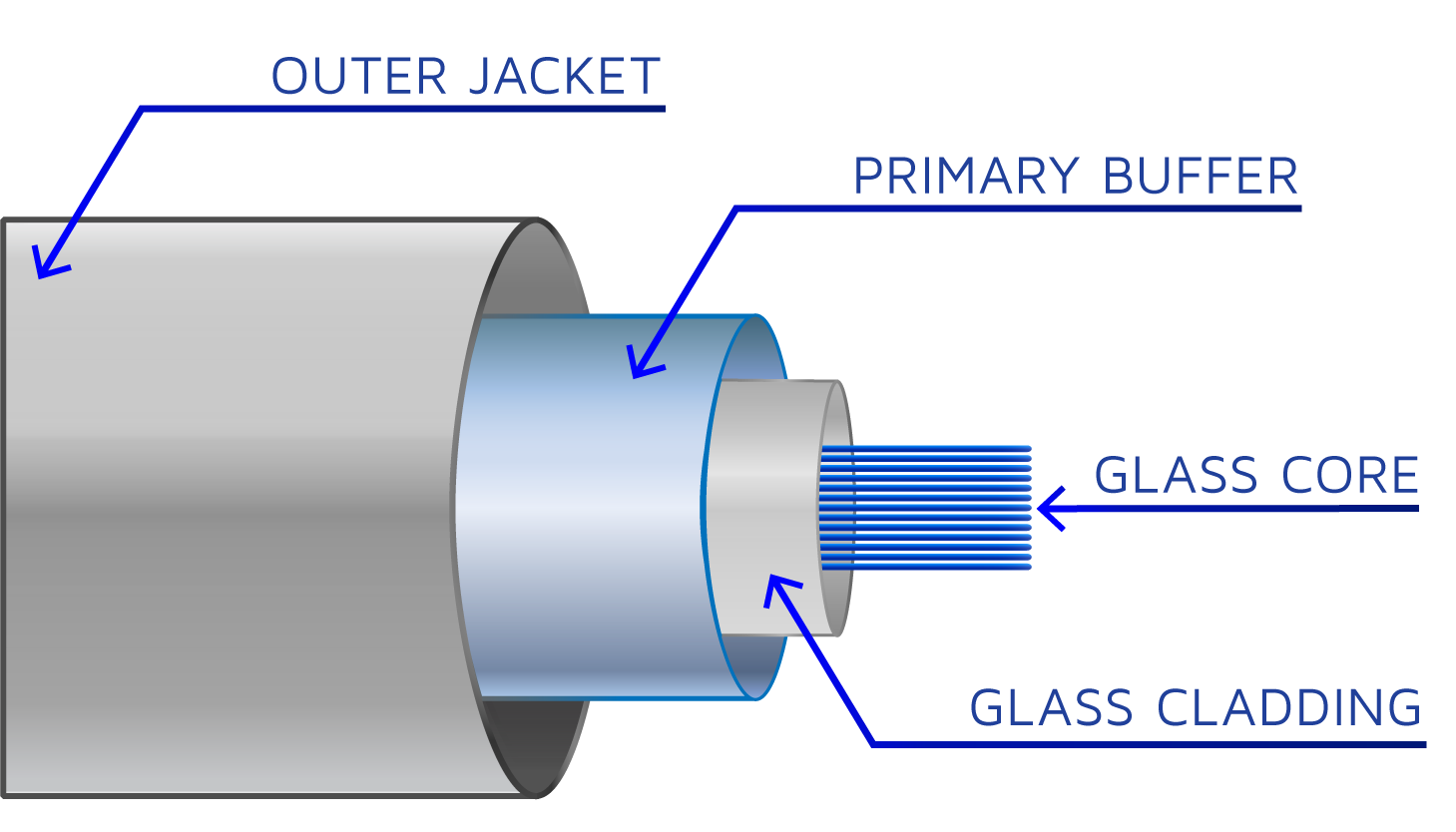
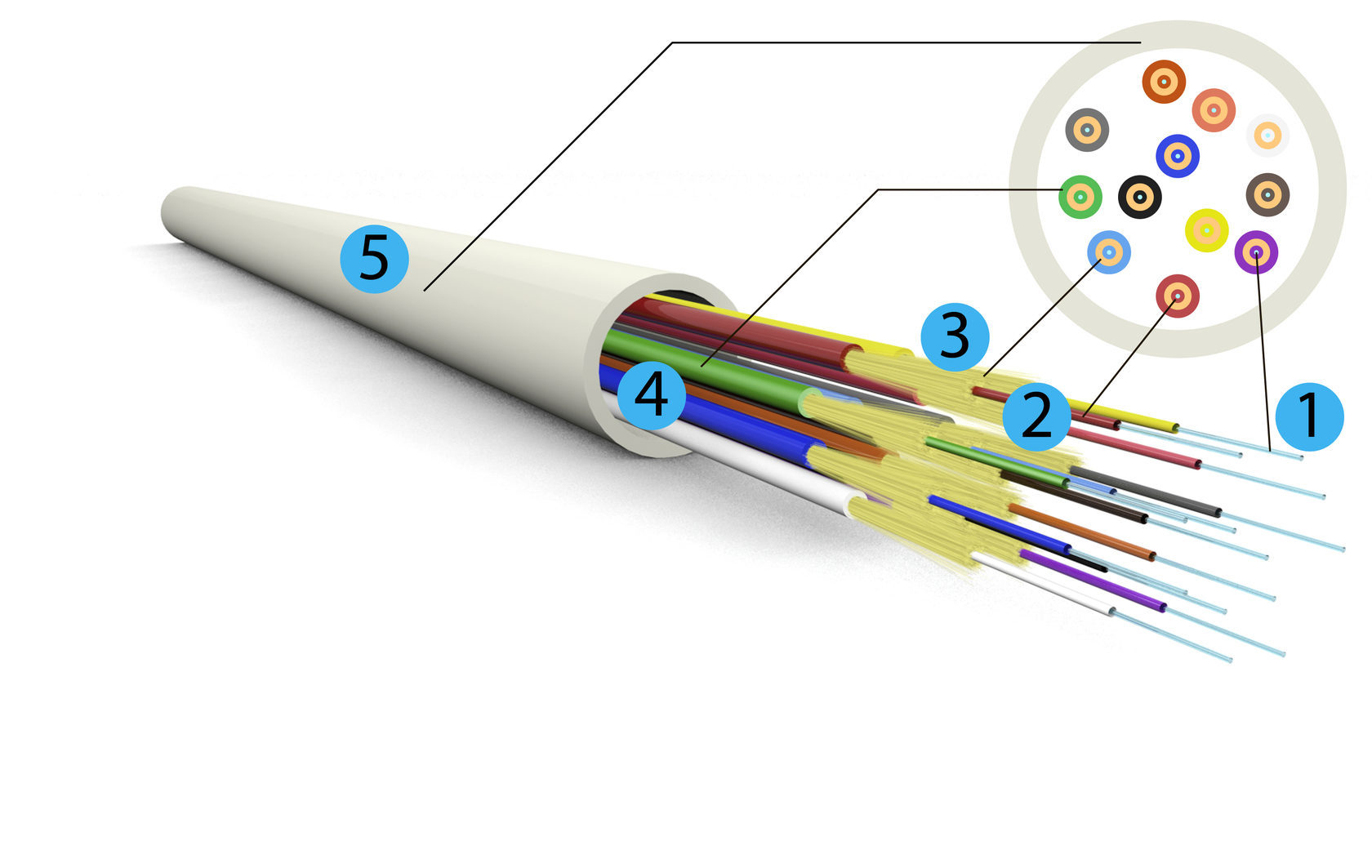
fiberopticcableanatomydiagram01 One Ring Networks
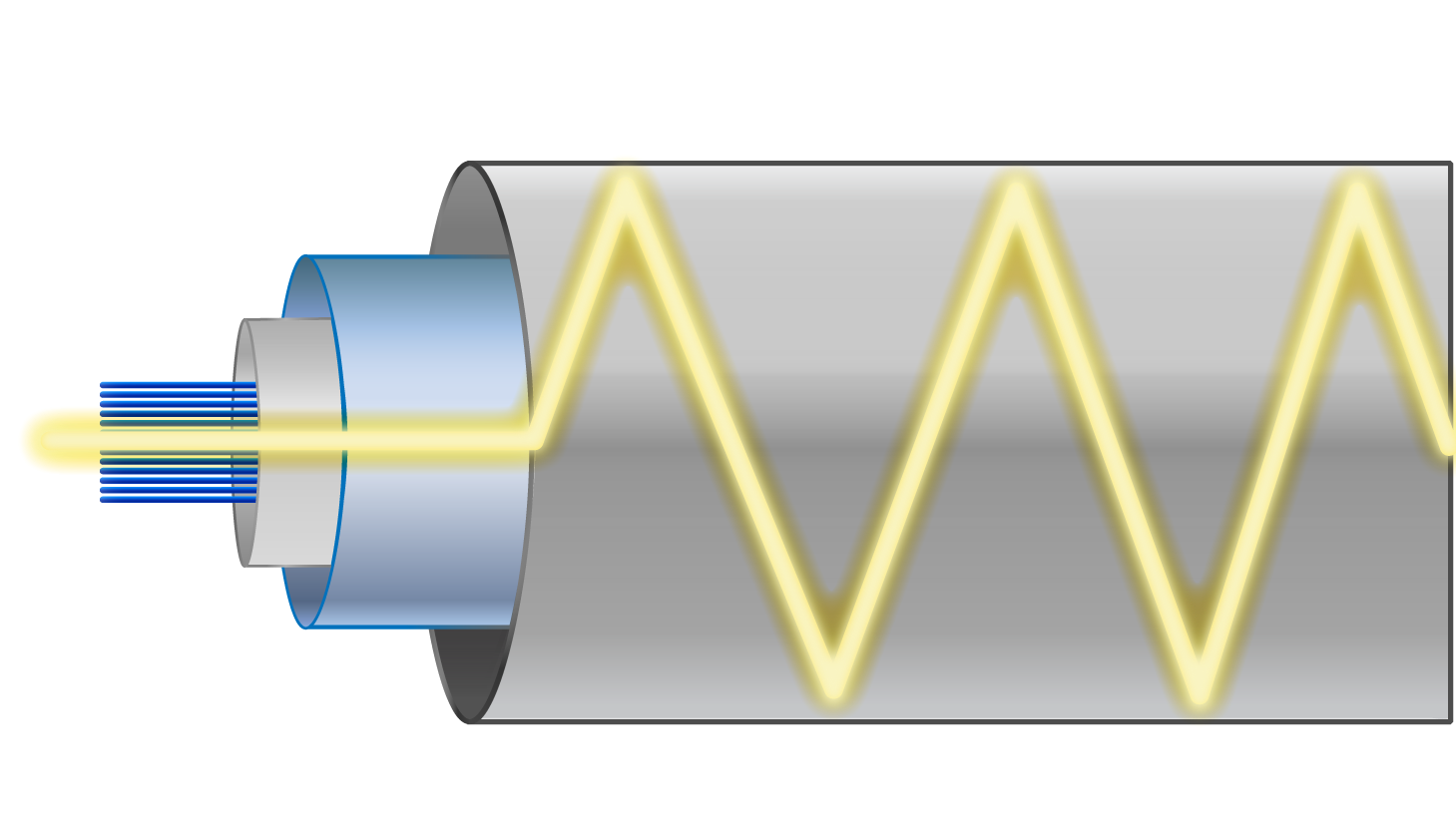
I. Advantages Fiber optics has many advantages over copper wire (see Table 1) including: Increased bandwidth: The high signal bandwidth of optical fibers provides significantly greater information carrying capacity. Typical bandwidths for multimode (MM) fibers are between 200 and 600MHz-km and >10GHz-km for single mode (SM) fibers.

Electrical and Electronics Engineering Fiber Optic Cable (Type, Using, Additional Information)!!!
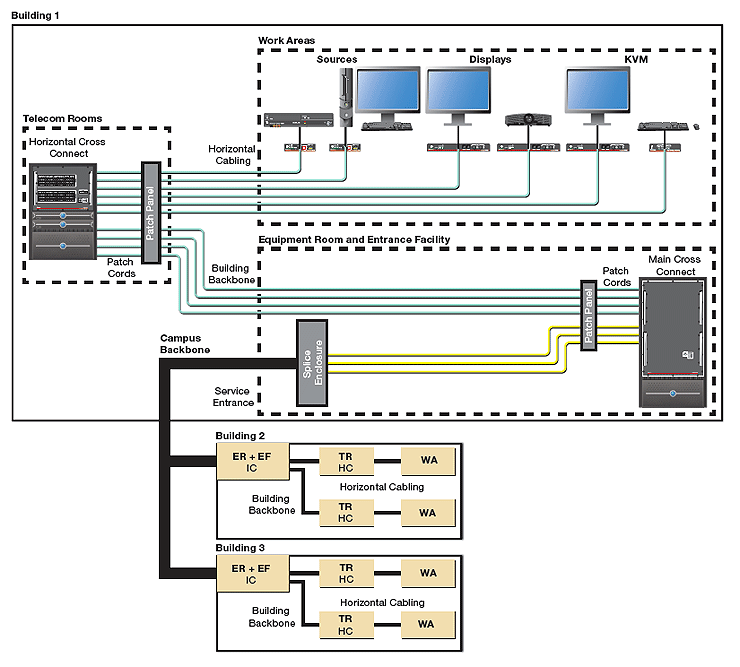
Fiber Optic Network Design. Fiber optic network design refers to the specialized processes leading to a successful installation and operation of a fiber optic network. It includes first determining the type of communication system (s) which will be carried over the network, the geographic layout (premises, campus, outside plant (OSP, etc.), the.

Terrestrial fiberoptic networks Download Scientific Diagram
The core diameter is generally (40um) and that of cladding is (70um). The relative refractive index difference is also greater than single mode fiber. There is signal degradation due to multimode dispersion. It is not suitable for long-distance communication due to large dispersion and attenuation of the signal.

Indoor/Outdoor Fiber Optic Composite Cables Optical Fiber Hitachi Cable America
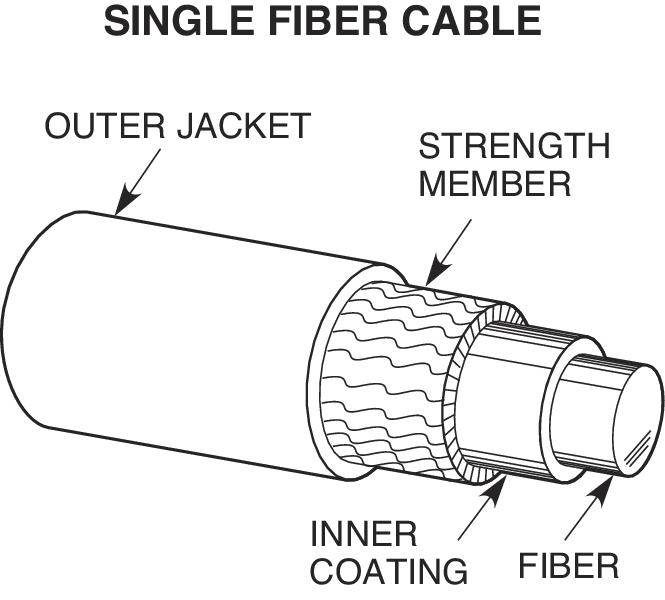
Figure 1 is a diagram of the basic construction of both loose-tube and tight-buffer fiber optic cable. Figure 2 is a drawing of the cross section details of a single and a two conductor fiber optic cable as well as a more complex multi-fiber cable.
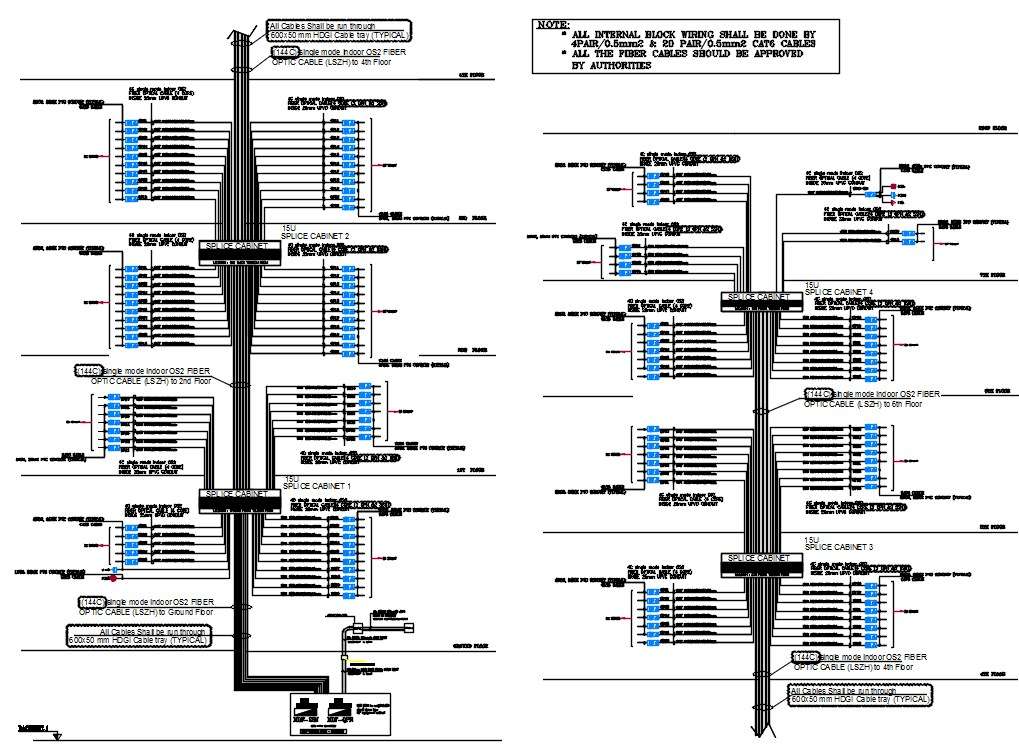
Optic Cable Wiring Distributions Diagram AutoCAD Drawing Free Download Cadbull
Broadband fiber-optic cables can be grouped into three categories: Outside plant cables—These cables are designed specifically for outdoor applications, including aerial, underground and direct burial. They feature polyethylene jackets and may also be armored.
Fiber Optic Cables in AV Systems Extron
Multimode Fiber Optic Cables. Multimode fiber optic cables are characterized by a much broader internal core, measuring either 50µm or 62.5µm which allows multiple streams of data to be sent down the cable. This allows for the use of more affordable LEDs and vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSELs) in their design, which typically.
FiberOptic Cabling NetworkAcademy.io
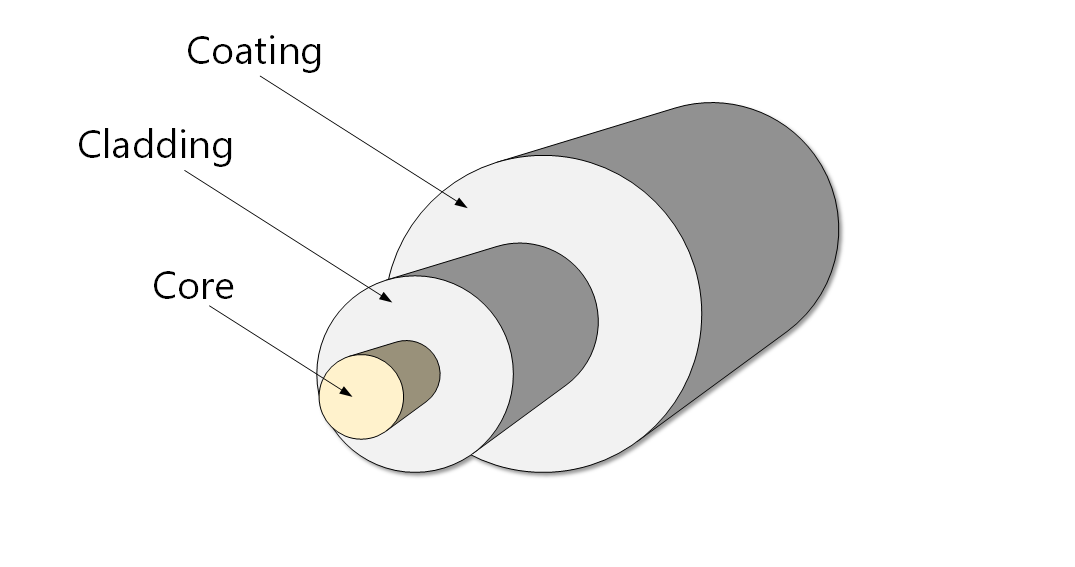
The diameter of the core of a single mode fiber is 8 - 10 μm while multimode fibers are 50 μm in diameter. It is also called the optical waveguide since it is the main channel through which light signals are transmitted. Cladding − The core is surrounded by a glass cladding. The glass of cladding has a lower refractive index than the core.
Local network cables. Distribution fiber optic cable ОКВР construction 02
The differences between these two phases are: Household Passed: fiber optic cable "goes by" a home along the street, meaning the home is "capable" of being served by a provider's fiber optic distribution plant, but it may not be "connected" yet Connected: a fiber optic "drop" cable from the closest network access point connects to the home.

Scientific Animation Fibre Optic by Russell Kightley Media
4.2 FIBRE-OPTIC CABLE TYPES AND APPLICATIONS There are many fibre-optic cable types and designs available. Fibre cables can be classified into the following categories: fibre-optic cables for indoor applications, those for outdoor applications and for indoor/outdoor applications. The following sections explain each category in detail. Francis
Step Index Multimode Optical Fibers
There are three types; below explain each one - Single-Mode Fiber Multi-Mode fiber Single-Mode Fiber Single mode fiber cable has small core diameter with ranging of 5 to 9.05 um, and it is capable only one way transmission with 1310 or 1550nm.
4 Common Myths You Might Believe About Fiber Optic Cables TP Communications
All fiber optic cables should be color-coded by jacket colors and/or marked with orange or yellow tags or whatever color is designated for your cable plant to identify it as fiber optic cable. j. Carefully mark all cables and connections for identification in a manner consistent with the company documentation processes.

(a) Schematic diagram of fibreoptic cables installed in two boreholes... Download Scientific
To date, fiber-optic cable installations have brought high-speed network communications to corporations, campuses, universities, hospitals, libraries, offices and homes. Presently, fiber-optic.
fiberopticcableanatomydiagram02 One Ring Networks
A fiber optic cable is a network cable that contains strands of glass fibers inside an insulated casing. They're designed for long-distance, high-performance data networking, and telecommunications. Compared to wired cables, fiber optic cables provide higher bandwidth and transmit data over longer distances.

Optical Fiber Cables Construction and Application FOCONEC
The FOA Reference For Fiber Optics - Fiber To The Home Network design. the design pages on the FOA Guide Reference Guide to Fiber Optic Network Design the Fiber Optic Network Design self-study course this complete series on FTTH. Multi-dwelling Units. PONs work on the principle that splitters allow one central port to communicate with 32 or 64.
Crosssection view of an optical fiber... Download Scientific Diagram
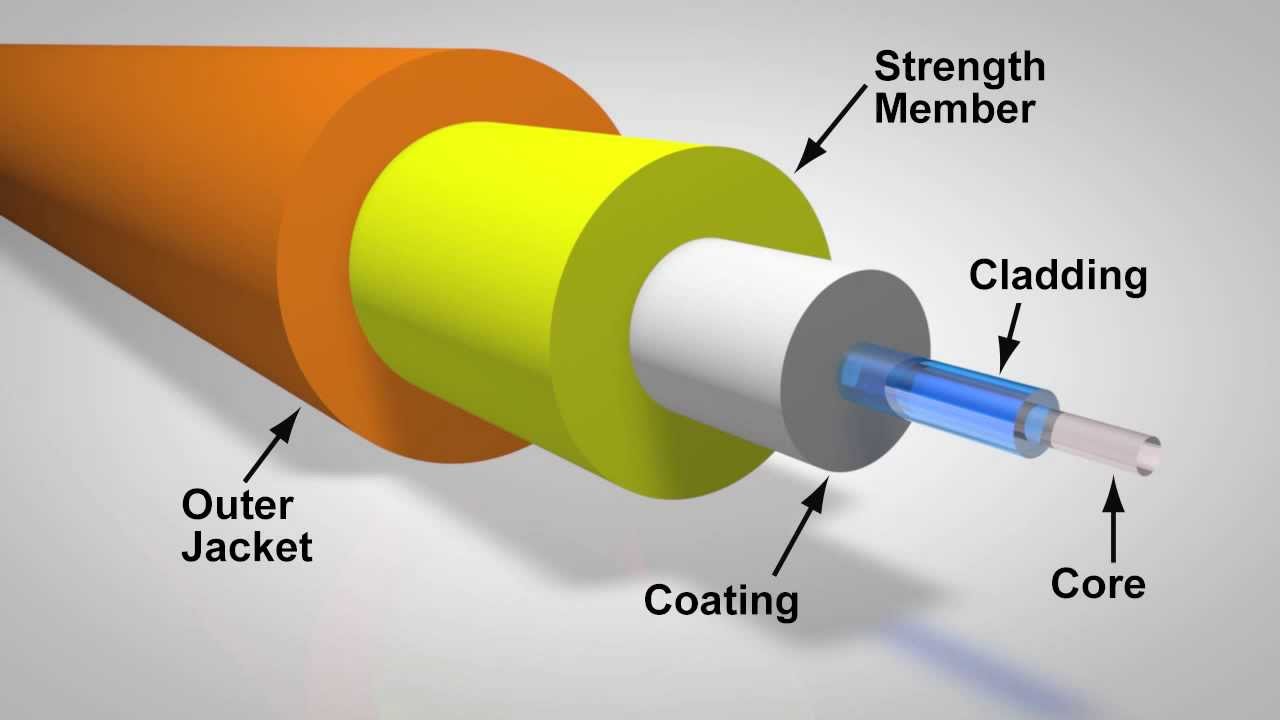
A fiber optic cable consists of five main components: core, cladding, coating, strengthening fibers, and cable jacket. Basic Construction of a Fiber Optic Cable Core: This is the physical medium that transports optical signals from an attached light source to a receiving device.
Thorlabs Fiber Optic Patch Cables Internal Structure YouTube
Introduction to Fiber Optic Converters. Fiber Optic Converters (also known as Media Converters) are devices that convert the electrical signal used in copper wiring such as Ethernet or Serial Data into light waves for transmission over fiber optic cable. They are commonly used in pairs, one at each end of the fiber cable span, enabling two.