
NASA The Sun
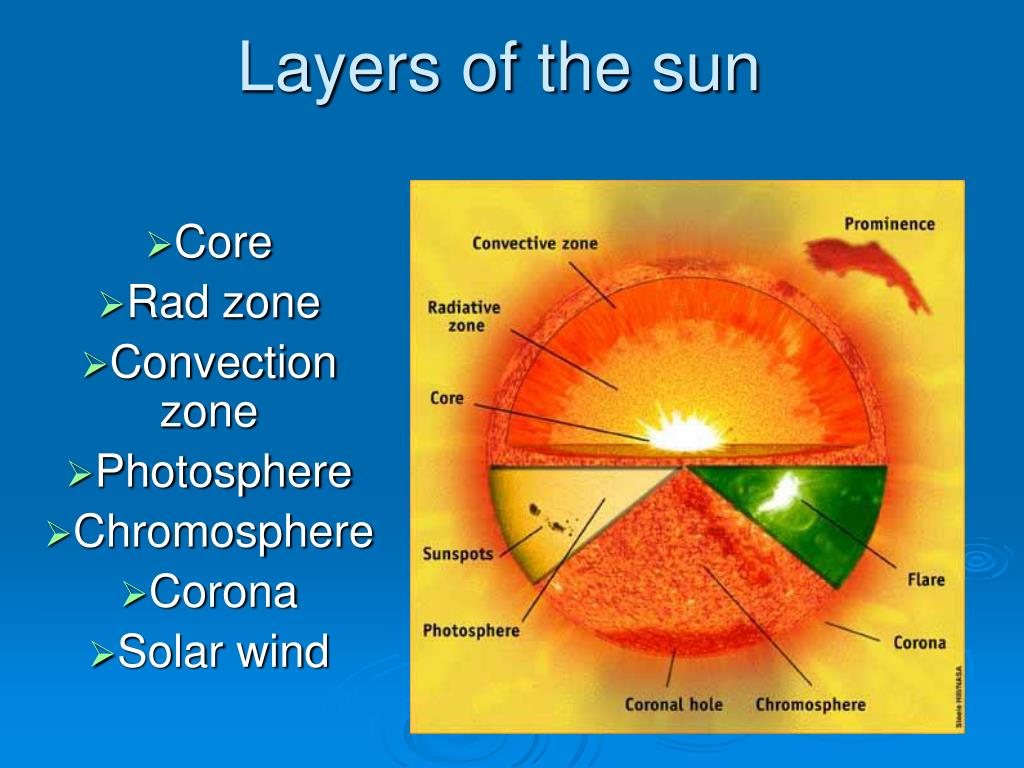
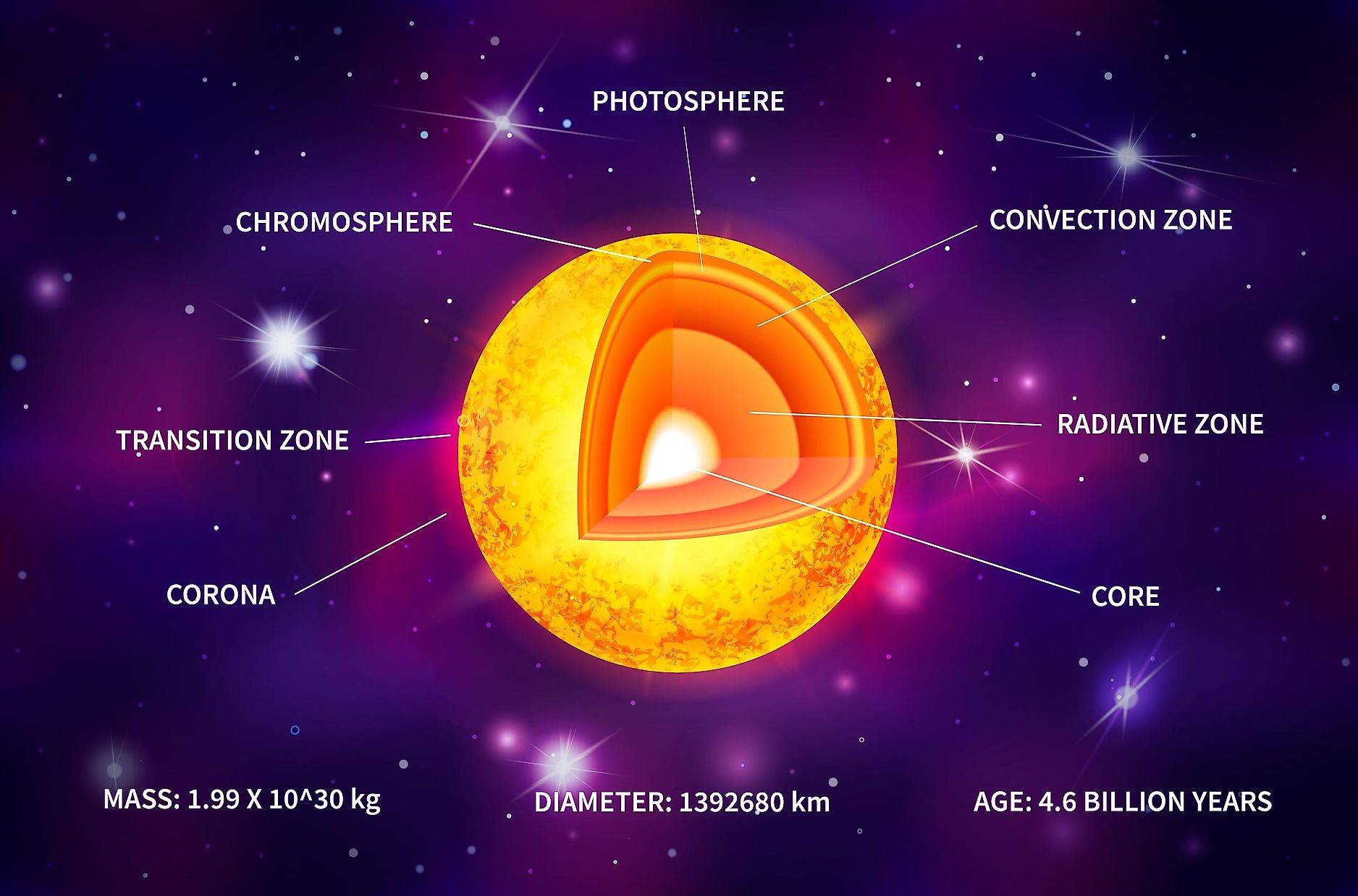
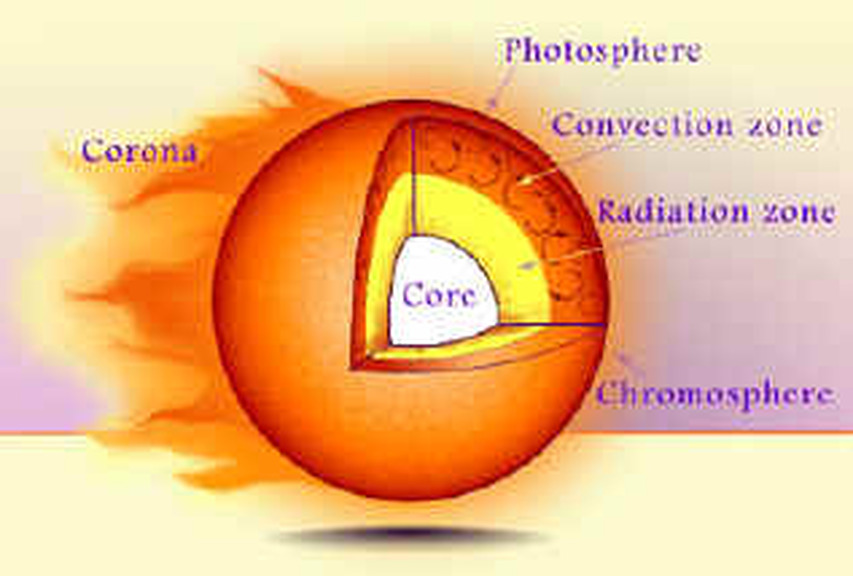
The Sun is made up of three inner layers and three outer layers, six layers in total. The layers are the core, the radiative zone, the convective zone, the photosphere, the chromosphere, and the.
Premium Vector The sun detailed structure with layers illustration. outer space science
About 73% of the Sun's mass is hydrogen, and another 25% is helium. All the other chemical elements (including those we know and love in our own bodies, such as carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen) make up only 2% of our star. The 10 most abundant gases in the Sun's visible surface layer are listed in Table 15.1.2 15.1. 2.

Layers of the Sun
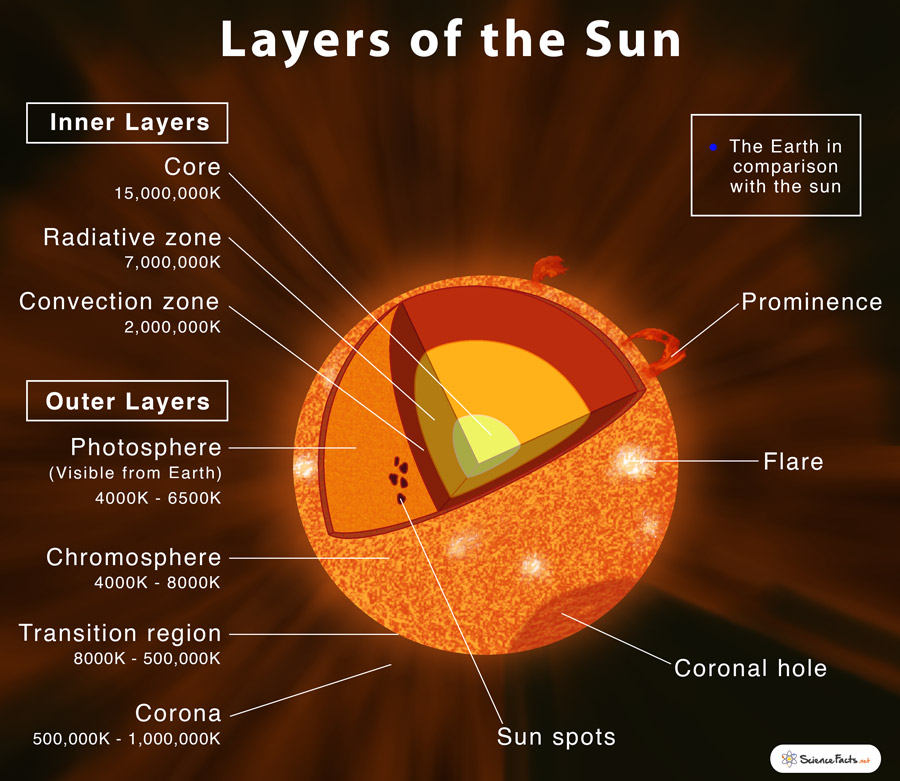
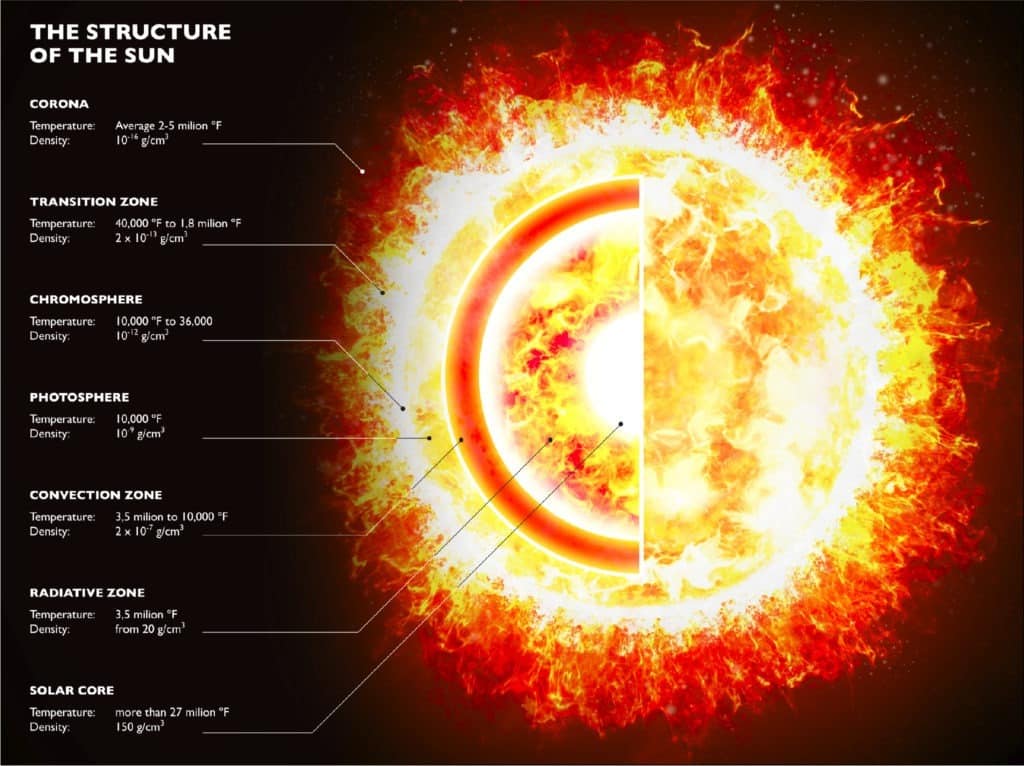
The hottest part of the Sun is its core, where temperatures top 27 million °F (15 million °C). The part of the Sun we call its surface - the photosphere - is a relatively cool 10,000 °F (5,500 °C). In one of the Sun's biggest mysteries, the Sun's outer atmosphere, the corona, gets hotter the farther it stretches from the surface.
7 Layers of the Sun Explained (+ Interesting Facts)
These layers, which collectively make up the Sun's atmosphere, burn far hotter than its surface— in the case of the corona, about 1.6 million degrees Celsius.

Layers of the sun Stock Photo Alamy
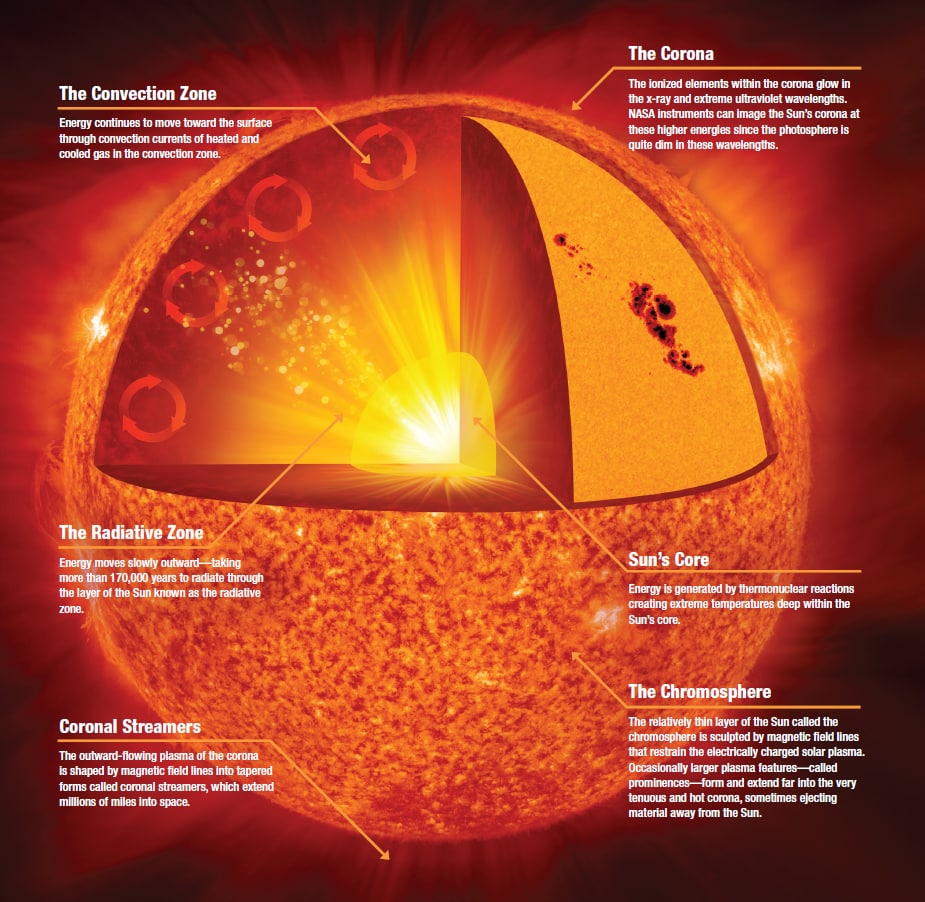
The parts of the inner layer are: 1. Core. It is the innermost layer of the sun, which is extremely dense where nuclear fusion generates energy in terms of photons by converting hydrogen into helium. The core is approximately 20% of the size of the solar interior and is found to be the hottest part of the sun. 2.
PPT Layers of the sun PowerPoint Presentation ID253550
The 10 most abundant gases in the Sun's visible surface layer are listed in Table 15.2. Examine that table and notice that the composition of the Sun's outer layer is very different from Earth's crust, where we live. (In our planet's crust, the three most abundant elements are oxygen, silicon, and aluminum.)
Layers of the Sun Structure & Composition with Diagram
The solar atmosphere is made up of: The Photosphere - the visible surface of the Sun. The Chromosphere - an irregular layer above the photosphere where the temperature rises from 6000°C to about 20,000°C. A Transition Region - a thin and very irregular layer of the Sun's atmosphere that separates the hot corona from the much cooler.

NASA Layers of the Sun
The third layer of the sun's atmosphere is the corona. Like the chromosphere, the sun's corona can only be seen during a total solar eclipse (or with NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory ).
What Are The Layers Of The Sun? WorldAtlas
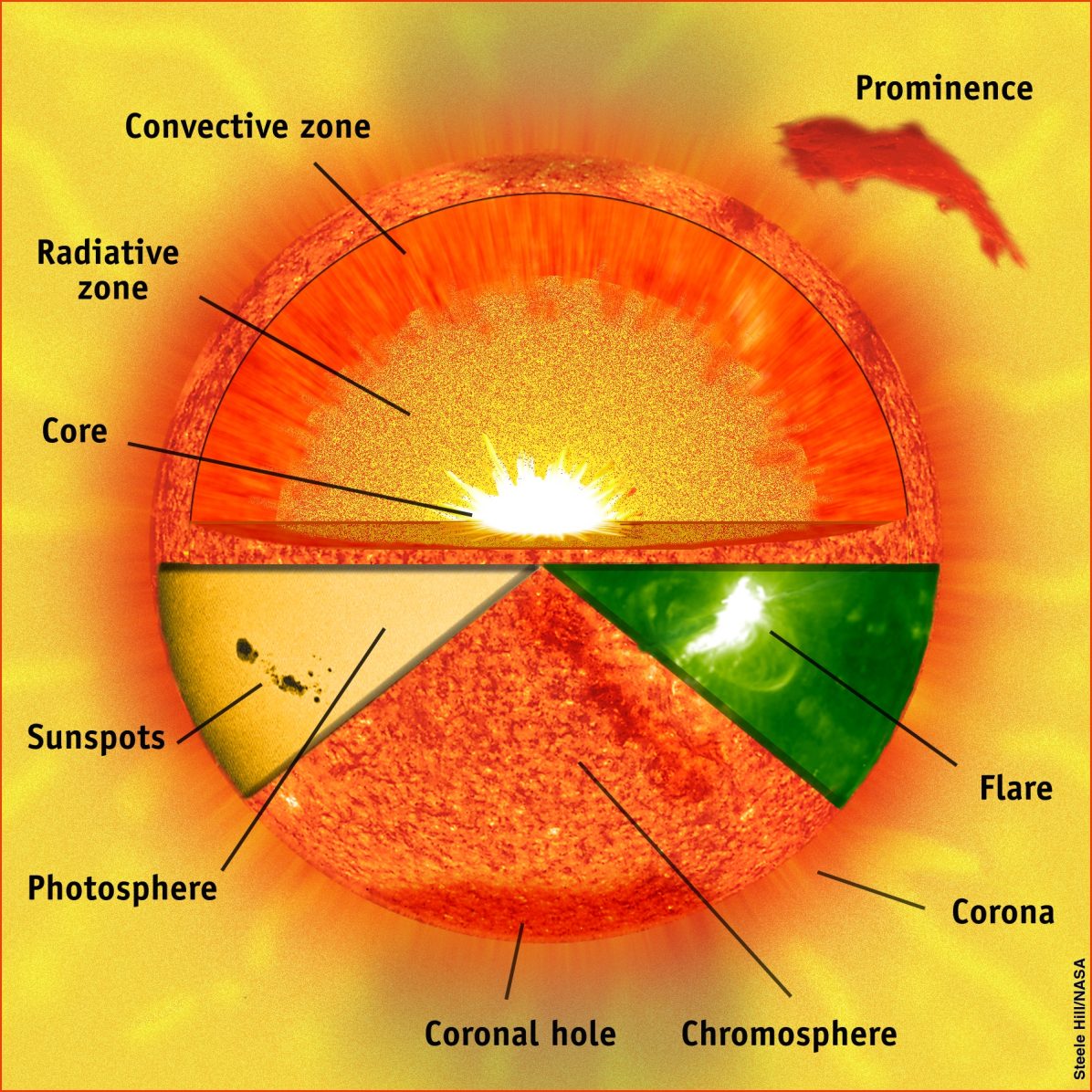
The outer layers are the Corona, the Transition Region, the Chromosphere, and the Photosphere, while the inner layers are the Core, the Radiative Zone, and the Convection Zone. There are four outer layers of the Sun, and the Corona is the outermost one. It starts at about 1300 miles above the photosphere, and its temperature is measured to be.
Sun's Layers The Life Cycle of a Star
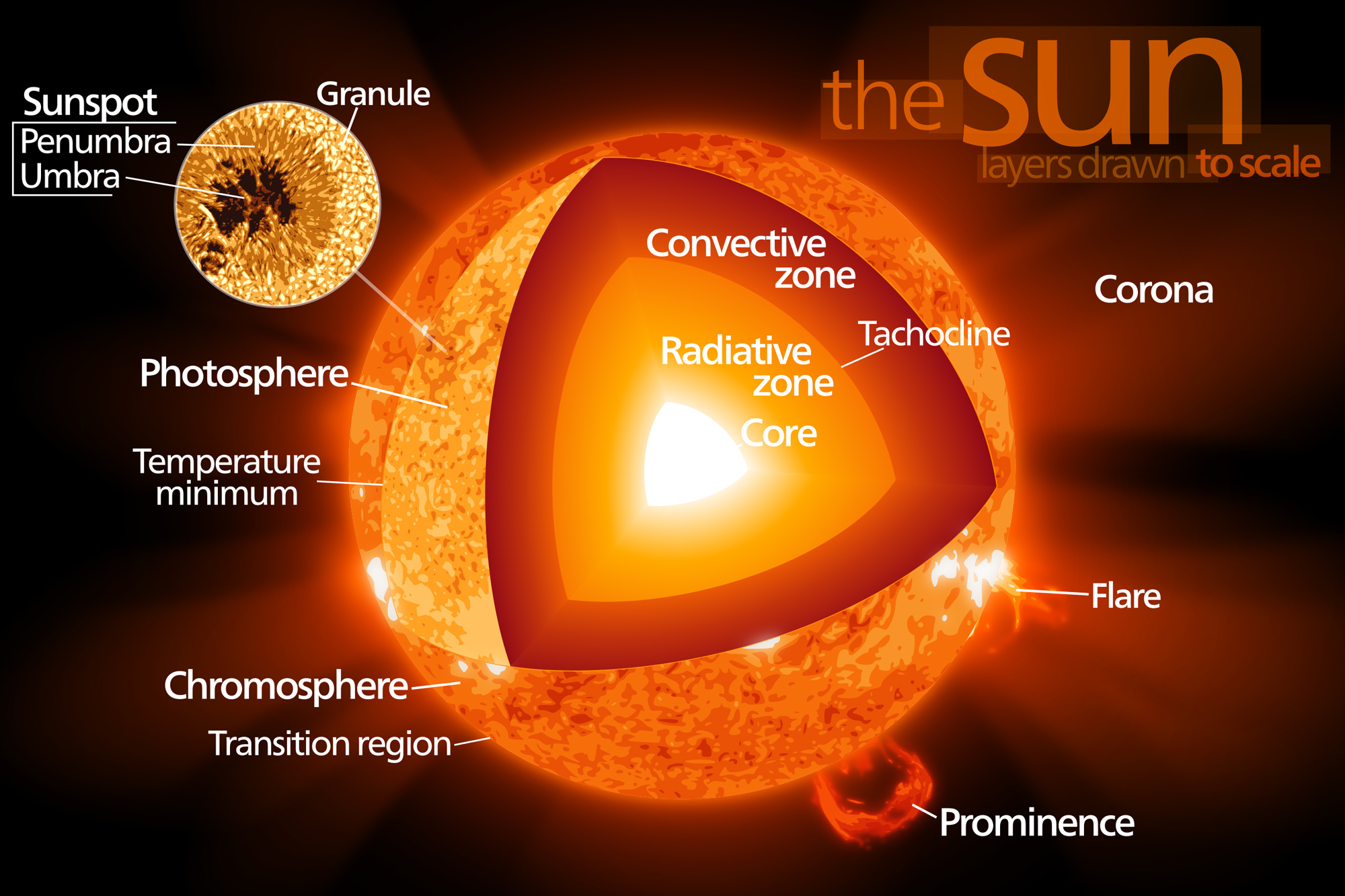
The Chromosphere - This relatively thin layer of the Sun is sculpted by magnetic field lines that restrain the electrically charged solar plasma. Occasionally larger plasma features, called prominences, form and extend far into the very tenuous and hot corona, sometimes ejecting material away from the Sun. The Corona - The ionized elements.
7 Layers of the Sun in Order Explained (+ Interesting Facts)
The sun's atmosphere comprises the only layers of the Sun that can be observed directly are the outer layers: the photosphere, chromosphere, and corona. These three layers make up the solar atmosphere. Starting from the Sun's interior core and moving outward, the layers of the Sun are: 1. Solar Core.
Sun formation, thermal nuclear fusion, structure, future life
Sun's Structure The sun is made up of six layers: core, radiative zone, convective zone, photosphere, chromosphere, and corona. Core The sun's core, more than a thousand times the size of Earth and more than 10 times denser than lead, is a huge furnace. Temperatures in the core exceed 15.7 million kelvin (also 15.7 million degrees Celsius.
Solar Structure The Sun Today with C. Alex Young, Ph.D.
The sun's magnetic fields rise through the convection zone and erupt through the photosphere into the chromosphere and corona. The eruptions lead to solar activity, which includes such phenomena as sunspots, flares, prominences, and coronal mass ejections. The sun and its atmosphere consist of several zones or layers.
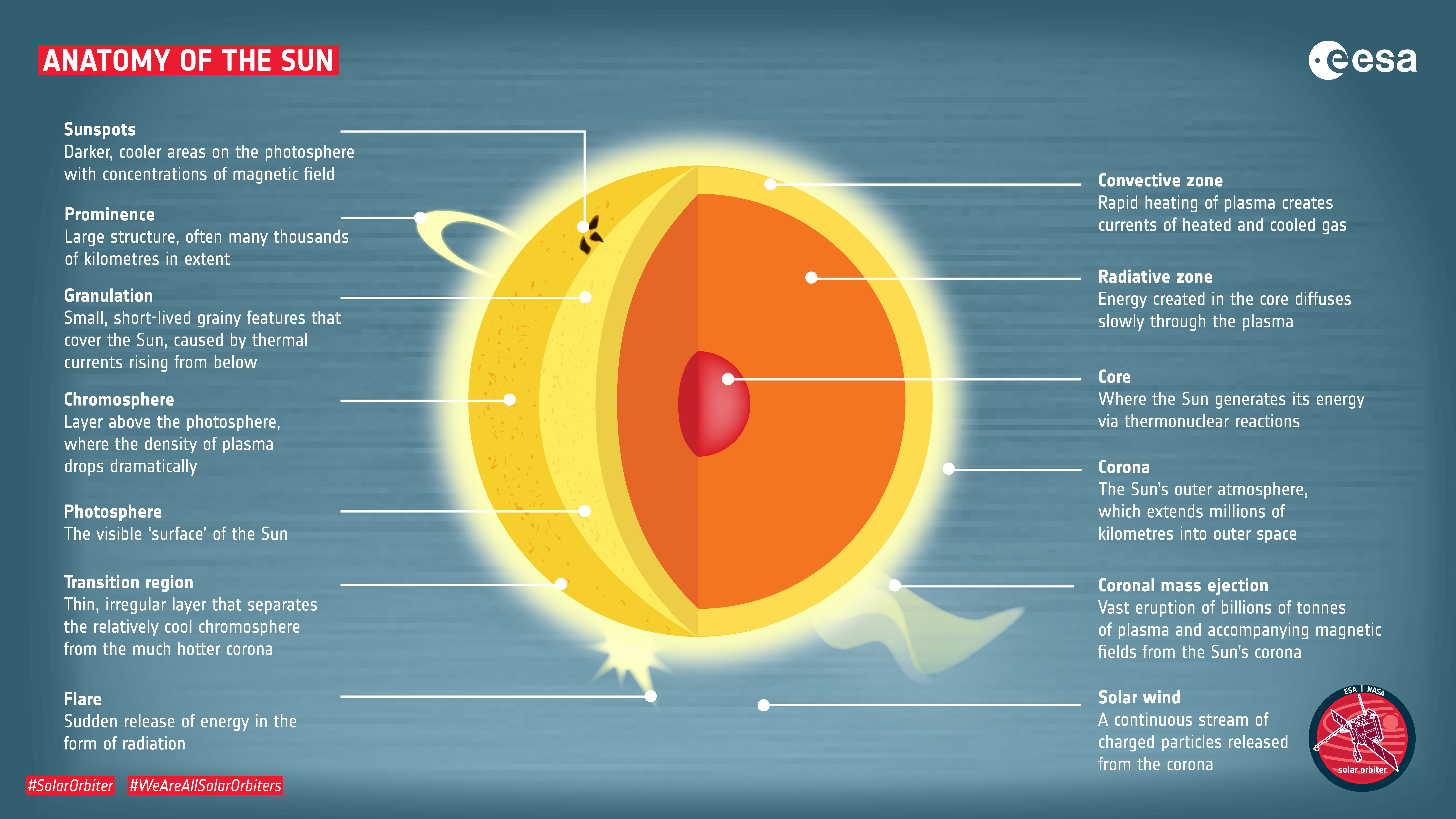
ESA Anatomy of the Sun
Corona - The corona is the outermost layer of the Sun, starting at about 1300 miles (2100 km) above the solar surface (the photosphere). The temperature in the corona is 500,000 K (900,000 degrees F, 500,000 degrees C) or more, up to a few million K. The corona cannot be seen with the naked eye except during a total solar eclipse, or with the.
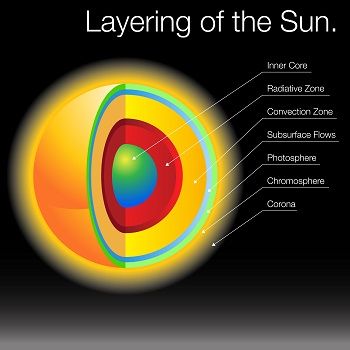
The Sun's layers Northumbria University, Newcastle
The sun has 7 layers that are divided roughly in half into two categories. The first four are the outer layers and the last three are the inner layers. We'll go in order from exterior to interior when explaining each layer. Each concentric layer is similar to a gobstopper or an onion. However, each layer has different physical characteristics.
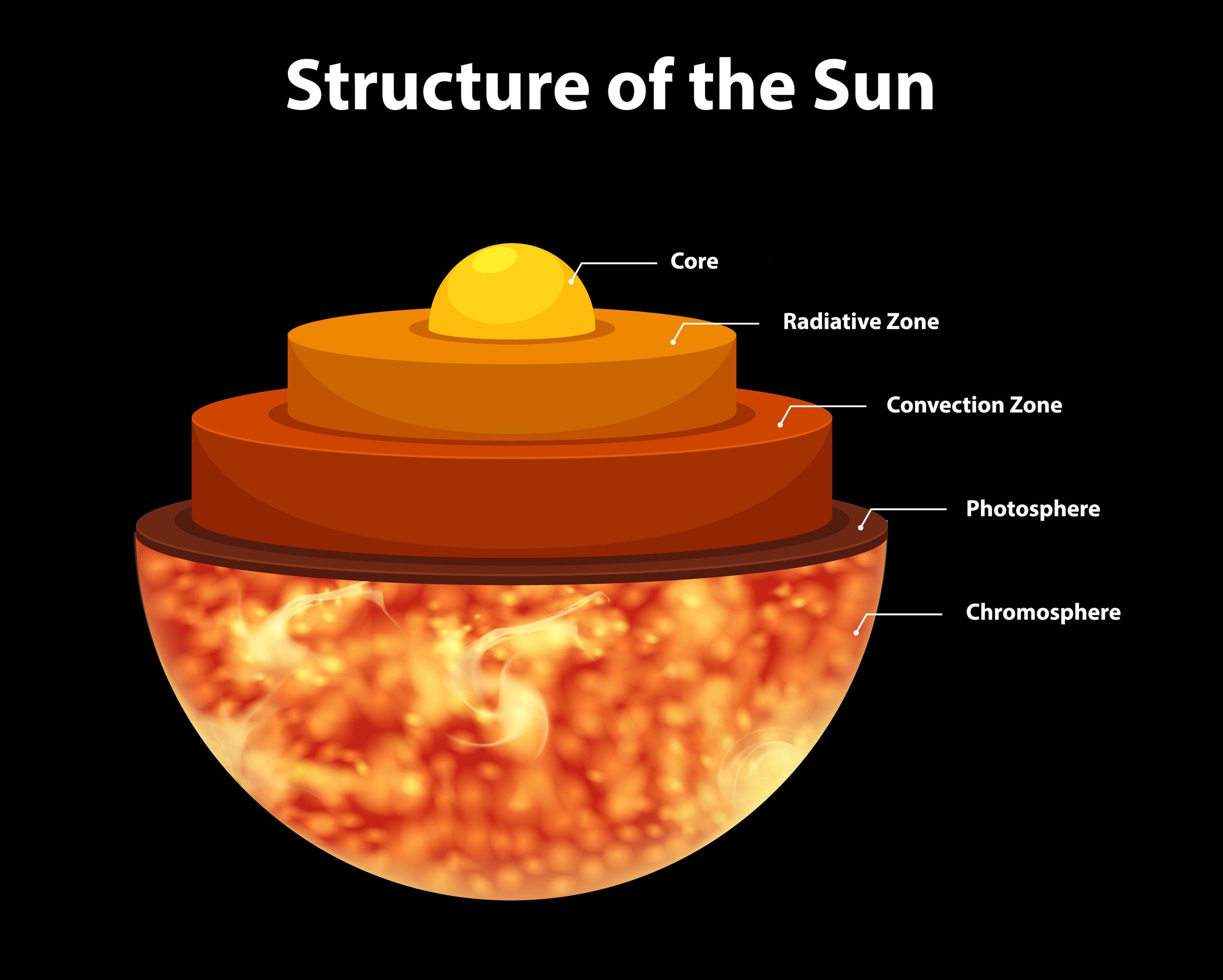
Diagram showing structure of the sun 1142243 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Three layers, a core, radiative zone, and convective zone, comprise the insides of our star. Deep within the Sun's interior lies the core . Initially, all the power, energy, and heat generated by the Sun is born here. In other words, the core is the Sun's heart. Pressures and temperatures are at their highest levels within the core.