
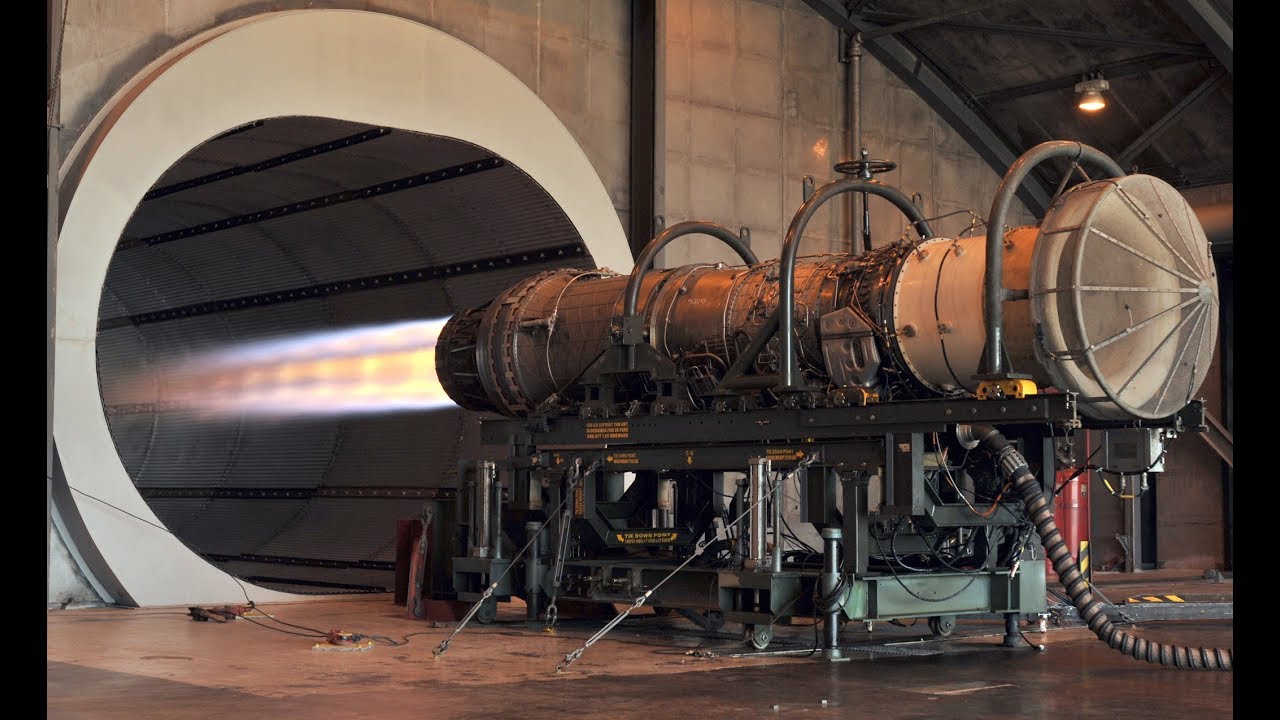
Museum of the History of Aircraft Engine Building. Aircraft Engines on Stands. Turbine Engines
The Merlin engine in the "mustang" (designated V-1650-3 Packard Merlin engine) produced 1,520 horsepower and allowing the plane to have a cruising speed of 340 knots at 10,000 feet. Towards the end of WWII, jet technology was dawning and would forever change the way aircraft were powered. aviation-history.com The Rise of Turbojet Technology

The History of Jet Engines World Of Aviation
As the jets of gas shoot backward, the engine and the aircraft are thrust forward. As the hot air is going to the nozzle, it passes through another group of blades called the turbine. The turbine is attached to the same shaft as the compressor.. The First Jet Engine - A Short History of Early Engines.

Museum of the History of Aircraft Engine Building. Aircraft Engines on Stands. Turbine Engines
Jet engines can be dated back to the invention of the aeolipile around 150 BC. This device used steam power directed through two nozzles so as to cause a sphere to spin rapidly on its axis. [1] So far as is known, it was not used for supplying mechanical power, and the potential practical applications of this invention were not recognized.

Museum of the History of Aircraft Engine Building. Aircraft Engines on Stands. Turbine Engines
This article tells the story of the invention of the airplane and the development of civil aviation from piston-engine airplanes to jets. For a history of military aviation, see military aircraft; for lighter-than-air flight, see airship. See airplane for a full treatment of the principles of aircraft flight and operations, aircraft configurations, and aircraft materials and construction.

Aircraft Engines History Engineering Channel
The J-79 jet engine, exponentially more powerful than the radial engine, made for faster fighters that could carry bomb loads greater than World War II bombers. The F-4 was a multi-role aircraft.

Museum Of The History Of Aircraft Engine Building. Aircraft Engines On Stands. Turbine Engines
In 1971, Safran Aircraft Engines (formerly Snecma) of France selected GE as a partner to develop a new turbofan engine in the 20,000 pound thrust class. Three years later, the 50/50 joint company - named CFM International - was formally established and would become one of the greatest success stories in aviation history.

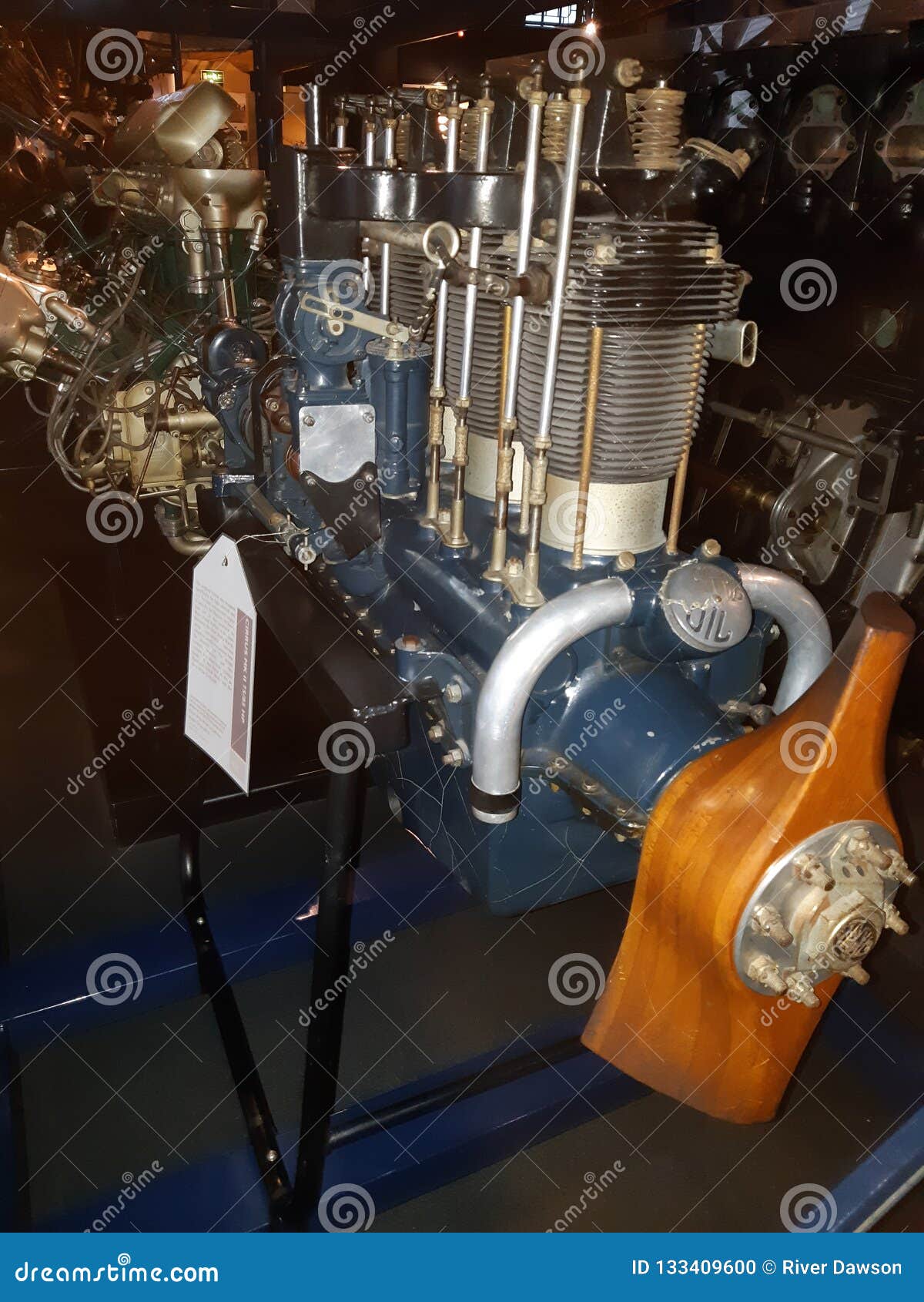
History of Flight Aircraft Engines Editorial Image Image of london, science 133409605
Aircraft Engine Co (Aircraft Engine Co Inc, Oakland, CA) Aircraft 1911 80 hp; Aircraft & Ind. Motor Corp (See Schubert) AiResearch. See: Garrett, Allied Signal and Honeywell. Airex. Airex Rx2; Airex Rx10; Airmotive-Perito See: Adept-Airmotive Airship Aircraft Engine Company. Airship A-Tech 100 Diesel; Airtrike

Museum Of The History Of Aircraft Engine Building. Aircraft Engines On Stands. Turbine Engines
The jet age Origins. From the very invention of flight at the beginning of the 20th century, military aircraft and engines generally led the way, and commercial aviation followed. At first this was also the case in the jet age, which began with the invention of jet engines under military sponsorship in the 1930s and '40s. By the late 20th century, however, commercial jet-engine technology.

Museum of the History of Aircraft Engine Building. Aircraft Engines on Stands. Turbine Engines
The AEHS publishes Torque Meter, the only journal dedicated to aircraft engine history. The AEHS also operates a web site with articles, images, and reference information on aircraft engines.

Vought F4U Corsair Warplane Technical Specs, History and Pictures Aircrafts and Planes
Due to the unreliability of early jet engine designs, in 1943 the U.S. Navy asked Ryan Aircraft to create a fighter aircraft that utilized both the traditional piston engine and a turbojet. The result was the Ryan XFR-1 Fireball—the Navy's first aircraft to include jet propulsion. A Wright R-1820 piston engine in the nose powered the.

Museum Of The History Of Aircraft Engine Building. Aircraft Engines On Stands. Turbine Engines
An aircraft engine, often referred to as an aero engine, is the power component of an aircraft propulsion system. Aircraft using power components are referred to as powered flight . [1] Most aircraft engines are either piston engines or gas turbines , although a few have been rocket powered and in recent years many small UAVs have used electric.
Bmw aircraft engines history
Logo of GE Aviation. GE Aerospace is an aircraft engine supplier, headquartered in Evendale, Ohio, outside Cincinnati.Not only does GE Aerospace manufacture engines under its umbrella, it also partners with other manufacturers. CFM International, the world's leading supplier of aircraft engines and GE's most successful partnership, is a 50/50 joint venture with the French company Safran.
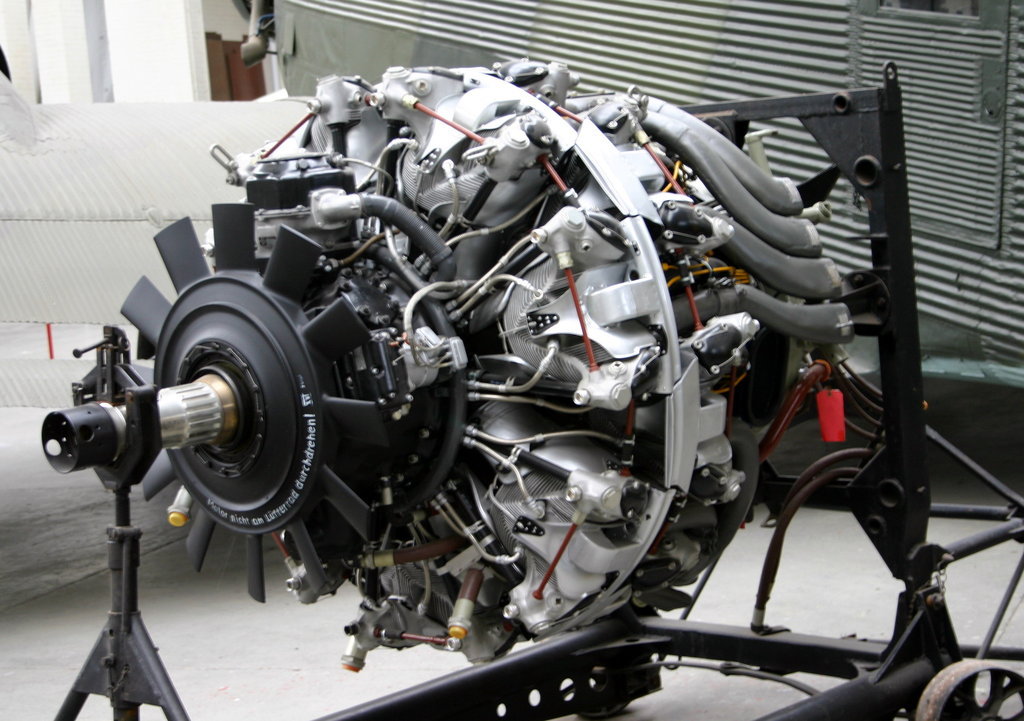
History of Flight Aircraft Engines Editorial Image Image of museum, engines 133409600
It was 1936 before the Rolls-Royce Merlin was perfected enough to be mass produced, but it ended up being the second most produced engine during wartime, with a final production number of around 165,000. In total, the engine was used in 40 aircraft during World War II. It is primarily associated with the Supermarine Spitfire, Hawker Hurricane.

Museum Of The History Of Aircraft Engine Building. Aircraft Engines On Stands. Turbine Engines
History of flight - Engines, Airframes, Progress: Two stages in the jetliners development marked the 1960s. The first was the adoption of the turbofan engine. The turbofan gains economy by having much of its thrust pass around the engine core rather than through it. The second stage was marked by the introduction of the wide-bodied, 400-seat Boeing 747 in 1969.

Pin on Engines
Development History: 1848: John Stringfellow made a steam engine for a 10-foot wingspan model aircraft which achieved the first powered flight, albeit with negligible payload. 1903: Charlie Taylor built an inline aeroengine for the Wright Flyer (12 horsepower). 1903: Manly-Balzer engine sets standards for later radial engines.
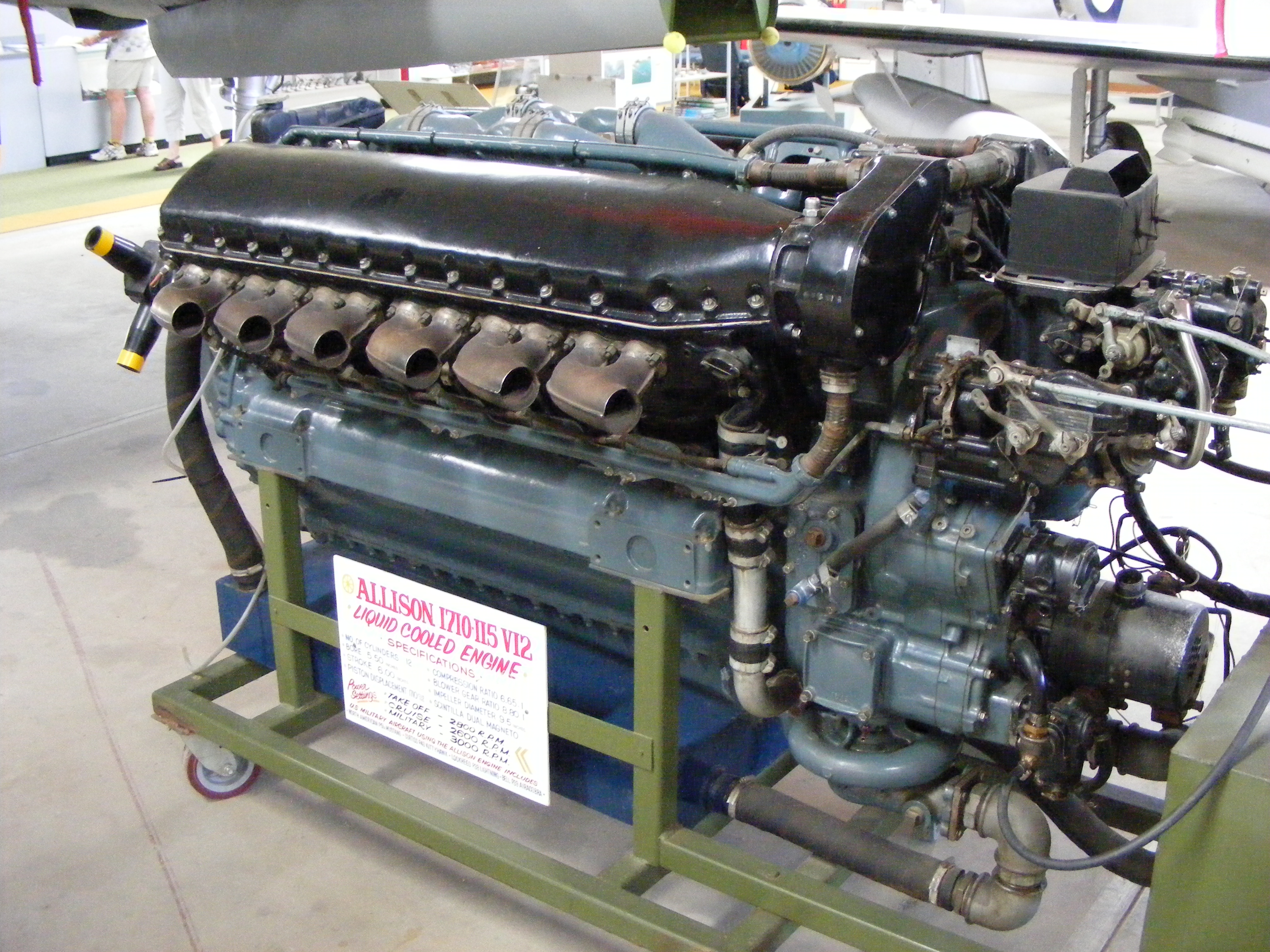

FileAllison 1710115 V12 Aircraft engine.jpg Wikipedia
A cutaway drawing of the 1903 Wright Flyer engine. The earliest aero engines were stationary—either radial in style or in line. The Antoinette series was the most commonly used. These were succeeded by the popular rotary engine. The best known were the Gnome and Le Rhône, which were used on the majority of aircraft until the in-line Liberty.