
Snake Anatomy Drawing, Step by Step, Drawing Guide, by Dawn DragoArt
Snake Subspecies: Snake in the Thai rainforest. Image credit Siripong Jitchum via Shutterstock. According to the now-outdated Snake Species of the World series (though it may have been updated since first published), there exists more than 31 families, 450 genera, and over 2,500 species of snakes currently living in the world.
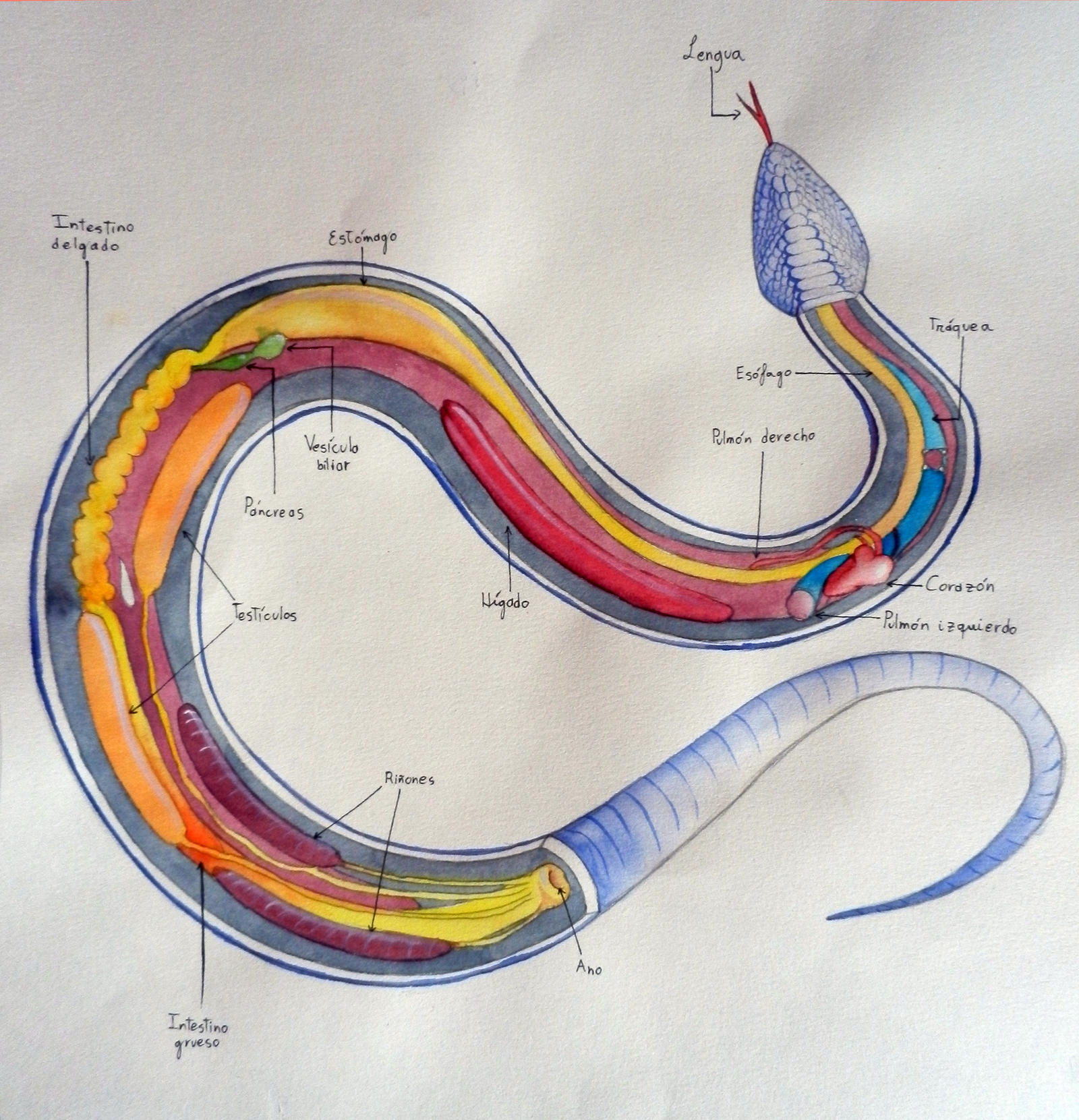
Snake organs (Anatomy study) by Erobertix on DeviantArt
yellow anaconda Yellow anaconda (Eunectes notaeus). green mamba East African green mamba (Dendroaspis angusticeps). The most characteristic aspect of the snake form is the elongate body and tail and the absence of limbs.

Anatomy of snake
Habits. About once a month snakes shed their skin, a process called ecdysis that makes room for growth and gets rid of parasites. They rub against a tree branch or other object, then slither out.

Snake Anatomy & Physiology Bugs In The News
Just about everyone knows what a Snake is. These creatures have long bodies, no legs, and their skin has a covering of scales. Most species also have extremely flexible jaws, or even possess extra joints, so that they can swallow prey larger than themselves! Researchers recognize about 3,600 different species of Snakes.
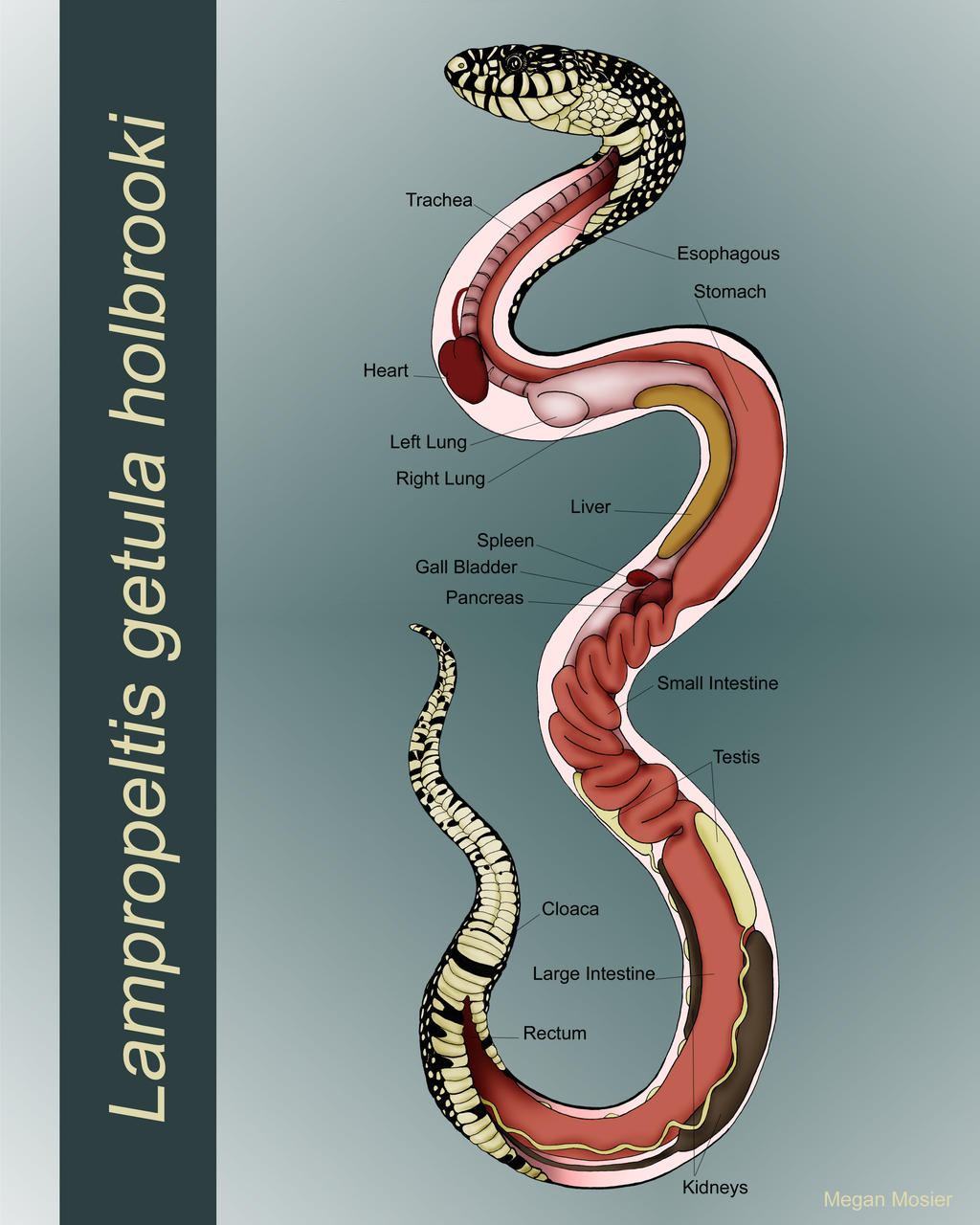
Anatomy of a Snake by MeganMosier on DeviantArt
Snakes have no moveable eyelids, limbs, ear openings, sternums, or urinary bladders. Most species have only one functioning lung, although many have a second, vestigial (essentially non-functioning, or only marginally functional) lung. The organs in the snake body are necessarily elongated, to fit within the narrow confines of its body cavity. Lizards differ from snakes anatomically by having.
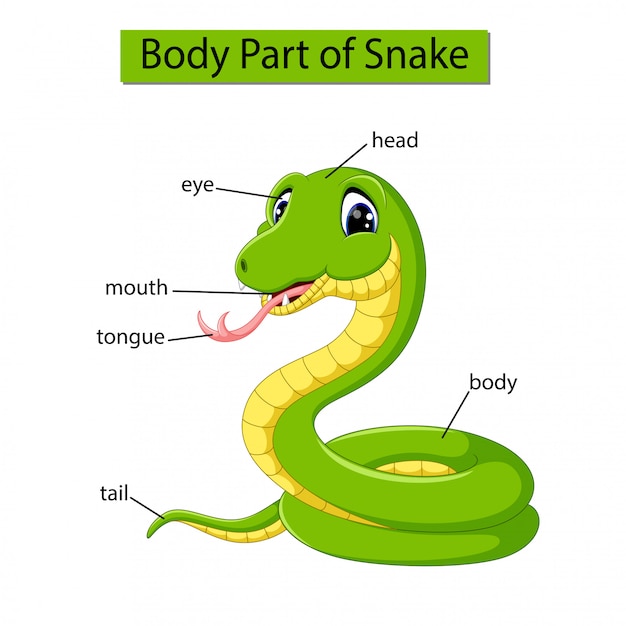
Premium Vector Diagram showing body part of snake
Snake - Skull, Sense Organs: Snakes rely on several senses to inform them of their surroundings. The pits are sensitive to changes in temperature. The lidless eyes are covered by a transparent cap of epidermis. Sound reception is entirely by bone conduction within the skull. The skull is characterized by mobility, with hinge joints at several levels. Kidney wastes are excreted in a solid state.

Snake Identification, Anatomy, & Life Cycle Types of Snakes
A fun way to learn the parts of the body of a snake - with the whole family. If you've used our snake anatomy poster, you'll know all about the body parts of a snake. Now you can prove your knowledge with this fun labelling activity!

About Snakes Friends of Snakes Society
one lung ectothermic long slender bodies There are over 3,500 individual species that fit these characteristics, with more being added each year. These 3,500+ species are split into 20 different families that can be further broken down into 520 genera.

Parts of a Snake Nomenclature Book Montessori Zoology Etsy
Category: Animals & Nature Also called: serpent rattlesnake cobra blind snake worm snake venomous snake See all related content → Recent News Jan. 5, 2024, 4:26 AM ET (Yahoo News) Aussies stunned as snake found inside belly of coral trout: 'So cool' Dec. 30, 2023, 11:39 AM ET (AP)

The anatomy of a snake Mike Cosgraves Weblog
A snake's body is made up of many parts. Each part has a specific function, or job.

Cobra Snake Facts Cobra Snake Information DK Find Out
As diverse as they are, all snakes share a common body plan, with a long, legless trunk and a short tail (you can tell trunk from tail by the skeleton: the trunk is the part with the ribs). They also share a common lifestyle - every snake, everywhere on earth, is a predator.

Snake Vocabulary Part Of Body Vector Stock Vector Image 46619340
Snake Anatomy Snakes belong to the reptile group. They lack the moveable eyelids, limbs, sternums, urinary bladder and ear openings. The body of the snake is so narrow and elongated. So the organs of the snake are also elongated to fit in the body structure The quadrate bones that connect the skull to the lower jaw are long and flexible.

Snake anatomy and physiology pet education, The anatomy and physiology of snakes differs from
Snake's head comprises of the eyes, nose, mouth, brain, and a special sensory organ known as the vomeronasal or Jacobson's organ. Its two apertures are located just in front of the choana, an open slit-like structure on the top interior of the reptile's mouth. Every snake has a forked tongue.
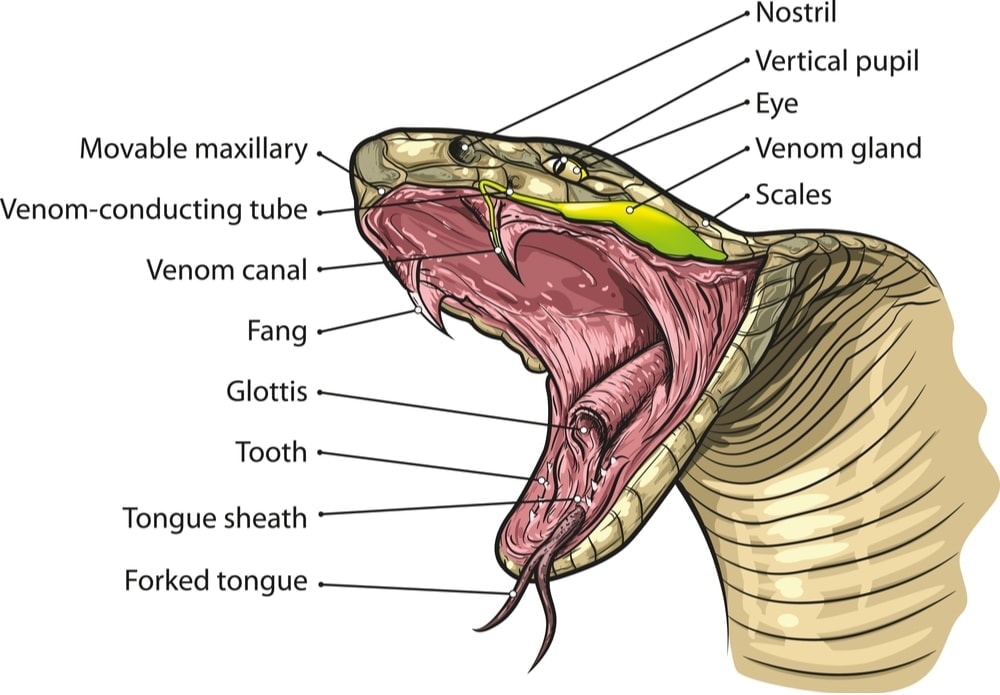
Snake Anatomy Information » Petsoid
Some possess venom that is potent enough to cause painful injury or death to humans. Nonvenomous snakes either swallow prey alive or kill by , itself from Proto-Germanic snak-an- 'ring snake', Swedish 'grass snake'), from Proto-Indo-European (s)nēg-o- 'to crawl to creep', which also gave 'snake'.

Snakes body parts Royalty Free Vector Image VectorStock
About snakes Snakes are fascinating creatures with unique anatomy. They have long, slender bodies with no legs, arms, or external ears. Instead of ears, they have a small opening on the side of their head that picks up vibrations. Snakes also have flexible jaws that allow them to swallow prey up to three times the size of their head.

98 best drawing snake study images on Pinterest Snakes, Amphibians and Reptiles
snake, Any member of about 19 reptile families (suborder Serpentes, order Squamata) that has no limbs, voice, external ears, or eyelids, only one functional lung, and a long, slender body. About 2,900 snake species are known to exist, most living in the tropics. Their skin is covered with scales.