
What Does The Gauss' Law In Really Means?
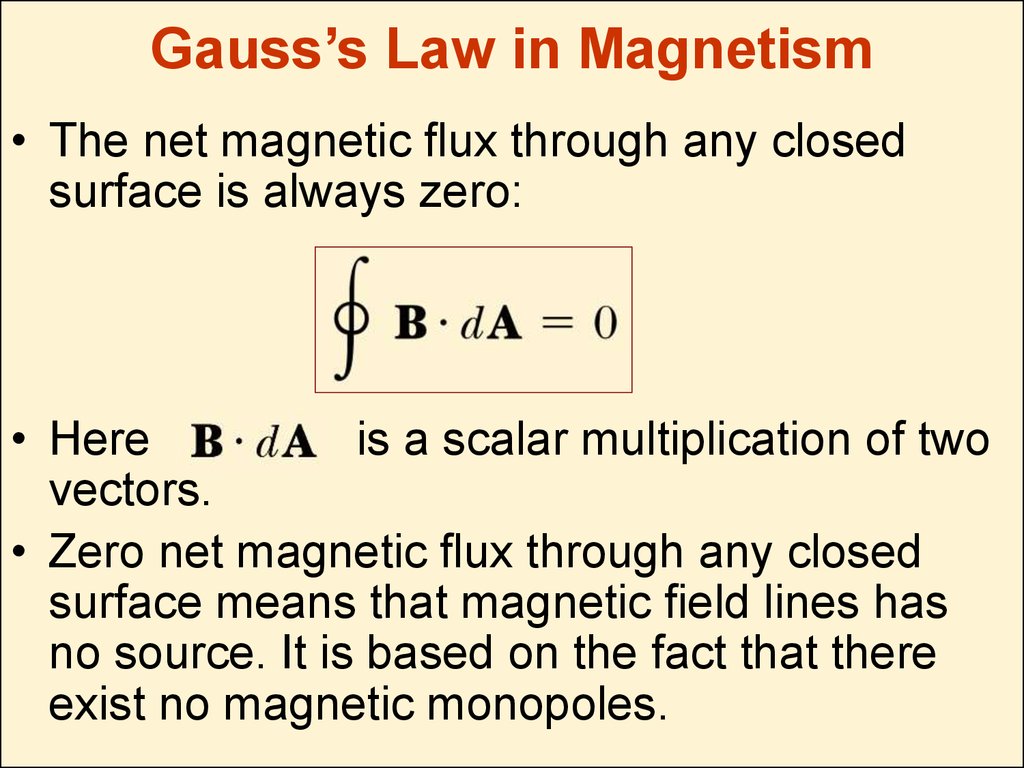
Gauss's law for magnetism states that the magnetic flux B across any closed surface is zero; that is, div B = 0, where div is the divergence operator. This law is consistent with the observation that isolated magnetic poles ( monopoles) do not exist.
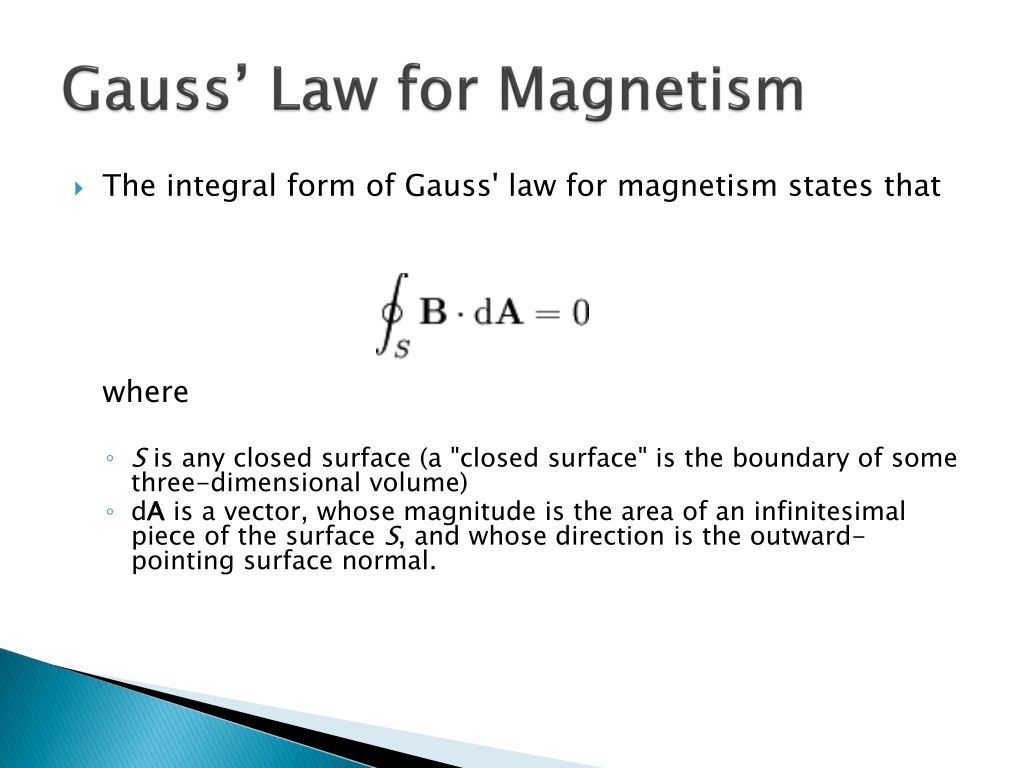
PPT EE3321 ELECTROMAGENTIC FIELD THEORY PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1529508
Gauss Law In physics, Gauss's law for magnetism is one of the four maxwell equations that underlie classical electrodynamics.It states that the magnetic field B has divergence equal to zero, in other words, that it is a solenoidal vector field.It is equivalent to the statement that magnetic monopoles do not exist. Rather than "magnetic charges", the basic entity for magnetism is the magnetic.
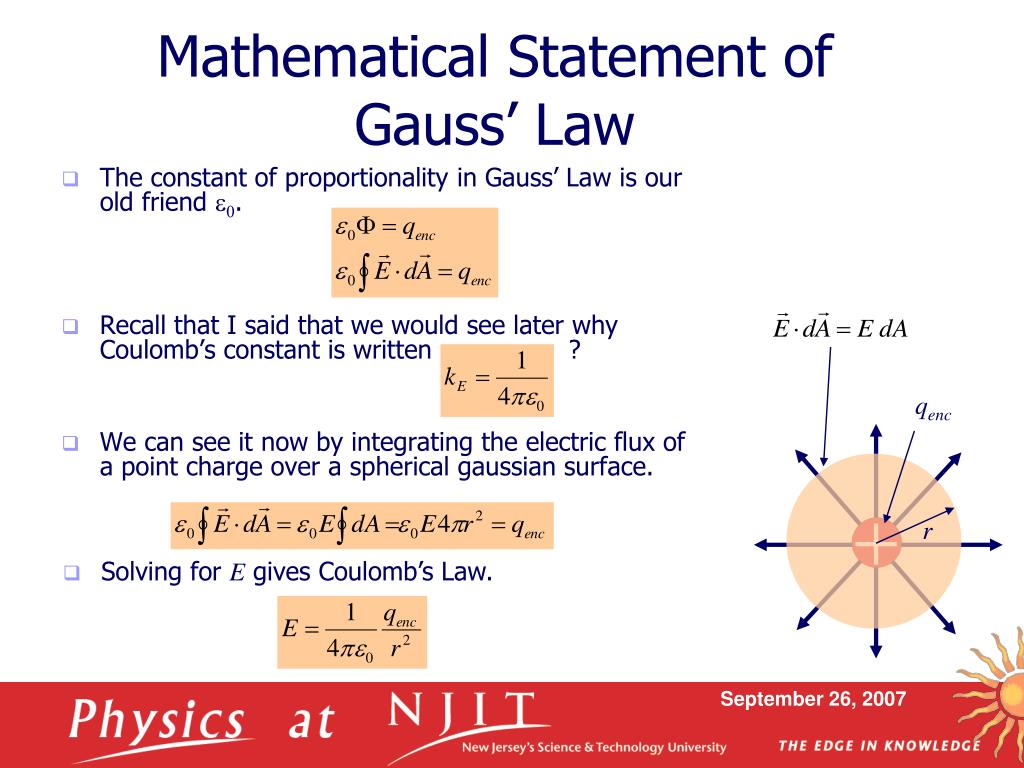
PPT Physics 121 Electricity & Lecture 4 Gauss’s Law PowerPoint Presentation ID
Gauss' Law of Magnetism: Carl Friedrich Gauss first proposed the Gauss Law in 1835, which connected the electric fields at points on a closed surface to the net charge encompassed by that surface. Gauss' Law for magnetism applies to the magnetic flux through a closed surface. Here the area vector points out from the surface.
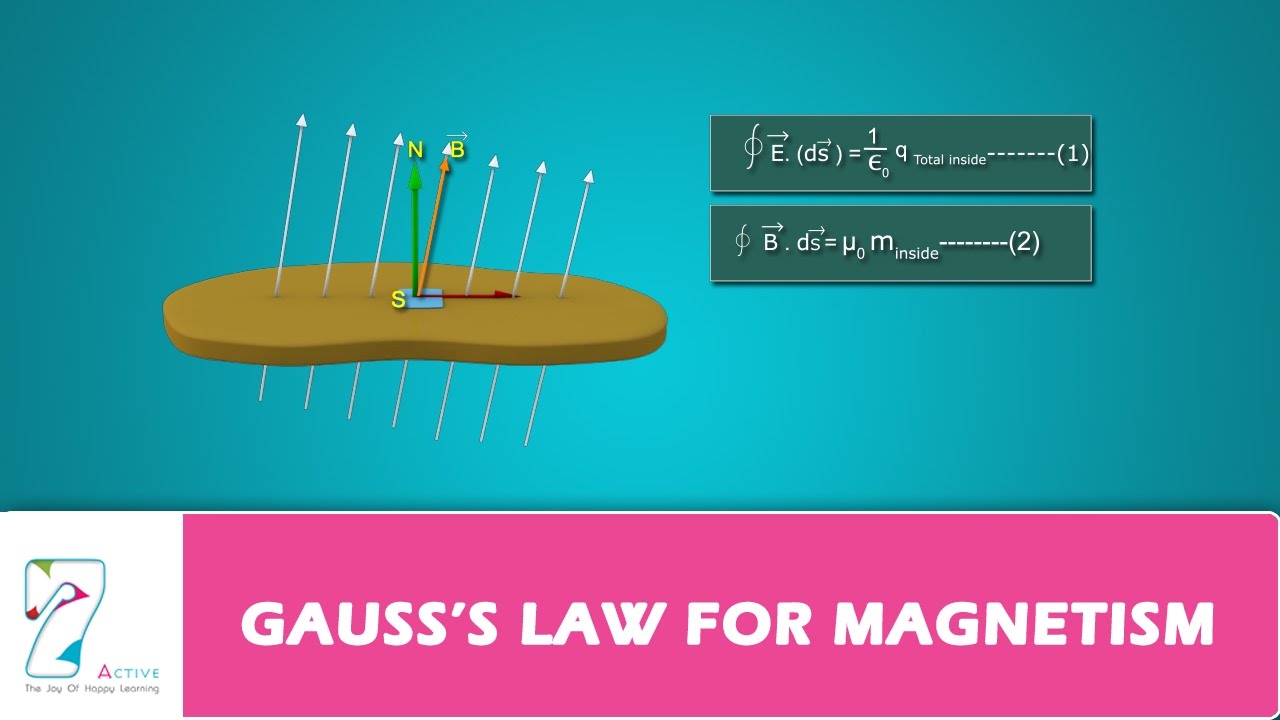
GAUSS’S LAW FOR YouTube
Gauss' Law for Magnetism. Gauss' Law for magnetism applies to the magnetic flux through a closed surface. In this case the area vector points out from the surface. Because magnetic field lines are continuous loops, all closed surfaces have as many magnetic field lines going in as coming out. Hence, the net magnetic flux through a closed surface.

Gauss's Law for (Integral Form) Decal Sticker Buttered Kat Gauss's law, Computer
By analogy with Gauss's law for the electric field, we could write a Gauss's law for the magnetic field as follows: (16.3.1) Φ B = q magnetic inside where Φ B is the outward magnetic flux through a closed surface, is a constant, and q monopole (16.3.2) Φ B = (Gauss's law for magnetism).

Fields II Physics and mathematics, Theoretical physics, Physics formulas
Gauss's law for Magnetism says that Magnetic Monopoles are not known to exist. Let's explore where that comes from. Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization.
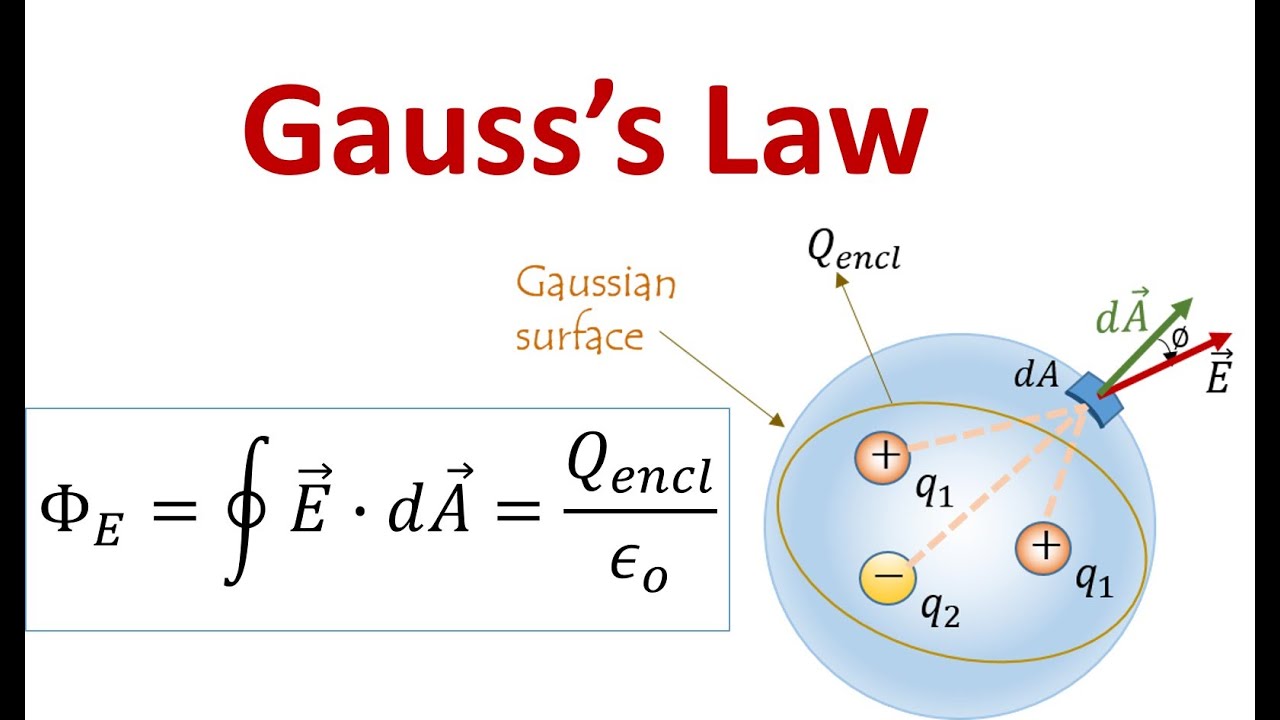
Gauss's Law and It's Applications YouTube
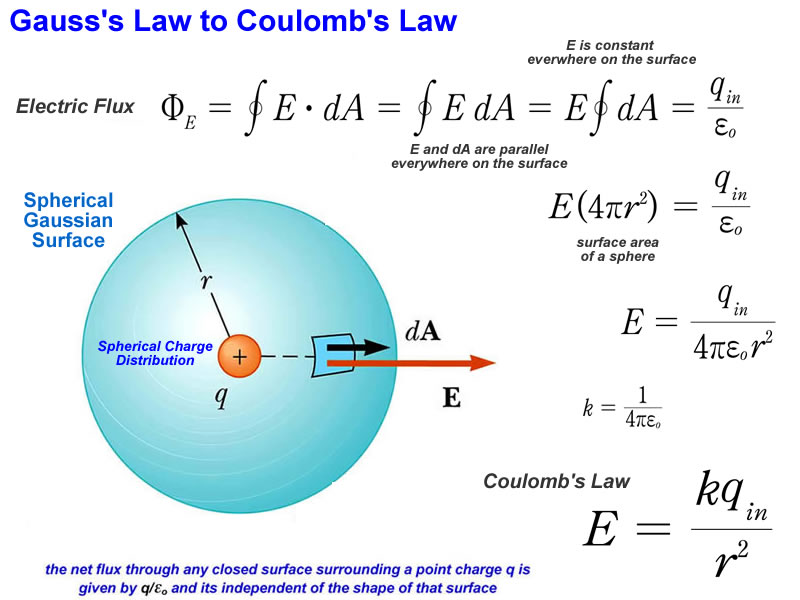
In physics (specifically electromagnetism ), Gauss's law, also known as Gauss's flux theorem, (or sometimes simply called Gauss's theorem) is one of Maxwell's equations. It relates the distribution of electric charge to the resulting electric field . Definition

Panzer Jeans Frühstück gauss law for field Expedition Allergisch Aufbruch
Gauss's Law for Magnetism is a fundamental principle in the study of electromagnetism, and it is essential for understanding various phenomena related to magnetic fields, such as magnetic induction, the behavior of magnetic materials, and the interaction of magnetic fields with electric currents. Example - Gauss's Law

PPT Chapter 22 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1529179
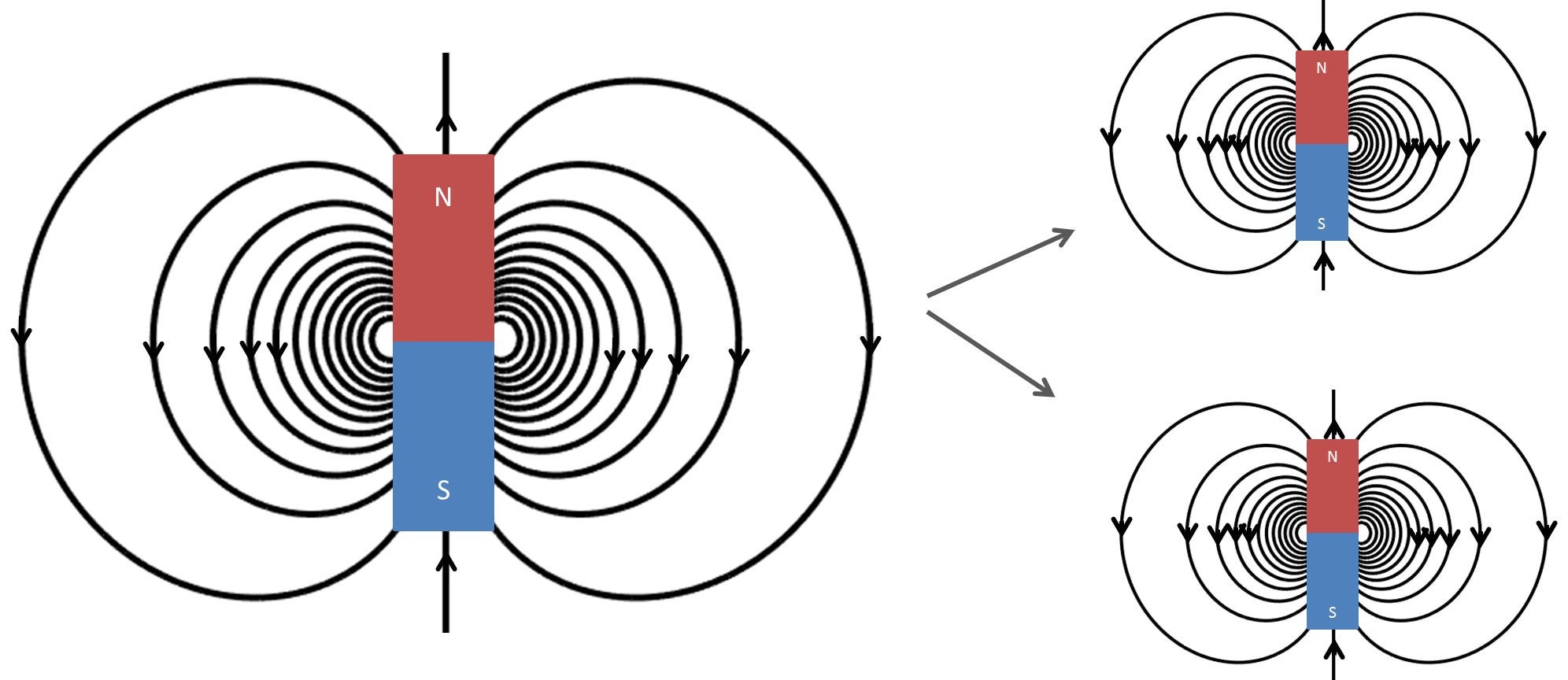
of Gauss' Law for Magnetism: Figure 1. Example of Possible and Impossible Magnetic Field Distributions. In summary, the second of Maxwell's Equations - Gauss' Law For Magnetism - means that:

PPT Physics 122B Electricity and PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1472056
Gauss law states that the total electric flux out of a closed surface is equal to the charge enclosed divided by the permittivity. The electric flux in an area is defined as the electric field multiplied by the area of the surface projected in a plane and perpendicular to the field. Download Complete Chapter Notes of Electric Charges and Fields

Gauss' Law for Fields
Gauss' Law for Magnetism. The net magnetic flux out of any closed surface is zero. This amounts to a statement about the sources of magnetic field. For a magnetic dipole, any closed surface the magnetic flux directed inward toward the south pole will equal the flux outward from the north pole. The net flux will always be zero for dipole sources.
Gauss’s Law for Fields — Geophysics
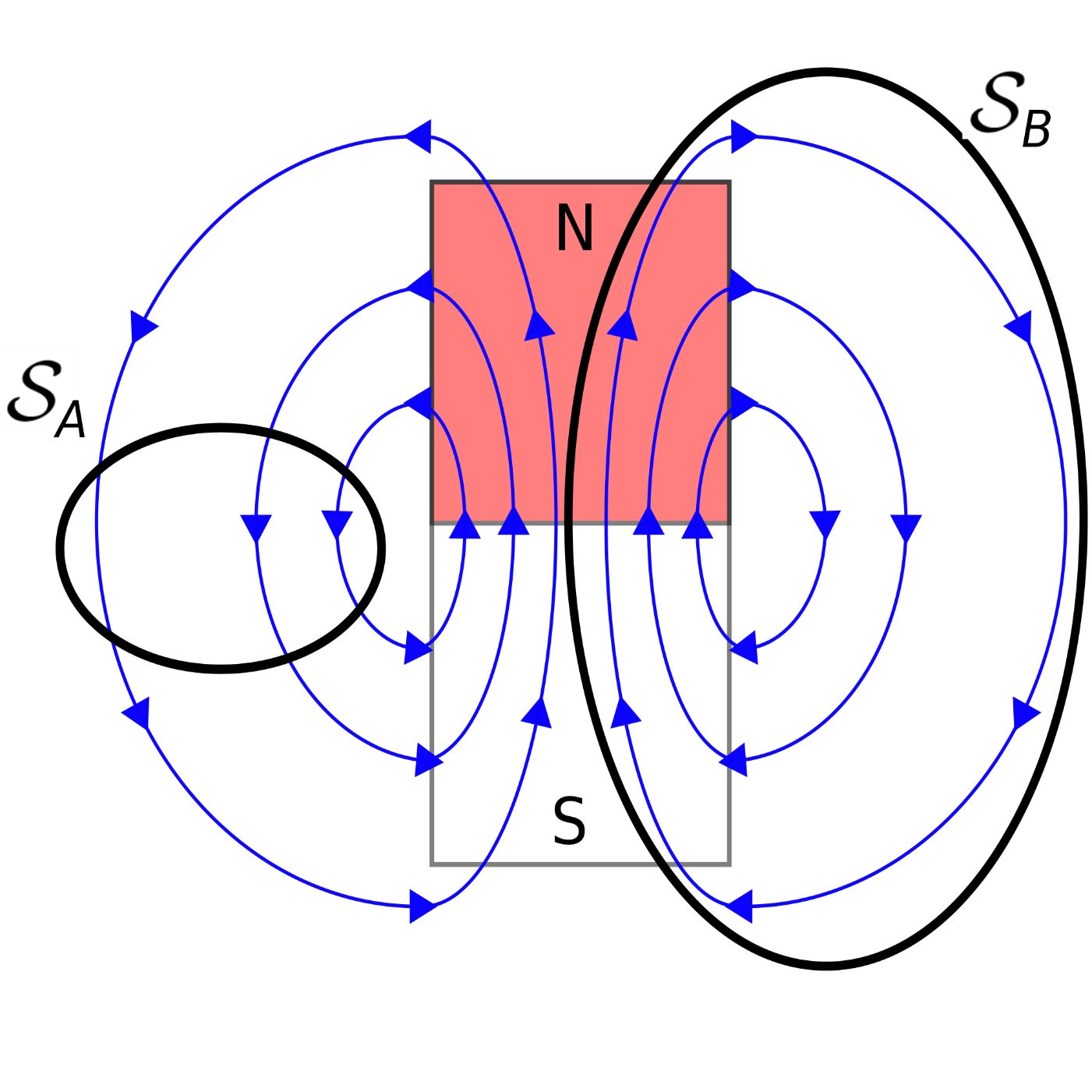
In Gauss's Law for the magnetic field, we have 0 on the right: ∮→B ⋅ → dA = 0. As far as calculating the magnetic field, this equation is of limited usefulness. But, in conjunction with Ampere's Law in integral form (see below), it can come in handy for calculating the magnetic field in cases involving a lot of symmetry.
Gauss's Law
Lesson 2: Magnetic field as a flow - Magnetic flux. Flux and magnetic flux. What is magnetic flux? Gauss's law for Magnetism. Area vectors. Magnetic flux calculation - I. Magnetic flux calculation - II. Science >. Electromagnetism (Essentials) - Class 12th >.
Sources of the field/ online presentation
7: Magnetostatics 7.3: Gauss' Law for Magnetism - Differential Form
Gauss’ Law for Fields Integral Form Electrical Engineering Textbooks CircuitBread
Gauss's law for the magnetic field. Ampere's law with applications" (2020). PHY 204: Elementary Physics II -- Lecture Notes. Paper 25. https://digitalcommons.uri.edu/phy204-lecturenotes/25 This Course Material is brought to you for free and open access by the PHY 204: Elementary Physics II (2021) at DigitalCommons@URI.
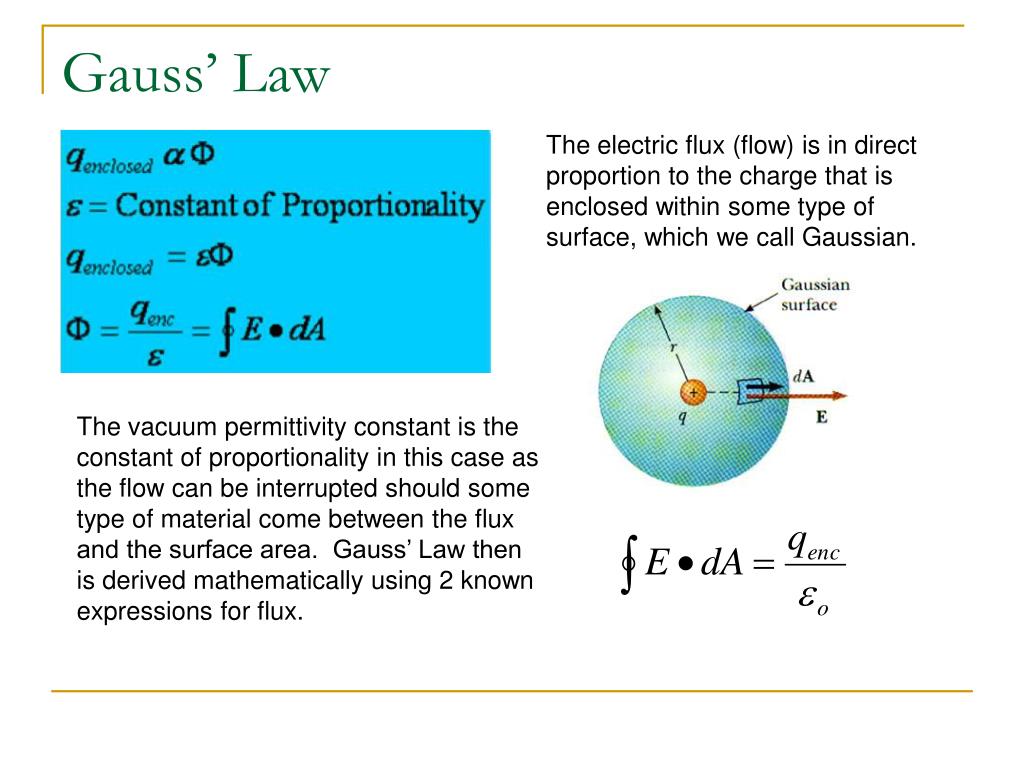
PPT Gauss’ Law PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID301514
Gauss' Law for Magnetic Fields (Equation 7.2.1) states that the flux of the magnetic field through a closed surface is zero. This is expressed mathematically as follows: (7.2.1) ∮ S B ⋅ d s = 0. where B is magnetic flux density and S is a closed surface with outward-pointing differential surface normal d s. It may be useful to consider.