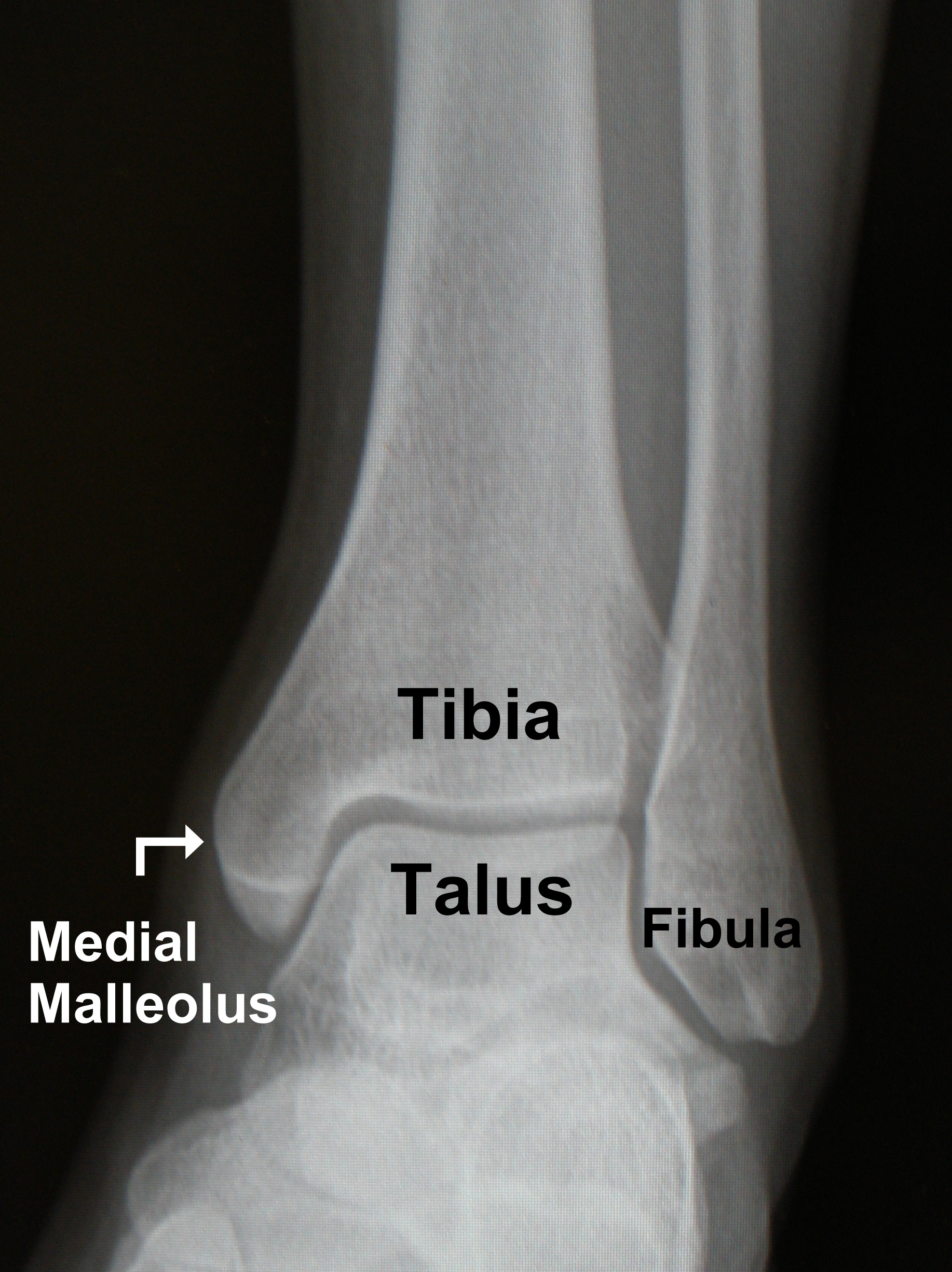
The basic principles about the ankle X-ray examination. Indication / Technique Normal anatomy Checklist Pathology - Part 1 Pathology - Part 2 Home Modules X-Ankle Normal anatomy add to favourites Anatomy Figure 5. Pure AP image of a normal left ankle. MM = medial malleolus, LM = lateral malleolus. Click image to see overlay

Normal Frontal Xray of the Ankle Stock Image P116/0532 Science Photo Library
Recognise normal variants and their significance (eg, accessory ossicles) Ottawa rules . These describe the requirements for plain x-rays within the clinical context of an ankle injury. They state that: an ankle radiograph is required only if there is pain in the "malleolar zone" and any of these findings:

Normal Foot X Ray Normal foot series Image Check you have the right
same horizontal plane as the medial malleolus and both are parallel to the x-ray tabletop. The mortise view is the true AP projection of the ankle joint. Oblique projections, 1 plain radiograph. The radiographic appearance of the normal child's ankle is seen in Figure 21.11. The distal tibial epiphysis appears during the 2nd year of life.
PPT XRay Rounds (Plain) Radiographic Evaluation of the Ankle PowerPoint Presentation ID
Health Library / Diagnostics & Testing / Foot X-Ray Foot X-Ray A foot X-ray is a test that produces an image of the anatomy of your foot. Your healthcare provider may use foot X-rays to diagnose and treat health conditions in your foot or feet. Foot X-rays are quick, easy and painless procedures.

Image
Bony anatomy The ankle is a synovial joint composed of the distal tibia and fibula as they articulate with the talus. The distal tibia and fibula articulate with each other at the distal tibiofibular joint which is more commonly referred to as the tibiofibular syndesmosis (or simply the syndesmosis).

EMRad Radiologic Approach to the Traumatic Ankle
Ankle anatomy - Normal AP 'mortise' The weight-bearing portion is formed by the tibial plafond and the talar dome The joint extends into the 'lateral gutter' ( 1) and the 'medial gutter' ( 2) The joint is evenly spaced throughout Ankle anatomy - Normal Lateral Hover on/off image to show/hide findings
Assessing Heel Pain Diagnostic Ultrasound of the Foot and Ankle
The true anteroposterior view of the ankle is often performed in the setting of ankle trauma and suspected ankle fractures in addition to the lateral and mortise views of the ankle. Other indications include: assessment of fragment position and implants in postoperative follow up evaluation of fracture healing

EMRad Can’t Miss Adult Ankle and Foot Injuries In the Setting of Trauma
An ankle x-ray, also known as ankle series or ankle radiograph, is a set of two x-rays of the ankle joint. It is performed to look for evidence of injury (or pathology) affecting the ankle, often after trauma. Reference article This is a summary article. For more information, you can read a more in-depth reference article: ankle series. Summary