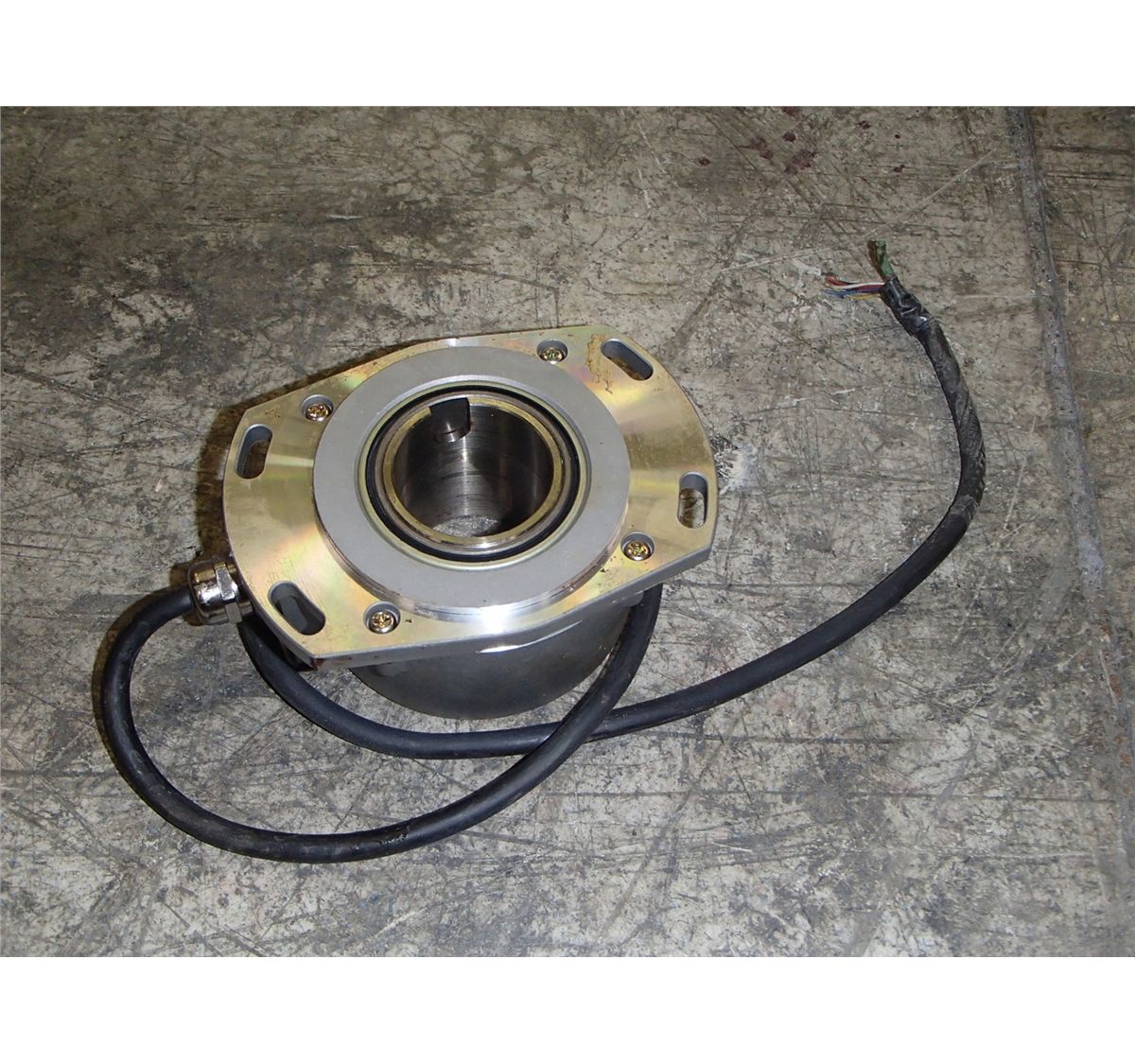

Okuma Encoder M/N ERTC1D, TS2670N1E1 BTM Industrial
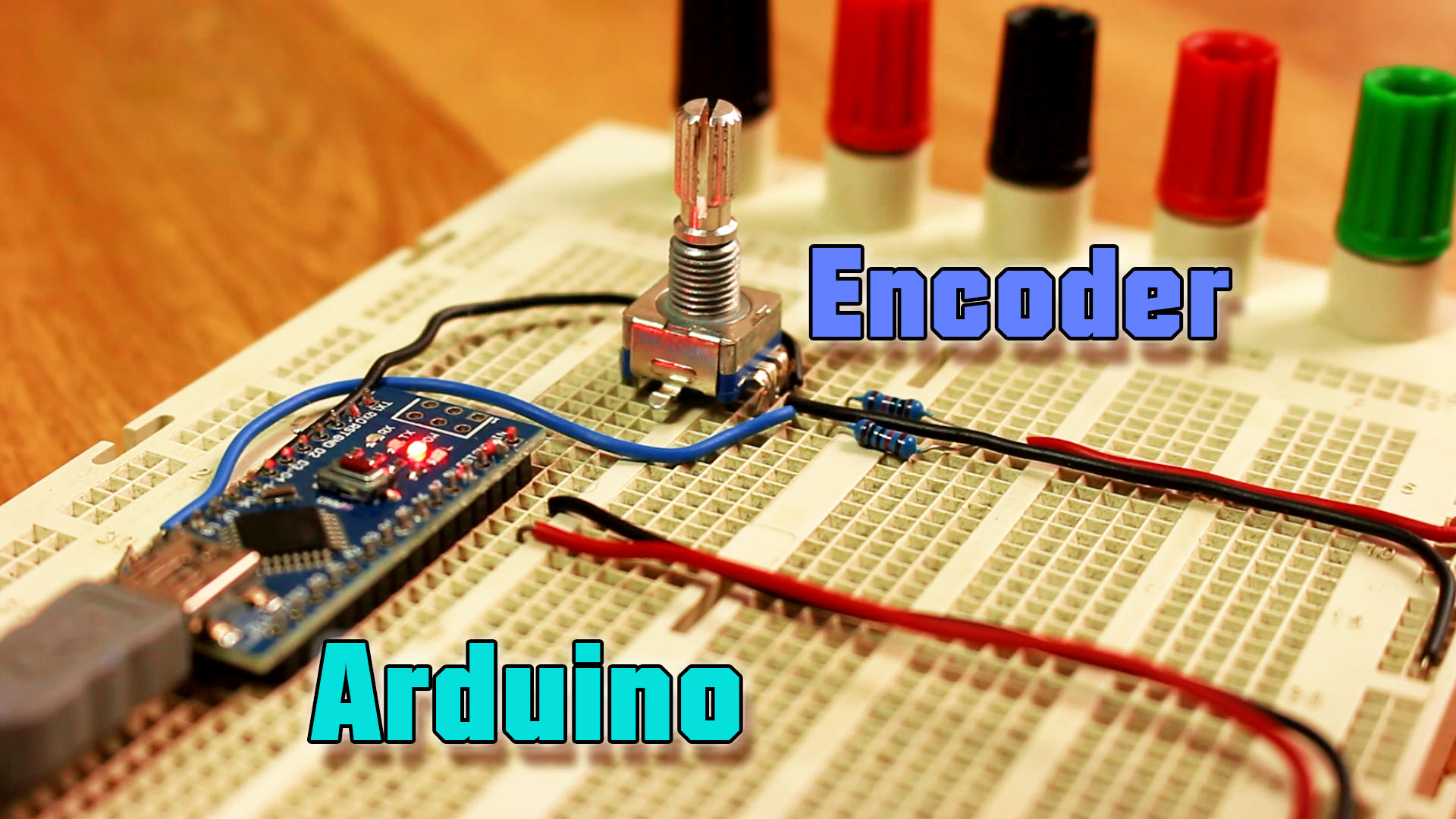
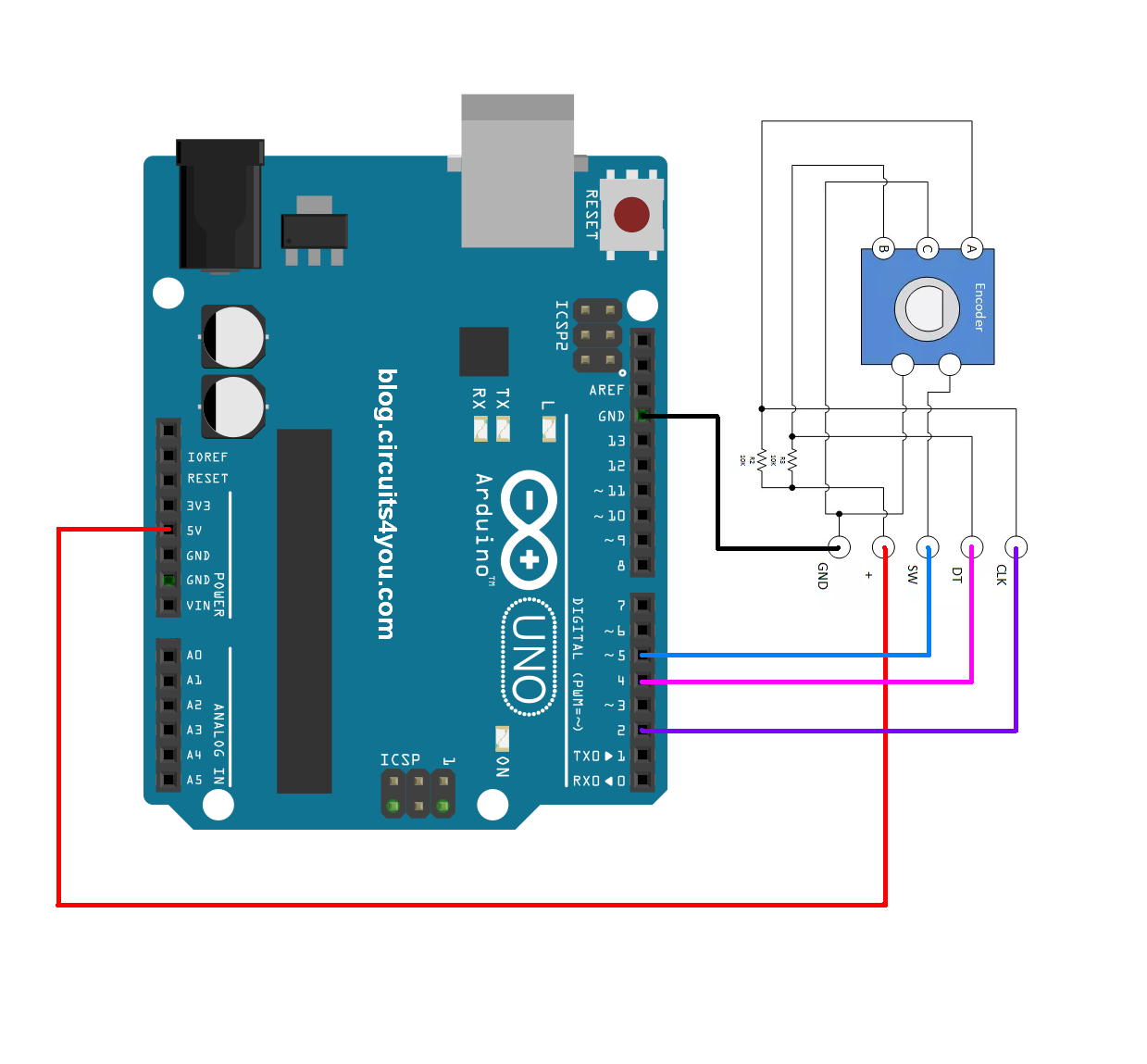
Rotary Encoder Module Pinout. The Rotary Encoder Module has 5 pins; those are GND, + (VCC), SW (Switch), DT, and CLK. All the pins of this sensor module are digital, except VCC and Ground. The Pinout of a Rotary Encoder Module is shown below: GND is the ground pin of the Rotary Encoder Module and it should be connected to the ground pin of the.
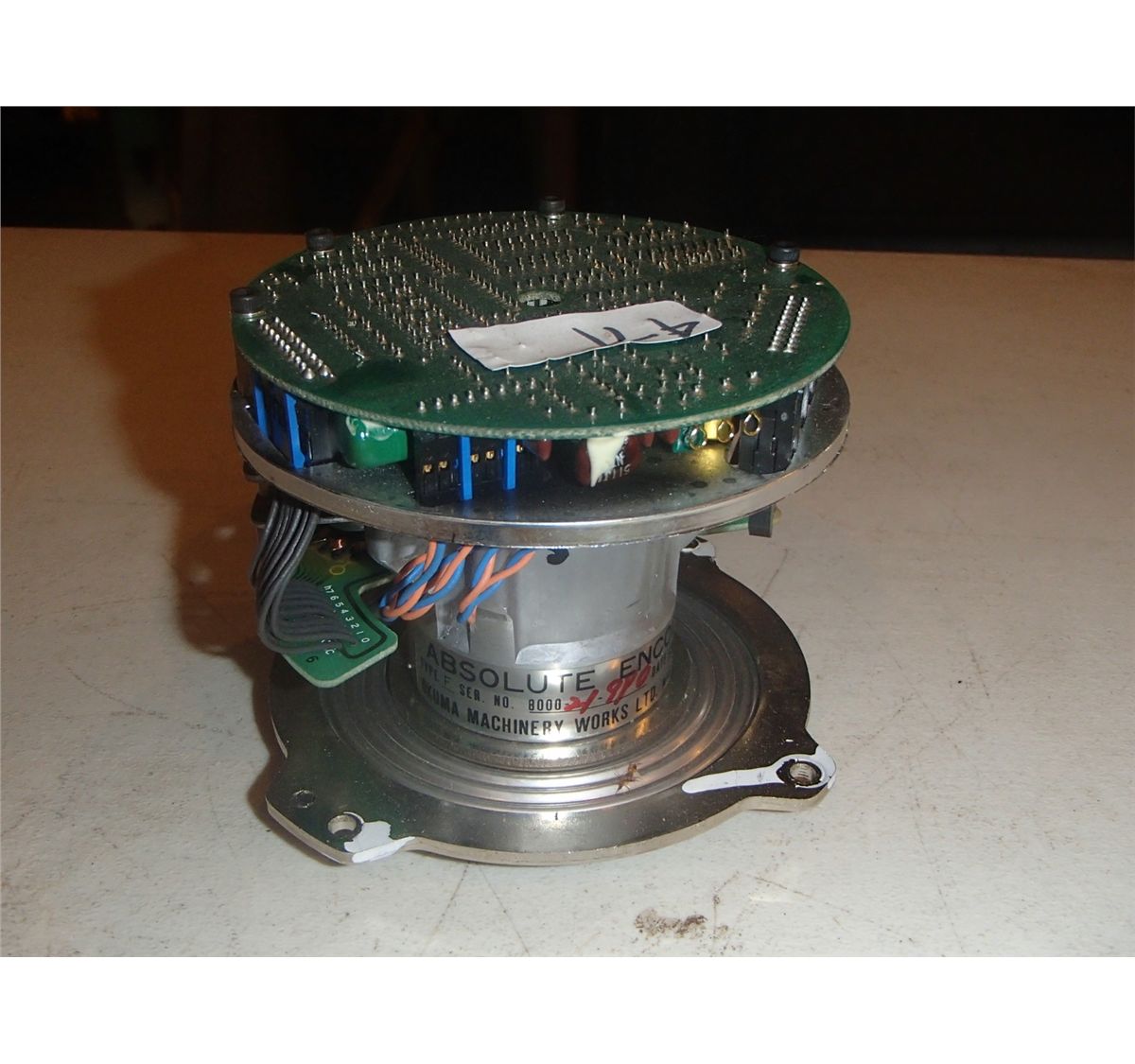

Okuma Absolute Encoder, Type F BTM Industrial
1 VIDEO 2 What is Optical rotary encoder 3 Types of Encoders 3.1 Incremental Encoders 3.2 Absolute Encoders 4 Connection optical encoder with arduino 5 CODE 6 If you also want to learn how to connect Arduino with ESP32 so you can read the following post. 7 Related VIDEO You can watch this video or continue to read below post
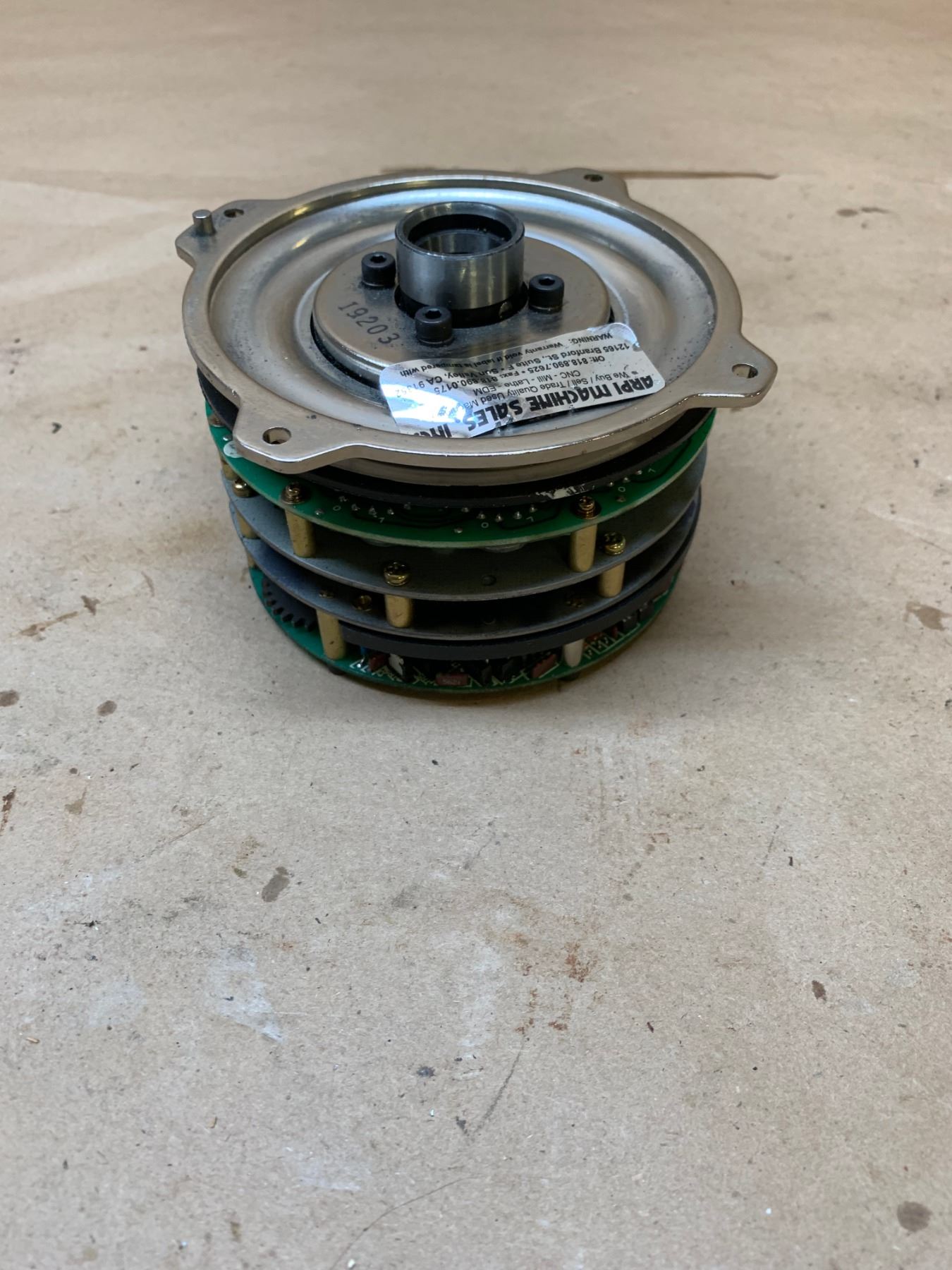

Okuma 26098 Encoder BTM Industrial
Arduino Rotary encoder Example code to read position and direction of Rotation: Now its time to upload the code. connect Arduino to a PC where Arduino IDE is installed. Choose the board as Arduino UNO or which ever you use and select the correct port from the Tools menu. Install required libraries from the built in Library manager or you can.

Okuma Encoder M/N ERTC1D, TS2670N1E1
Software Configurations and Arduino Library Code. Step 1: Install the Encoder Library in the Arduino IDE by hovering your cursor to Sketch -> Include Library -> Manage Libraries. Step 2: Search for the encoder in the pop-up window and find Encoder by Paul Stoffregen, choose the Version 1.4.1 and click install.

OKUMA ENCODER ERMB7200D A005801D CNC Electronic System
Rotary encoders are classified into two types: absolute and incremental. The absolute encoder reports the exact position of the knob in degrees, whereas the incremental encoder reports the number of increments the shaft has moved. The rotary encoder used in this tutorial is of the incremental type. Rotary Encoders Vs Potentiometers

Okuma Absolute Encoder BTM Industrial
Rotary Encoder Arduino Code Explanation: First we will import the servo motor library in the Arduino code if we not include the library the code will not work. Then define the clk and data pin at 3 and 4 respectively. Define the switch pin at 5. We will set the counter value at 90. State and lstate variables are used to store the state.
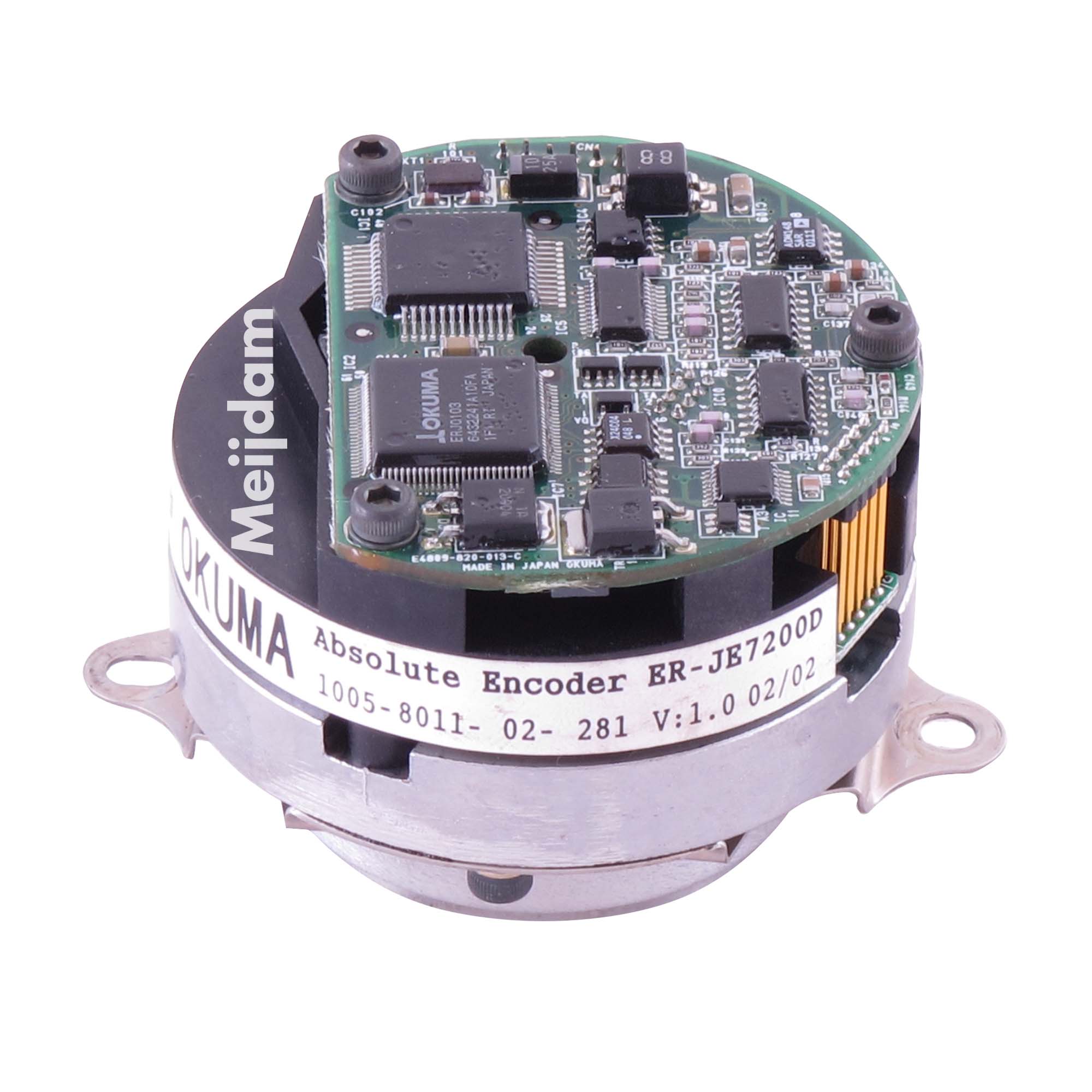

1005801102281 Okuma Absolute Encoder ERJE7200D Meijdam
Free Shipping Available On Many Items. Buy On eBay. Money Back Guarantee! But Did You Check eBay? Check Out Arduino Encoder On eBay.
Arduino rotary encoder tutorial with interruptions
Step 1: Pulse Flow of Rotary Encoder The pulse flow generated by the following rotary encoder is like the picture above. Ask Question Step 2: Pinout of Rotary Encoder Explanation: GND --> GND + --> +5V SW --> button of rotary encoder when pressed DT --> Data CLK --> Data 2

Okuma 26098 Encoder BTM Industrial
The circuit is so simple. You will need: • An ATMEGA328P based Arduino, such as the Uno, Pro Mini or Nano. • A mechanical (as opposed to optical) quadrature rotary encoder - this is the most common kind so don't worry too much if it isn't specified. eBay and Aliexpress listings will often mention Arduino in the description and this is a good indicator that one is suitable.

Okuma Absolute Encoder, Type F BTM Industrial
A rotary encoder, also called a shaft encoder, is an electro-mechanical device that converts the angular position or motion of a shaft or axle to analog or digital output signals. There are two main types of rotary encoder: absolute and incremental. The output of an absolute encoder indicates the current shaft position, making it an angle.

Okuma Encoder M/N ERTC1D, TS2670N1E1 BTM Industrial
In this tutorial we will learn how rotary encoder works and how to use it with Arduino. You can watch the following video or read the written tutorial below. Overview A rotary encoder is a type of position sensor which is used for determining the angular position of a rotating shaft.

Okuma Absolute Encoder, Type F BTM Industrial
There are two main types: Incremental encoder: which generates pulses to measure relative change Absolute encoder: which provides a unique digital code for each position, making them ideal for precise positioning even after power loss. This guide is about the incremental encoder. Rotary Encoder Module Pinout
Arduino Rotary Encoder Module KY040
1. Incremental encoders use a series of pulses in a quadrature arrangement to indicate how far and in what direction a shaft turns. 2. Absolute encoders inherently know their angular position. This article will focus primarily on incremental encoders, the type of encoder you'll see most commonly.

OKUMA ENCODER ERMSA
Connect the rotary encoder to the breadboard. Place the two 10 kΩ resistors R1 and R2 from A and B to 5V. Place the two 10 kΩ resistors R3 and R4 from A and B to the Arduino digital pins 10 and 11, respectively. Place the 0.1uF capacitors (C1 and C2) as shown in the schematic to debounce the encoder signal. Connect point C to ground.

Okuma Encoder, M/N E30513960121, Type ERMSA
Rotary Encoder - Example #1. We'll now go through a simple example to introduce you to the use of a rotary encoder. In this example we will: Determine the absolute position of the encoder going from -100 to 100. Each point is equal to one click in the encoder. If you continue rotating past +100 or past -100, the code will max out the count.

Arduino Bluetooth veri okuma YouTube
Encoder Signal Input/Output Counts quadrature pulses from rotary & linear position encoders. Encoder counts pulses from quadrature encoded signals, which are commonly available from rotary knobs, motor or shaft sensors and other position sensors. Author: Paul Stoffregen Maintainer: Paul Stoffregen Read the documentation Go to repository