
From steel to semifinished products magnesite carbon bricks supplier
steel research international is a metallurgy journal covering process metallurgy, metal forming, materials engineering, and process control related to steelmaking. Continuous casting is a mature, sophisticated technological process, used to produce most of the world's steel, so is worthy of fundamentally-based computational modeling.

Continuous casting of steel. Download Scientific Diagram
Continuous casting (CC) is a sophisticated metallurgical process used to manufacture most of the technological steel products (including billets, blooms, and slabs) around the world.

Metalchic Atlas Bronze A Guide to Continuous Casting
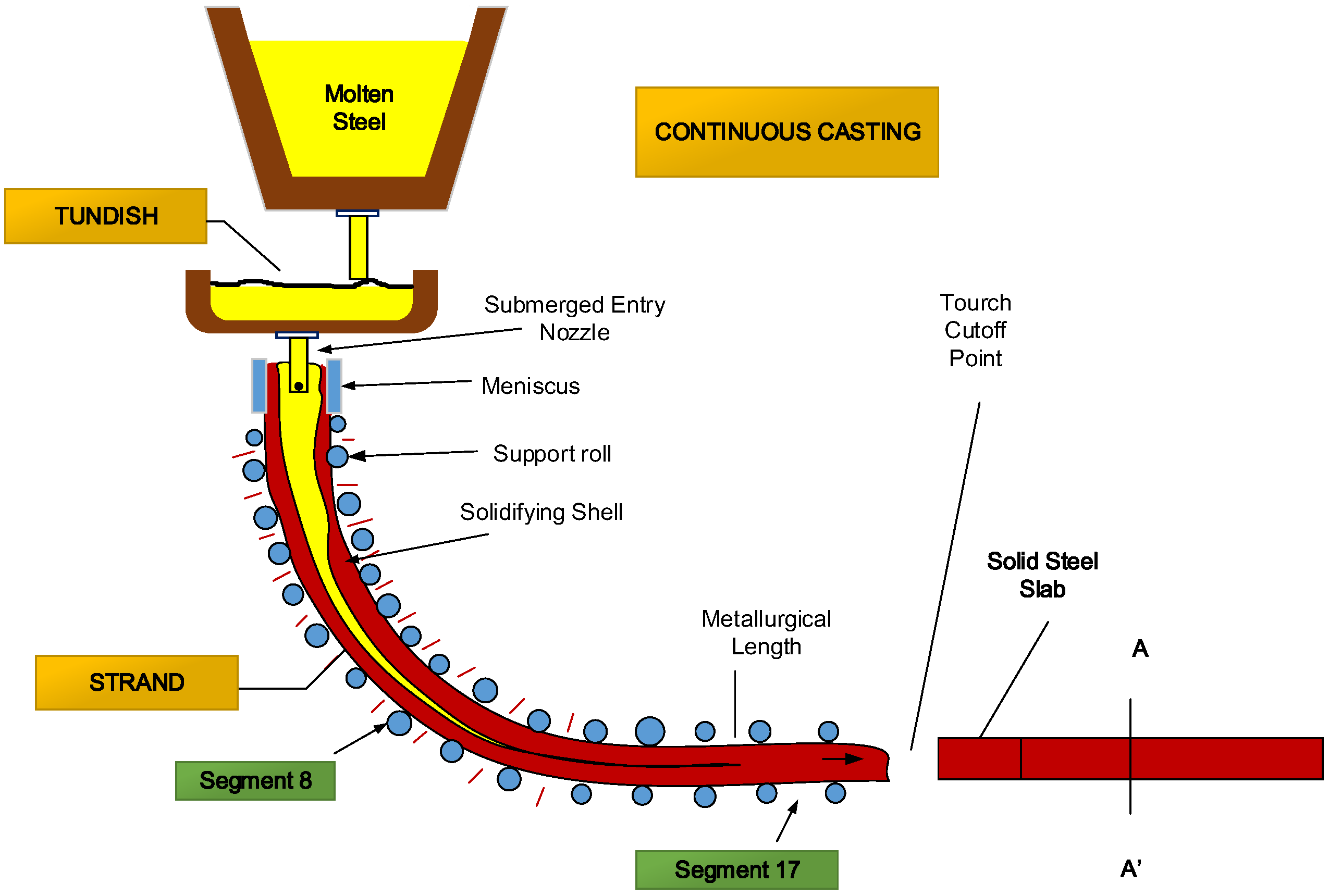
Continuous casting (CC) of steel is a process whereby liquid steel is solidified into a semi-finished steel product (billet, bloom, beam- blank, round or slab) for subsequent rolling in the rolling mills. The basic operation of a CC machine is to convert liquid steel of a given composition into a strand of desired shape and size through a group.
Optimizing the Continuous Casting Process with Simulation COMSOL Blog
Wang Q, Shi YM, Wang F. Investigation of fluid flow and heat transfer in a continuous casting tundish with channel type induction heating using mathematical modeling and water modeling.. A two-phase 2D finite element model for macrosegregation in steel continuous casting. In: Jones H. editor, Proceedings of SP07 5th Decennial International.

Continuous Casting Steel
The steel continuous-casting process and the digital computer appeared at about the same time in history. Continuous casting has grown to produce over 95% of steel in the world[1]. Similarly, computational modelling has grown due to tremendous advances in computer power and to great improvements in the sophistication of modelling software.

Continuous Casting, सतत कास्टिंग मशीन in Bistupur, Jamshedpur , Hitech
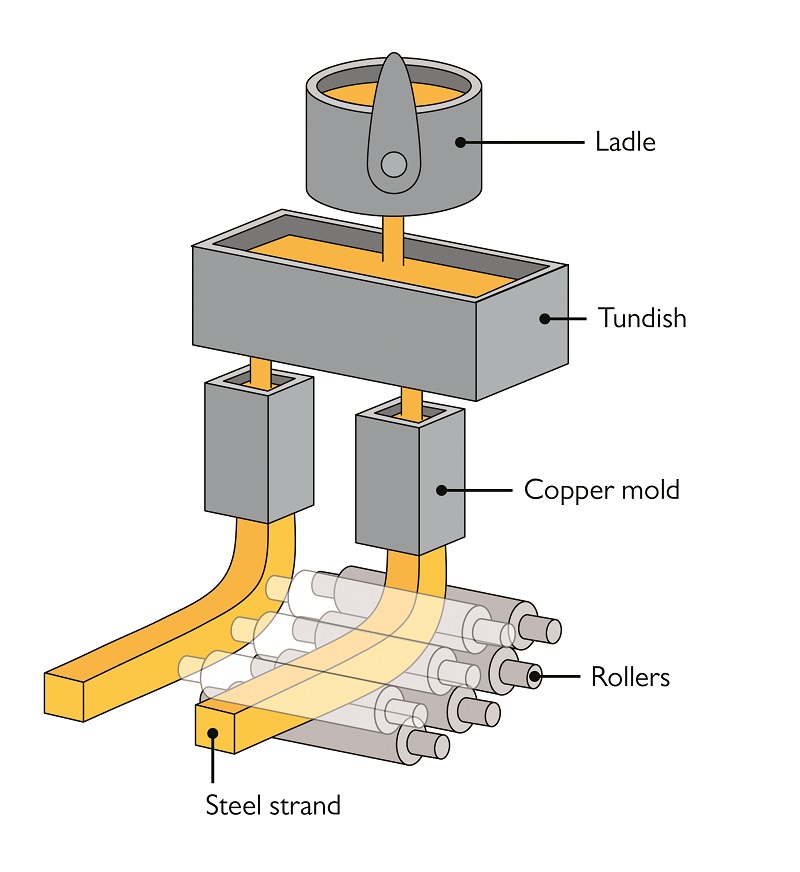
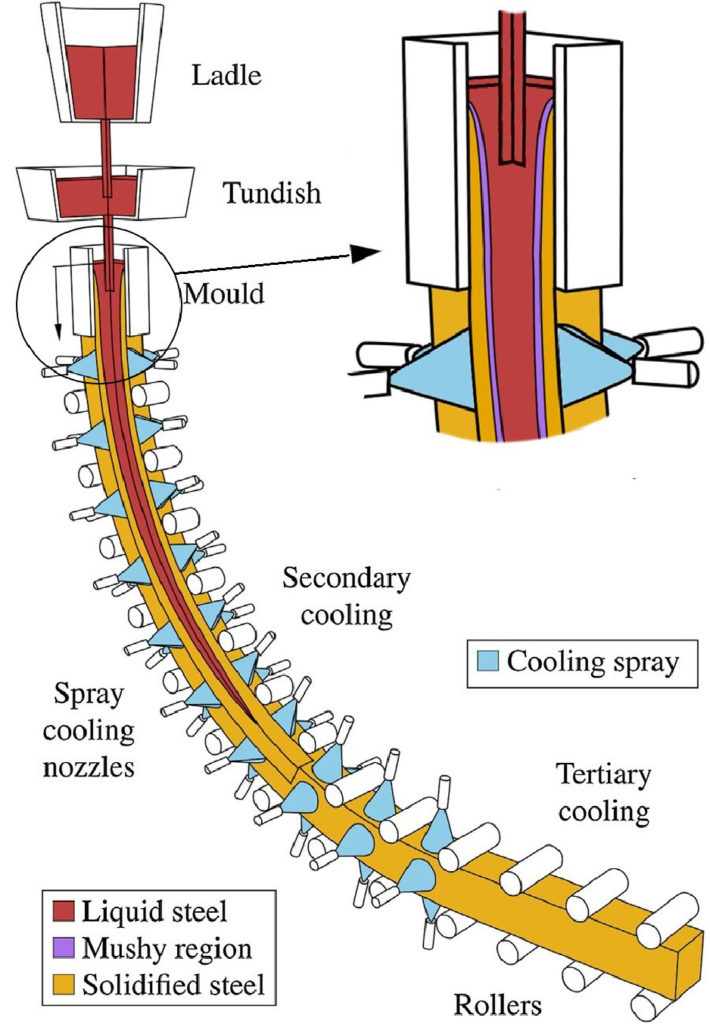
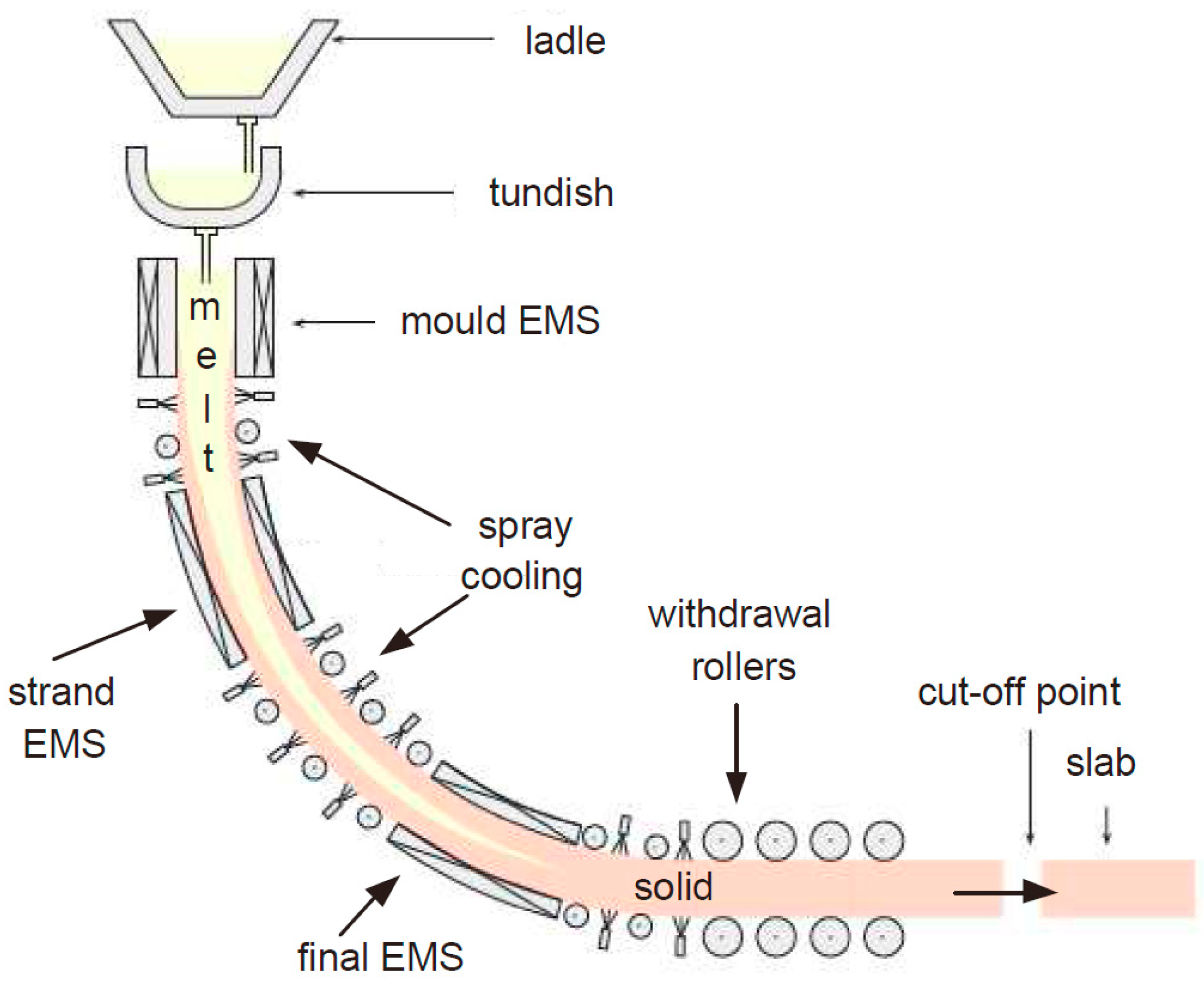
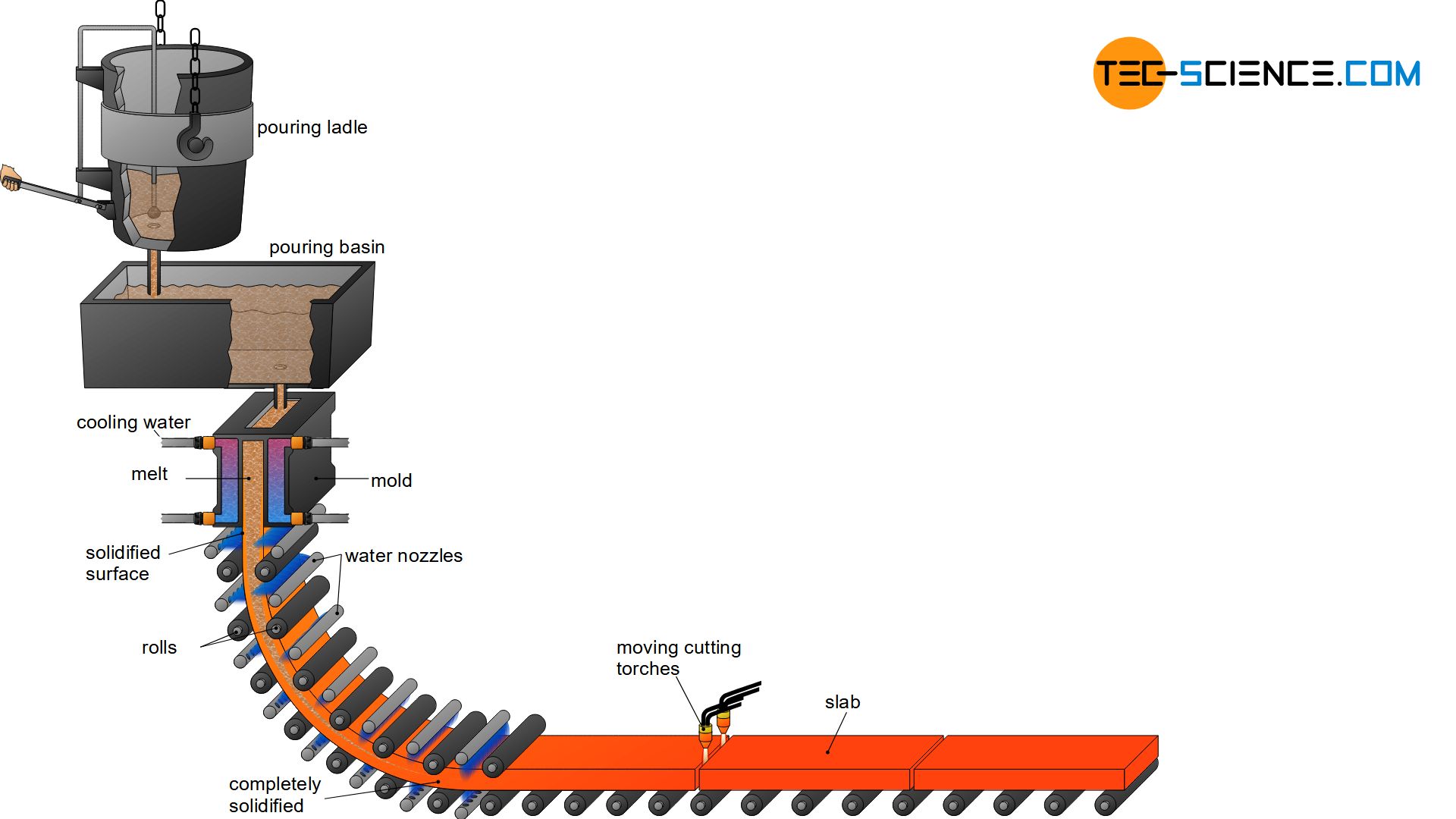
Continuous casting About 55 percent of the world's liquid steel production is solidified in continuous casting processes, the most widely used of which feeds liquid steel continuously into a short, water-cooled vertical copper mold and, at the same time, continuously withdraws the frozen shell, including the liquid steel it contains.
Continuous casting Modern techniques to solve an old industrial
Process : Continuous casting, also known as strand casting, is the process where a metal is heated until it liquefies. The molten metal is then allowed to solidify until it becomes a semi-finished slab that is later rolled in the finishing mill. It is used to cast metals of uninterrupted lengths.

(PDF) Breakout Problems Study of Continuous Casting Steel
The continuous casting process is shown in Figure 1.9.1. Steel is poured from the ladle into the tundish, which provides a constant head for molten steel to flow from the tundish into the mold via a submerged entry nozzle (SEN). The copper mold is water-cooled and the bottom of the mold is initially sealed by a dummy bar of steel.
Metals Free FullText Continuous Casting
Continuous casting is a relatively new process in historical terms. Although the continuous strip casting process was conceived by Bessemer in 1858, the continuous casting of steel did not gain widespread use until the 1960s.

continuous casting in steel making YouTube
Continuous casting is a metal casting process that produces continuous lengths of metal, with a constant (2D) cross-section. It's a highly efficient method for converting molten metal into long lengths of semi-finished product of a relatively small, potentially complex cross-section.
From steel to semifinished products tecscience
Continuous casting is the important linking process between steelmaking and rolling. As early as 1856, Henry Bessemer suggested a continuous casting method but just during the 1930s and 1940s continuous casting became a common production method for nonferrous metals and later from the 1960s for steels.

Continuous Casting Of Steel Stock Illustration Download Image Now
Continuous casting is used to solidify most of the 750 million tons of steel produced in the world every year. Like most commercial processes, continuous casting involves many complex interacting phenomena. Most previous advances have been based on empirical knowledge gained from experimentation with the process. To further optimize the design and improve the continuous casting process.

Continuous Steel Casting with Syalon Break Rings
Continuous Casting Practices for Steel: Past, Present and Future by Roderick I. L. Guthrie * and Mihaiela M. Isac McGill Metals Processing Centre, McGill University, Montreal, QC H3A 0C5, Canada * Author to whom correspondence should be addressed. Metals 2022, 12 (5), 862; https://doi.org/10.3390/met12050862
Materials Free FullText A New Predictive Model of Centerline
Continuous casting, also called strand casting, is the process whereby molten metal is solidified into a "semifinished" billet, bloom, or slab for subsequent rolling in the finishing mills. Prior to the introduction of continuous casting in the 1950s, steel was poured into stationary molds to form ingots.

Continuous casting Find suppliers, processes & material
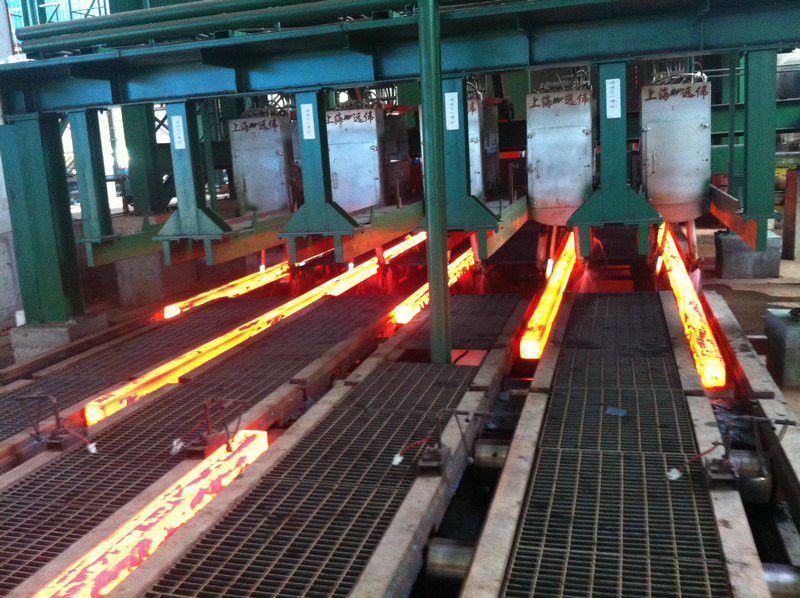
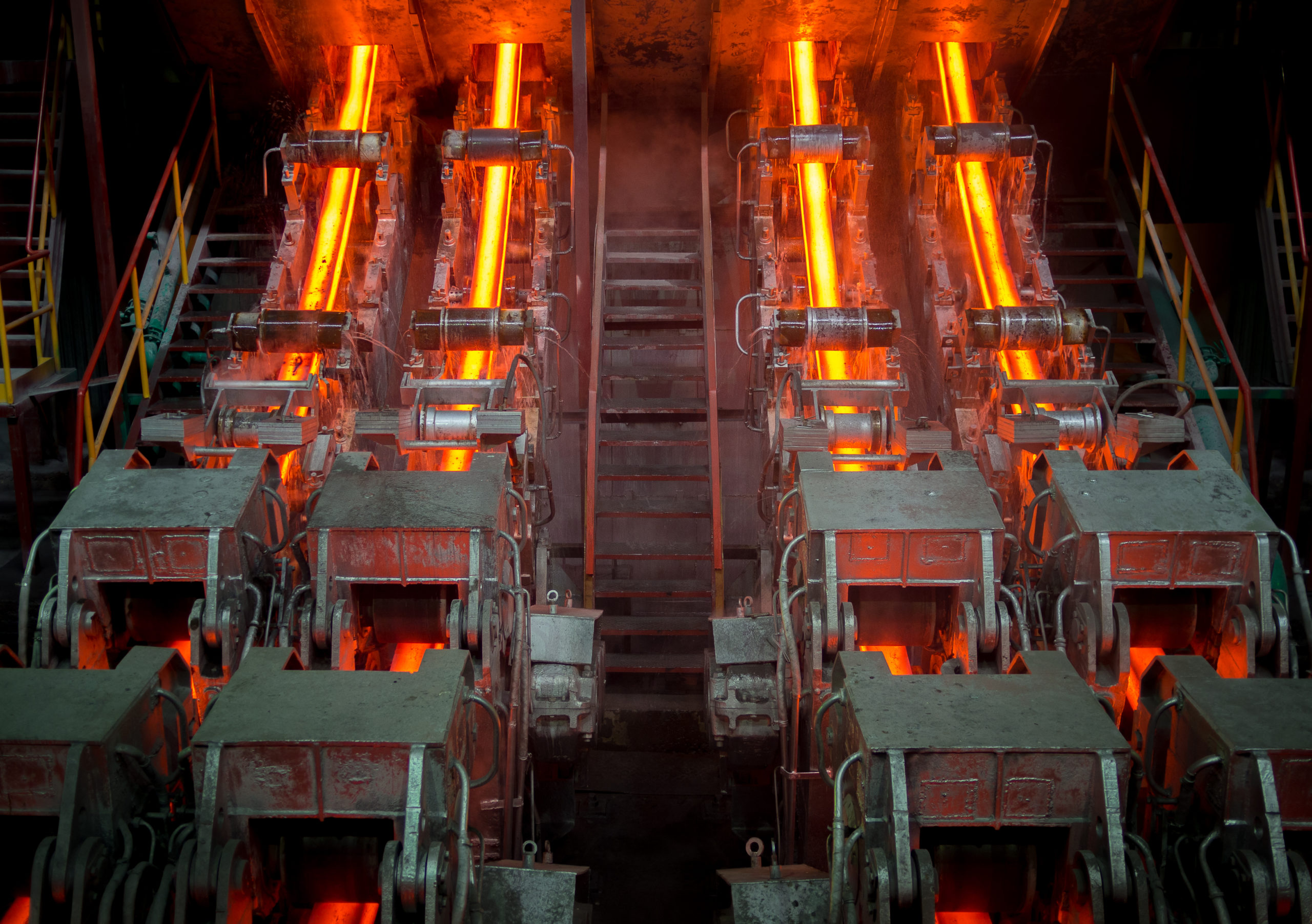
Continuous steel casting is a process to obtain casting billets by the molten steel casted into the caster, solidifying, and cutting. It is a process between steelmaking and rolling, also called continuous casting for short. The steel billets produced by continuous casting are raw materials for various products in hot rolling mills.
Continuous Steel Casting with Syalon Break Rings
The process of continuous casting of steel is a complex technological task, including issues related to heat transfer, the steel solidification process, liquid metal flow and phase transitions in the solid state.