
What are Saprophytes? (with pictures)
Examples As mentioned, saprophyte is an umbrella term used to refer to a number of organisms that feed on dead and decaying organic material (plant matter). The following are some examples of saprophytes: Fungi: Fungi and some of the most popular saprophytes.

PPT Kingdom Fungi PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3046843
Saprotrophs feed by a process known as absorptive nutrition, in which the nutritional substrate (e.g., dead organism or other nonliving organic matter) is directly digested by a variety of enzymes that are excreted by the saprotroph. The enzymes convert the detritus into simpler molecules, which are then absorbed by the cells to feed the organism.

Saprophytic Plants YouTube
Examples of saprophytes. As we saw at the beginning of the article, saprophytic organisms are represented by fungi, bacteria, and some protozoa, all of them included within the protist kingdom. Since of the three groups of organisms mentioned, fungi are the easiest to find in nature, here is a list of many of the saprophytic fungi more common:

Difference Between Saprotrophs and Saprophytes Compare the Difference Between Similar Terms
An example of a substance that is only broken down by saprophytes is lignin, which is a major component in many plants and is what gives trees their tough characteristics.

[Class 10] Difference between Saprophytes and Parasites [in Table]
Give two examples. Solution Verified by Toppr Saprophytes are living organisms that obtain their nutrition either directly from dead organic matter or indirectly by parasitizing fungi. For e xample, include fungi like mushrooms and bacteria like Lactobacillus. Was this answer helpful? Similar Questions

Saprophyte définition et explications
∙ Some of the common examples of saprophytes are bacteria fungi and many other microorganisms. Example:- mycorrhiza, mushrooms etc.

Difference Between Saprophytes and Parasites Definition, Characteristics, Role, Examples
Examples of Saprophytes Quiz FAQ What are saprophytes? Do saprophytes perform photosynthesis? Are all fungi saprophytes? How do saprophytes obtain their food? Why are saprophytes important in an ecosystem? What is the difference between saprophytes and parasites? Can plants be saprophytes?

Difference Between Saprozoic and Saprophytic Nutrition Compare the Difference Between Similar
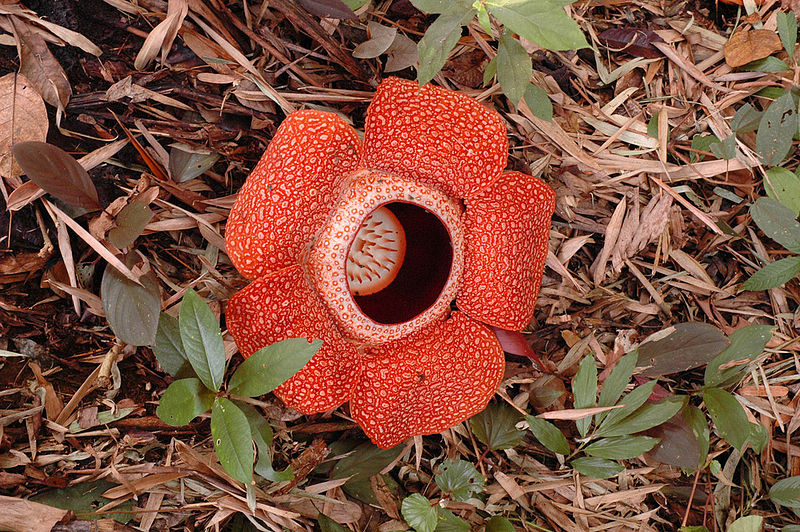
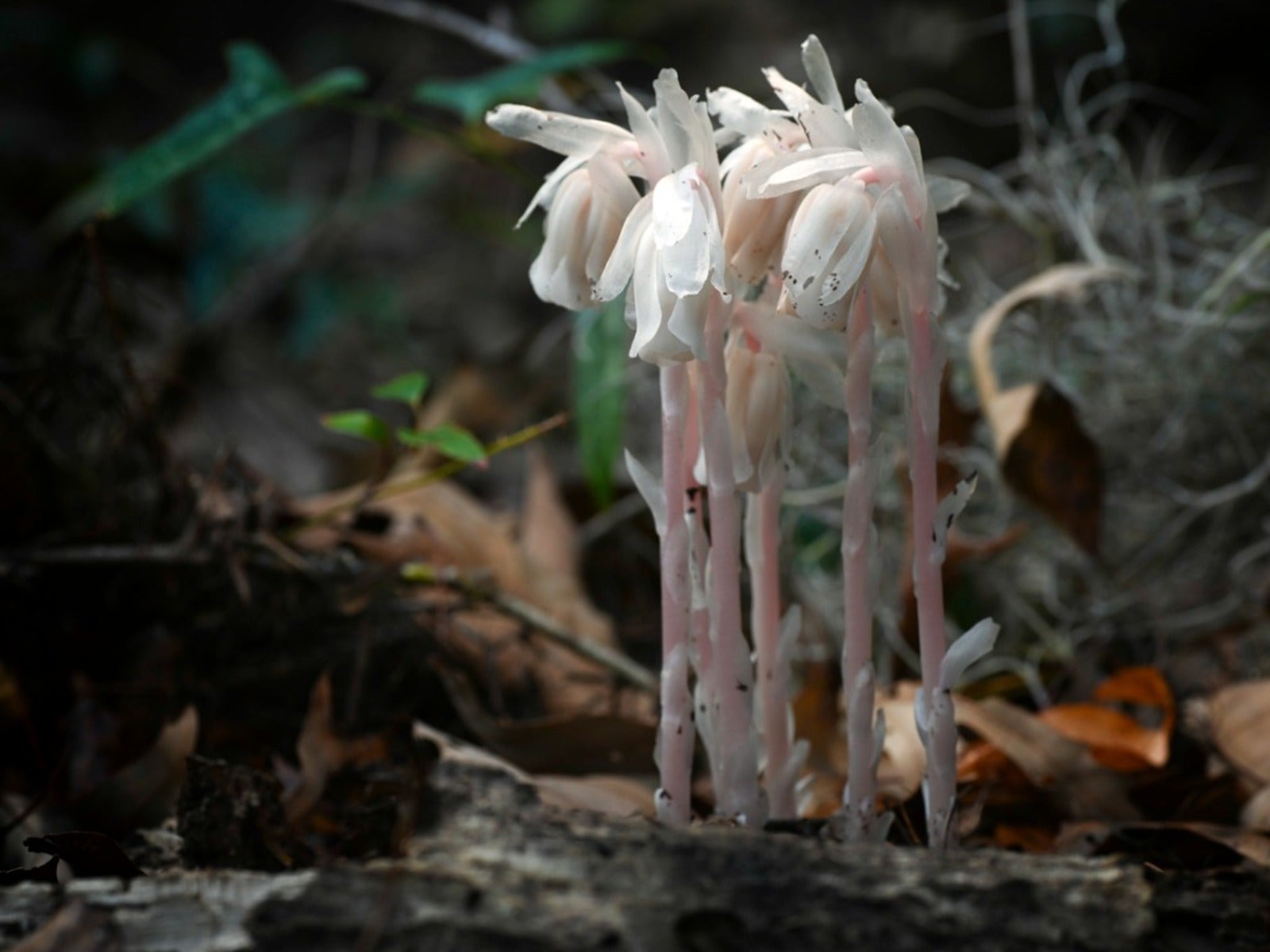
Saprophytes. A saprophyte is a plant that does not have chlorophyll and gets its food from dead matter, similar to bacteria and fungi (note that fungi are often called saprophytes, which is incorrect, because fungi are not plants). Plants like these use enzymes to convert organic food materials into simpler forms from which they can absorb nutrients (Figure 1b).
What are Saprophytes? Examples and Characteristics
The following are some examples of saprophytes: Fungi Fungi, as well as some of the most well-known saprophytes. Molds, mushrooms, yeast, penicillium, and mucor are examples of saprophytic fungi, as are other types of fungi.. Mucor can be found in large quantities on stale bread, vegetables, and excrement. There are two ways in which it.

Learn About Saprophyte Organisms And Plants
Following are a few examples of saprophytes: Mucor Mucor, also known as mould, is a saprophytic fungus that grows on decayed organic matter, especially those that are rich in carbohydrates. Mucor is majorly found on stale bread, vegetables and dung. It reproduces by sexual and asexual means. Yeast Yeast is commonly found on sugary substances.

PPT Food Relationships PowerPoint Presentation ID4001434
Saprophytes Examples. Saprophytes, includes a variety of organisms from different taxonomic groups. They share the common characteristic of obtaining their nutrients and energy by decomposing dead or decaying organic matter. Some examples of saprophytes are as follows: Fungi. Fungi are the most known group of saprophytes.

Saprophytes! Nature Up North
Solution Saprophytes: Saprophytes are any organisms that depend on or consume other dead, rotting, or degraded organic substances. They do not consume living organisms, in contrast to parasites. Decomposed or decaying materials are converted by them into simple organic materials, which plants eventually consume.

The Ultimate Guide to Saprotrophic Mushrooms GroCycle
Give two examples Solution Saprophytes: Saprophytes are living organisms that eat other organisms' remnants. They decompose complex organic stuff into simpler molecules that plants can utilize in several metabolic processes. They are heterotrophs. Most fungi are saprophytes. Example of saprophytes: Yeast Mucor Suggest Corrections 22

PPT Relationships In Ecology. PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5392575
Example - Mucor, yeast. Saprophytes are mostly fungus and/or bacteria. Saprophytes decompose dead plants and animals and convert complex molecules into simpler molecules. These converted molecules are returned to the soil, thereby increasing soil fertility. Plants intake these simple molecules and use them for their survival.

Difference Between Saprophytic and Symbiotic Plants Compare the Difference Between Similar Terms
The most important source of BNF is the symbiotic interaction between soil bacteria and legume plants, including many crops important to humans (Figure 31.3.1 31.3. 1 ). The NH 3 resulting from fixation can be transported into plant tissue and incorporated into amino acids, which are then made into plant proteins.

Explain the Two Different Types of Nutrition That Fungi Undergo
Saprophytes obtain their nutrients from dead and decomposed organic material. They consist of spores and perform metabolic activities. Mucor and yeast are common examples of saprophytes. Key Terms: Saprophytes, Mucor, Yeast, Ecosystem, Plant, Photosynthesis, Heterotrophic, Environment, Roots, Stems, Enzymes, Decomposition.