
membrane called pericardium peri around cardium greek this actually image Double Layered
Rarely, a pericardial cyst can lead to heart failure.. Constrictive pericarditis is chronic inflammation of the pericardium, which is a sac-like membrane that surrounds the heart. READ MORE.

Heart Anatomy · Anatomy and Physiology
Your pericardium is a protective, fluid-filled sac that surrounds your heart and helps it function properly. Your pericardium also covers the roots of your major blood vessels as they extend from your heart. These are known as your "great vessels," and they include your: Aorta. Main pulmonary artery. Pulmonary veins.

Image result for pericardium Circulatory system, Cardiovascular system, Anatomy and physiology
In fact, each day, the average heart beats 100,000 times, pumping about 2,000 gallons (7,571 liters) of blood. Your heart is located between your lungs in the middle of your chest, behind and slightly to the left of your breastbone (sternum). A double-layered membrane called the pericardium surrounds your heart like a sac.
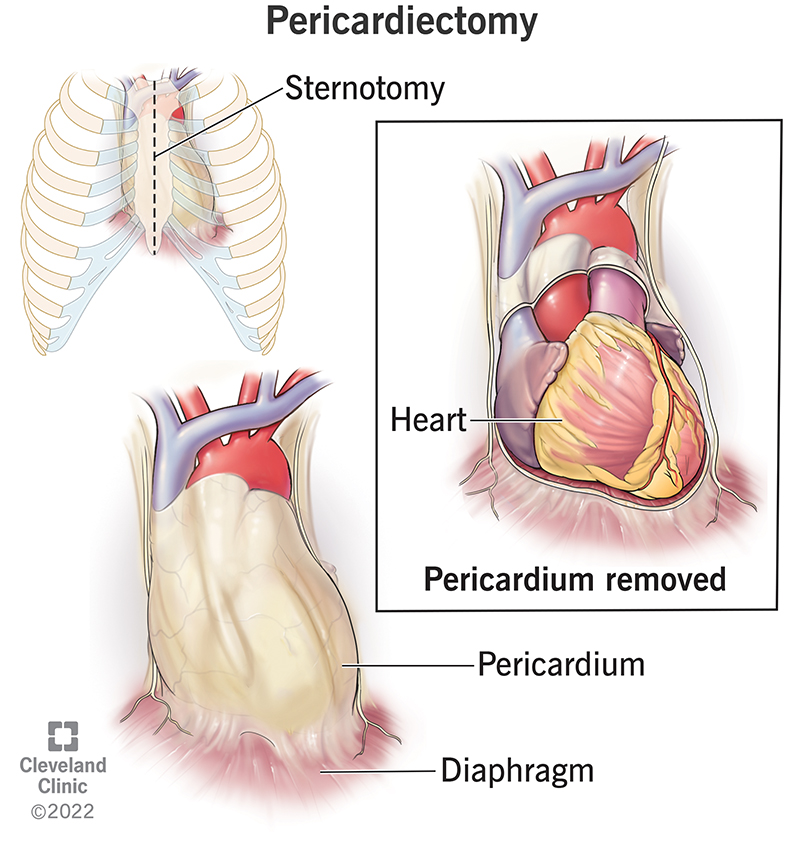
Pericardiectomy Details, Recovery and Outlook
If the heart is the fun, interesting inside bit of an orange, the pericardium could be compared to the peel around it.Like peel, it can seem vaguely unexciting - that is until you learn some of its very important (appeeling. ahem.) physiological functions 1. In scientific terms, the pericardium is a fibro-serous, fluid-filled sack that surrounds the muscular body of the heart and the roots.
Print The Heart flashcards Easy Notecards
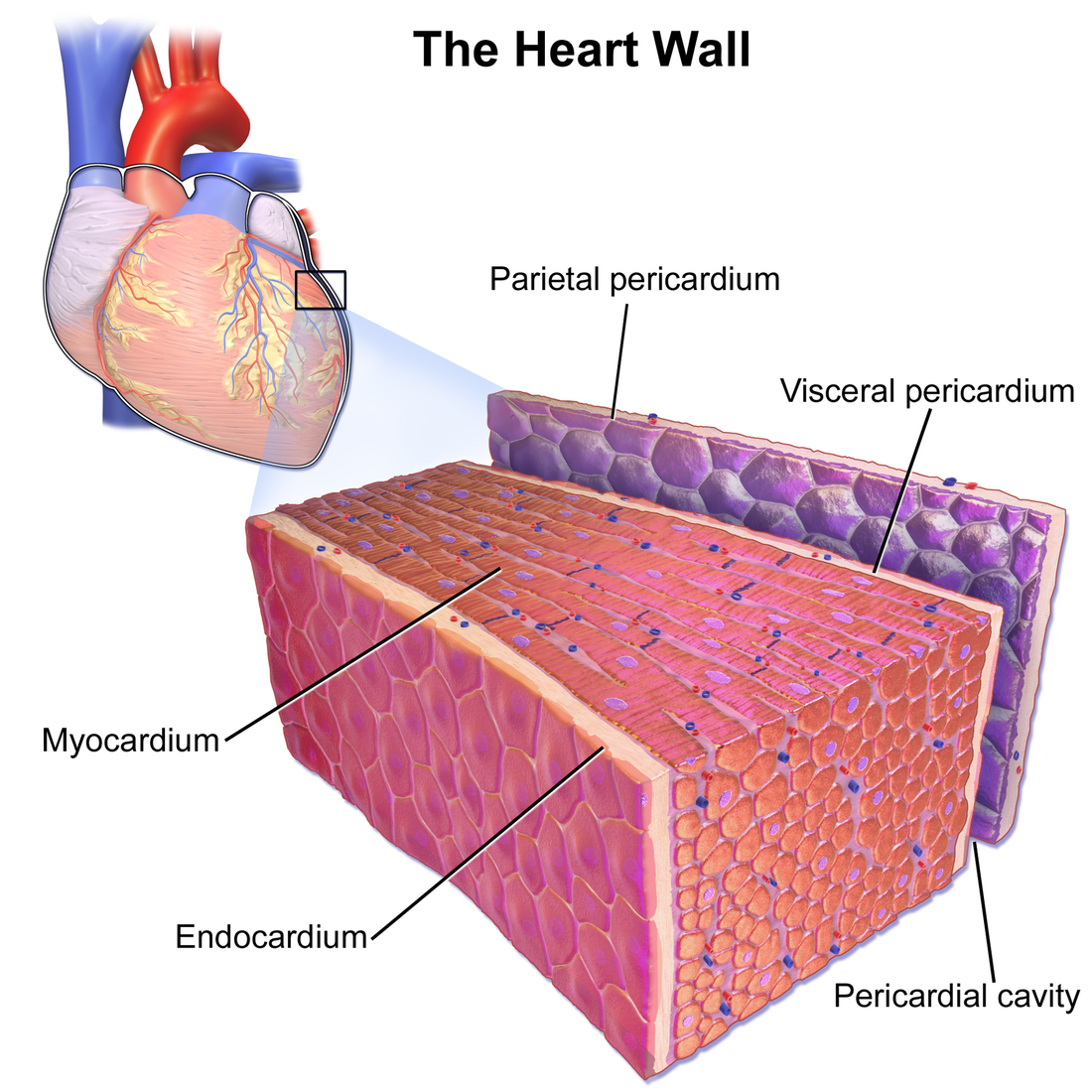
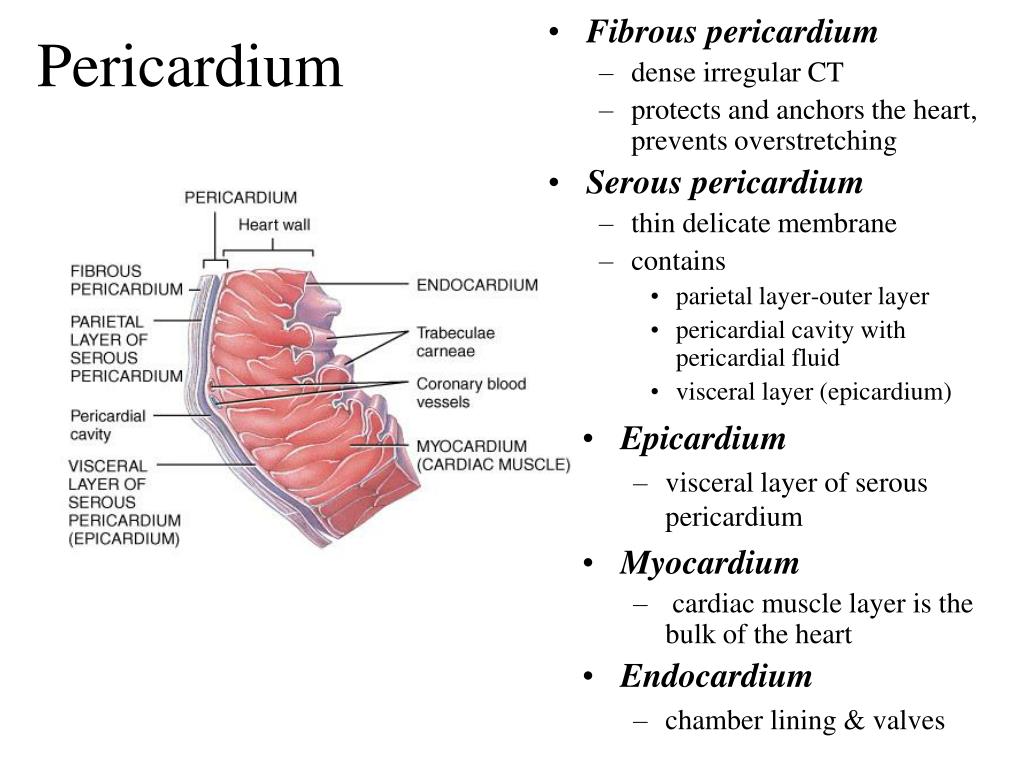
The epicardium is the outermost layer of the heart. It is actually the visceral layer of the serous pericardium, which adheres to the myocardium of the heart. Histologically, it is made of mesothelial cells, the same as the parietal pericardium. Below the mesothelial cells is a layer of adipose and connective tissue that binds the epicardium to.
Pericardial Fluid Urinalysis and Body Fluids
The pericardium is the thick, membranous, fluid-filled sac that surrounds the heart and the roots of the vessels that enter and leave this vital organ, functioning as a protective membrane. The pericardium is one of the mesothelium tissues of the thoracic cavity, along with the pleura which cover the lungs. The pericardium is composed of two.
PPT The Cardiovascular System The Heart PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID312194
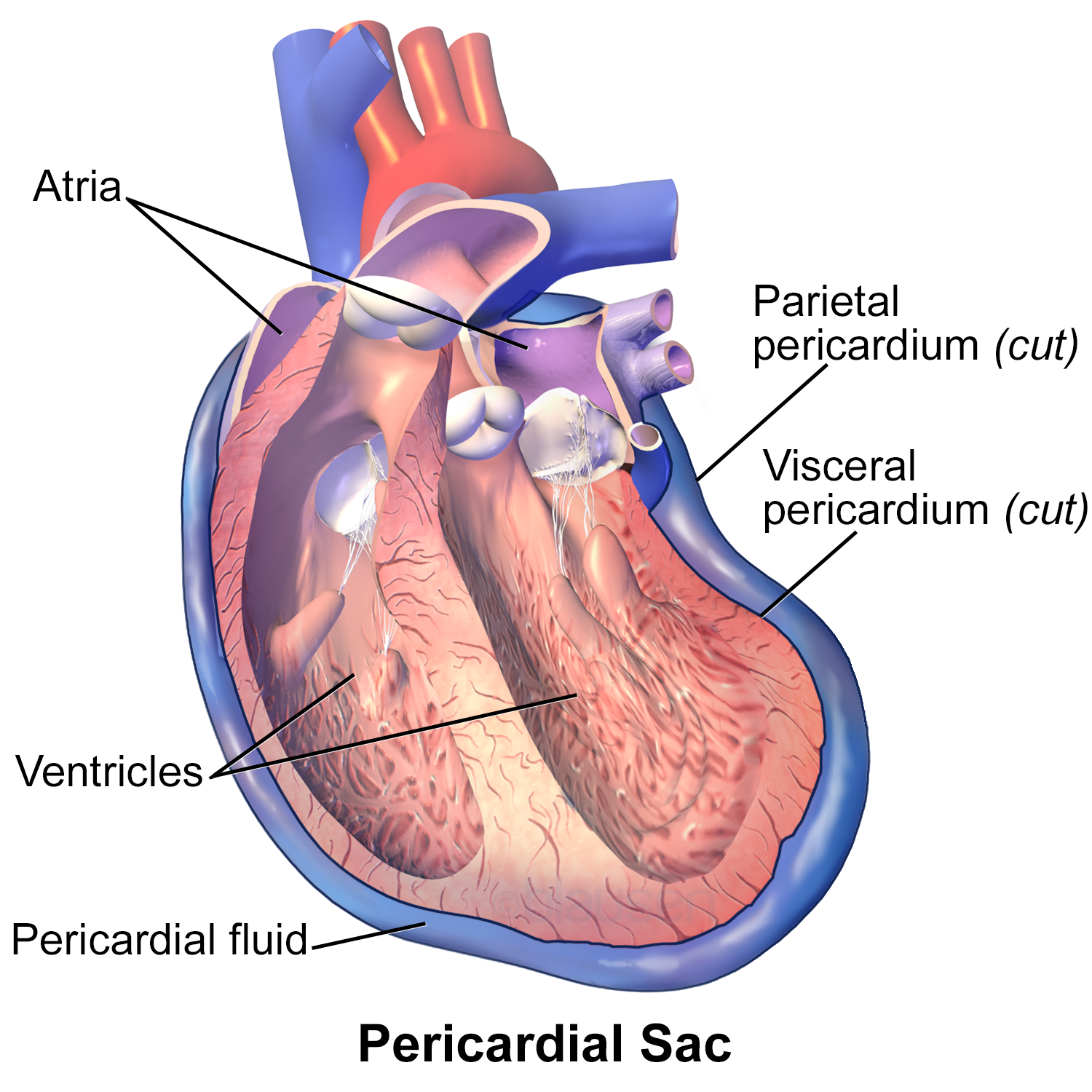
The pericardial membrane and the heart wall share the epicardium. Disorders of the Heart: Cardiac Tamponade. If excess fluid builds within the pericardial space, it can lead to a condition called cardiac tamponade, or pericardial tamponade. With each contraction of the heart, more fluid—in most instances, blood—accumulates within the.
Pericardium The Heart Protector Dr. Elizabeth Cox, ND, LAc
Pericarditis is inflammation of the pericardium. The pericardium is a thin, protective, bag-like membrane surrounding the heart. It has two layers, with a lubricating fluid between the layers. Normally the layers can move against each other without irritation. An inflamed pericardium, however, causes irritation, swelling and pain.

Location of the heart Human Cardiovascular System
The pericardium is a fluid-filled sac that encases the muscular body of the heart and the roots of the great vessels (including the aorta, pulmonary trunk, pulmonary veins, and the inferior and superior vena cavae ). This fibroserous sac is comprised of a serous membrane supported by a firm layer of fibrous tissue.
/pericardium-57a8a12e5f9b58974a2b4fb7.jpg)
Pericardium—Anatomy and Function
When you have pericarditis, the membrane around your heart is red and swollen, like the skin around a cut that becomes inflamed. The pericardium is a thin, two-layered, fluid-filled sac that covers the outer surface of your heart. It provides lubrication for your heart, shields it from infection and malignancy, and contains your heart in your.
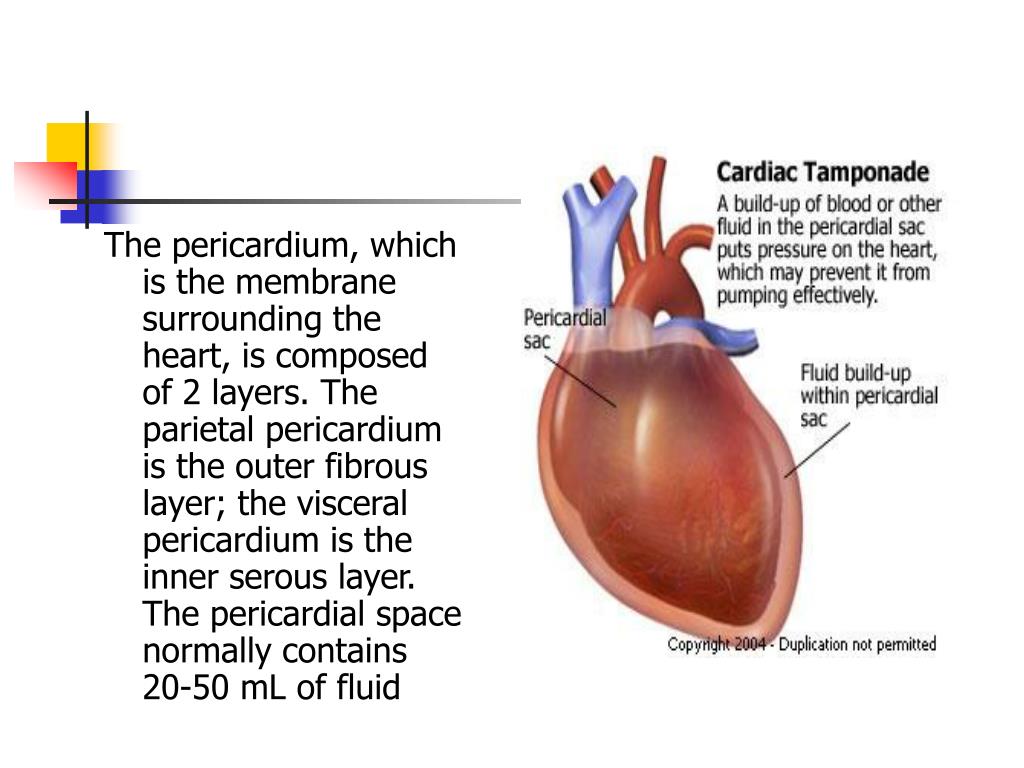
PPT Anesthesia with Cardiac Tamponade PowerPoint Presentation ID299640
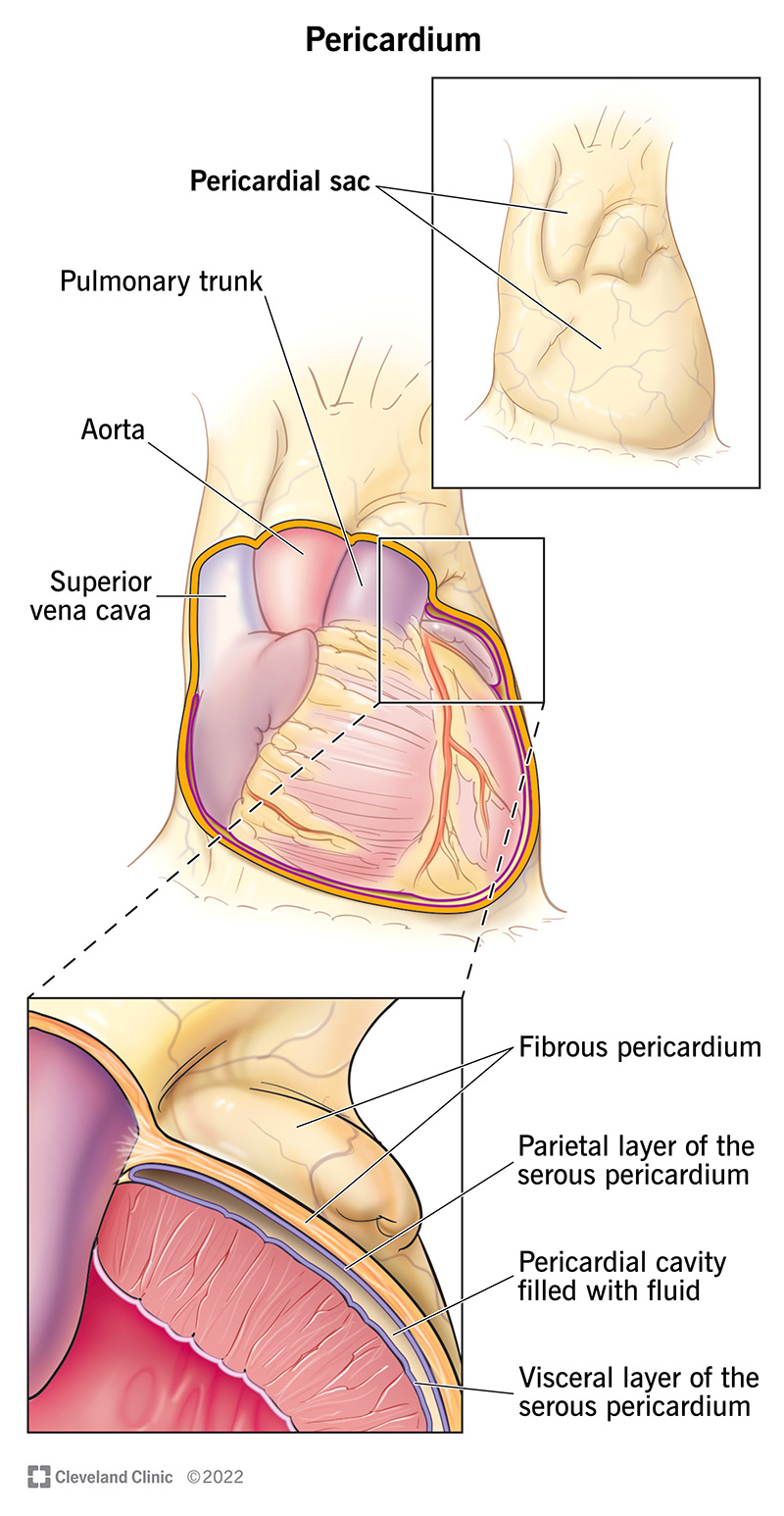
Figure 16.3. 1: Pericardial Membranes and Layers of the Heart Wall The pericardial membrane that surrounds the heart consists of three layers and the pericardial cavity. The heart wall also consists of three layers. The pericardial membrane and the heart wall share the epicardium. (CC-BY-4.0, OpenStax, Human Anatomy)
Pericardium Function and Anatomy
The pericardium is a fluid-filled doubled-walled membrane sac that surrounds the heart. The fluid is separated by two layers, the fibrous and serous pericardium.[1] The fibrous pericardium is the outer layer and holds the heart in place and protect it from surrounding infections.[1] It is composed of thick connective tissue. The serous pericardium has two layers, the visceral and parietal layers.

The pericardium is a doublewalled sac that encloses the heart. Between the visceral and
The heart resides within the pericardial sac and is located in the mediastinal space within the thoracic cavity. The pericardial sac consists of two fused layers: an outer fibrous layer and an inner parietal pericardial serous membrane. Between the pericardial sac and the heart is the pericardial cavity, which is filled with lubricating serous.

19.6 Pericardium. The protective layers of the heart include the pericardial sac composed of an
Serous pericardium The thin serous pericardium is a serous membrane, or serosa.Like all serous membranes, it consists of two layers: The outer parietal layer that lays directly on the cavity wall, that is, onto the inner surface of the fibrous pericardium; The inner visceral layer that directly covers the organs in the cavity, that is, the heart.It is also called the epicardium as it is the.

Medical Facts, Medical Science, Health Science, Respiratory System Anatomy, Biochemistry Notes
The pericardial membrane and the heart wall share the epicardium. Figure 9.5: Pericardial Membranes and Layers of the Heart Wall. Surface Features of the Heart. Inside the pericardium, the surface features of the heart are visible, including the four chambers. There is a superficial leaf-like extension of the atria near the superior surface of.

2114 LAB MID TERM HEART/VESSELS Anatomy & Physiology 2114 with Ozcan at Technical
The pericardium is a membrane, or sac, that surrounds your heart. It holds the heart in place and helps it work properly. Problems with the pericardium include: Pericarditis - an inflammation of the sac. It can be from a virus or other infection, a heart attack, heart surgery, other medical conditions, injuries, and certain medicines.