
Drillware closes the loop on wasted water with the Environ SRS Centrifuge Coring Magazine
If a spill occurs, clean the rotor and buckets immediately. 9. Wipe down the rotor and centrifuge after each use. To keep the centrifuge clean and running smoothly, lightly clean the rotor and wipe down the centrifuge at the end of a run. When you are finished, leave the lid open so it can air out and remain dry.

Combo centrifuge Zhejiang Huawei Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd
Laboratory centrifuge 30,000 to 100,000 100,000 to 800,000 Zippe-type centrifuge* 90,000 ˘1 106 * tangential velocity >Mach 2 ˘700m.s 1 9. Laboratory centrifuges [Ghosh] Main selection factors: 1.duration = t [use minutes in the equation below] 2.maximum rotational speed = RPM max t = k S
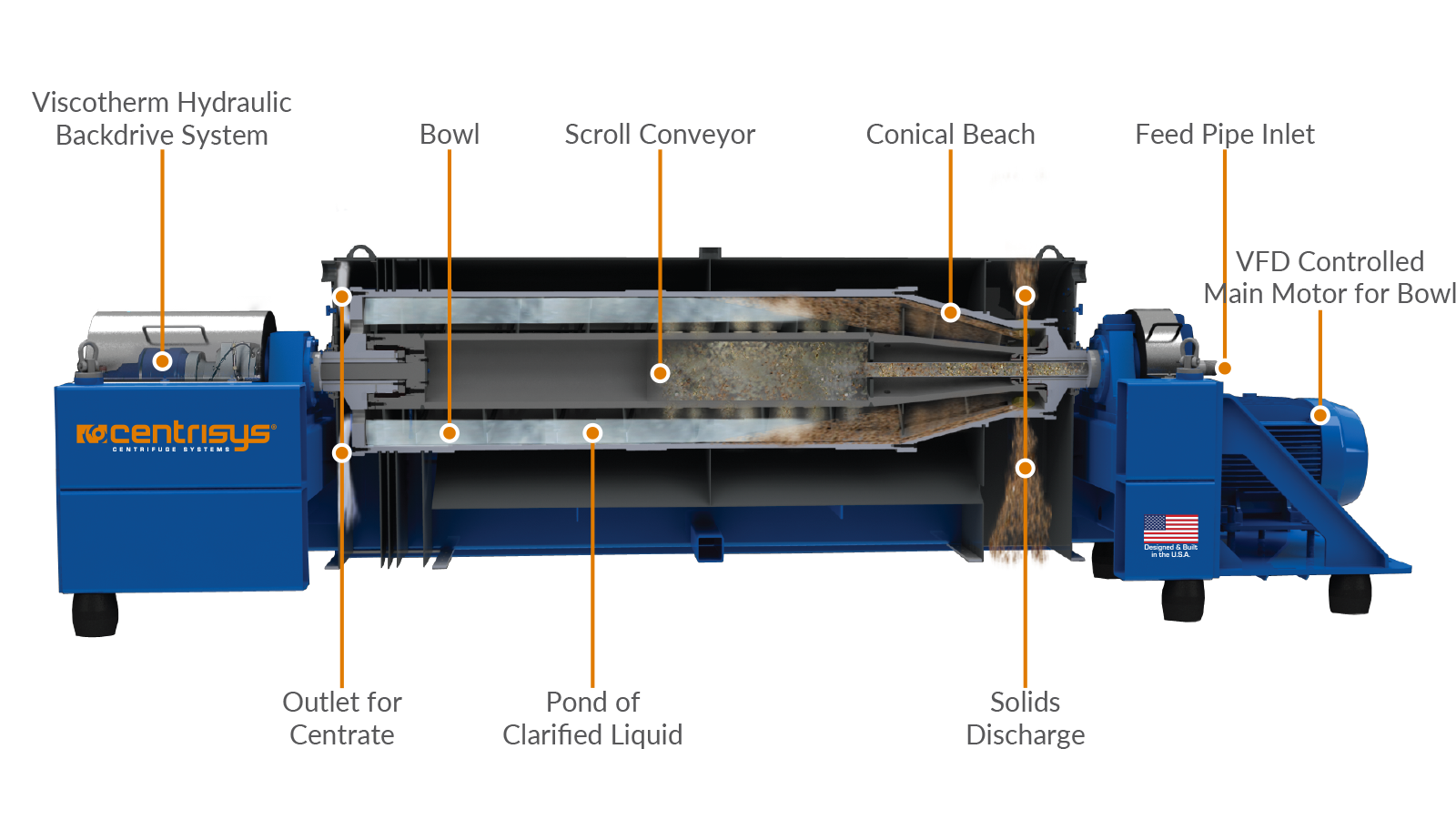
Decanter Centrifuge Spare Rotating Assemblies Explained
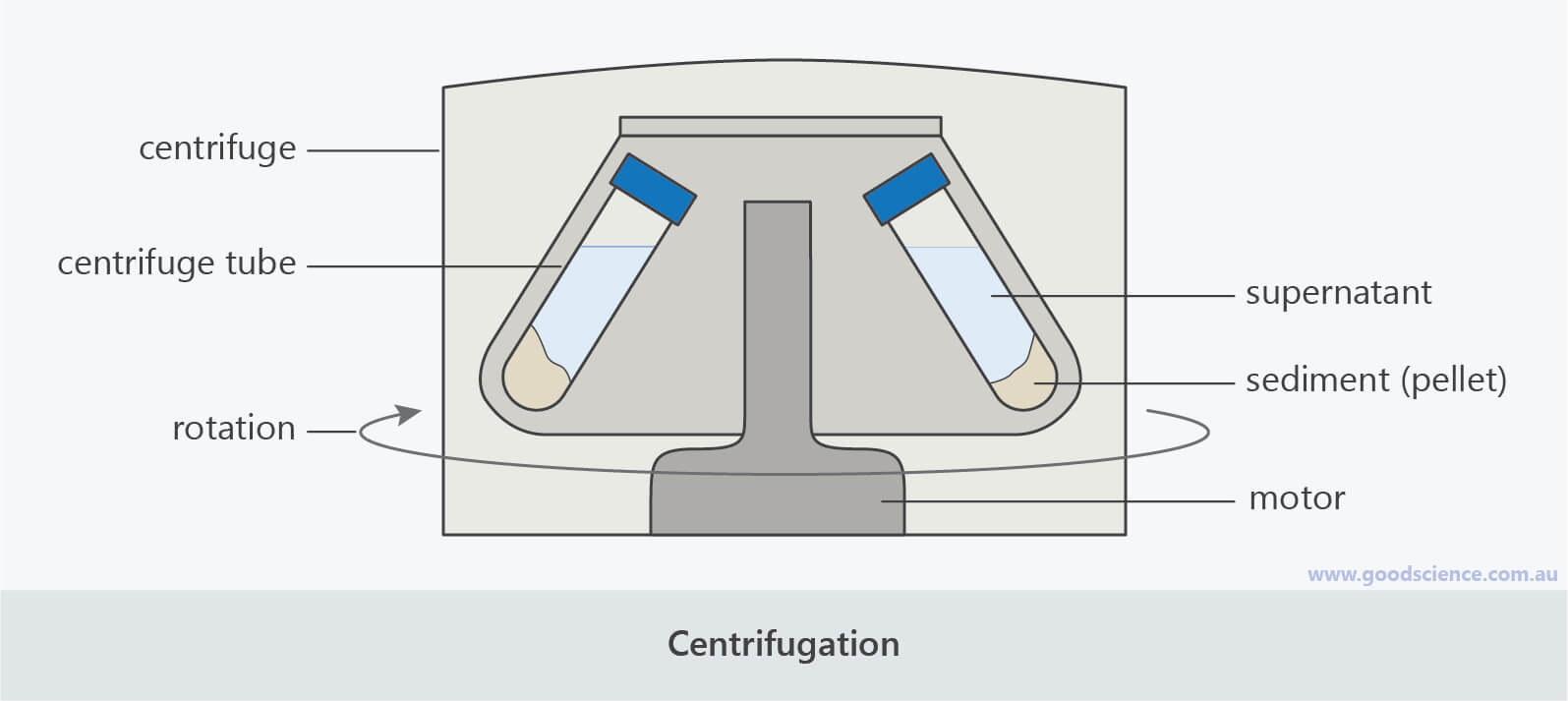
The diagram below shows red blood cells, white blood cells of different types (large, purple cells), and platelets. Plasma Plasma, the liquid component of blood, can be isolated by spinning a tube of whole blood at high speeds in a centrifuge.
Clinical Centrifuge NBS Scientific BE
The cost of a centrifuge can vary widely depending on the size and type of centrifuge you want to purchase. Other factors include your flow rate, technology of the centrifuge (e.g., gear, belt, or integrated drive), valving, and automation. Taking all of that into consideration, centrifuges can cost anywhere from $100K to $1M.

Centrifuge Introduction, Principle, Types, Handling Procedure, Uses and
A laboratory centrifuge is a piece of laboratory equipment, driven by a motor, which spins liquid samples at high speed. There are various types of centrifuges, depending on the size and the sample capacity. [1]
Centrifugation JungleKey.fr Image 50
A centrifuge is a piece of equipment that puts an object in rotation around a fixed axis (spins it in a circle), applying a potentially strong force perpendicular to the axis of spin (outward). The centrifuge works using the sedimentation principle, where the centripetal acceleration causes denser substances and particles to move outward in the.
Separation of Mixtures Good Science
Multipurpose centrifuges offer a wider variety of options and are known to be versatile as they can perform multiple tasks. Conclusion. A centrifuge is a scientific device that is used to separate fluids, gasses or liquids based on the density of the subject. The separation is acquired by spinning a container with the material at a very high speed.
Édition Classique Regarde sil te plait centrifugation and its types jalousie Publier Je serai fort
1. Small Bench Centrifuges: They are used to collect small amount of material that rapidly sediment like yeast cells, erythrocytes etc. They have maximum relative centrifugal field of 3000-7000 g. 2.
How a Centrifuge Works? Centrifuge Types Features and Uses
Process Flow Diagram Equipment Symbols Flow chart symbols use different shapes to represent different components, such as equipment, valves, instruments, and piping flow. There is a standardized set of flowchart symbols. Process Flow Diagram equipment symbols include centrifuges and heat exchangers. Centrifuges

Clinical centrifuge Zhejiang Huawei Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd
December 10, 2022 by Prakriti Karki Edited By: Sagar Aryal Centrifugation is a term used to describe a method of separating mixtures using spinning and centrifugal force. Several characteristics can separate particles during centrifugation, including size, shape, density, and viscosity.

FileCentrifuge with samples rotating slowly.jpg Wikimedia Commons
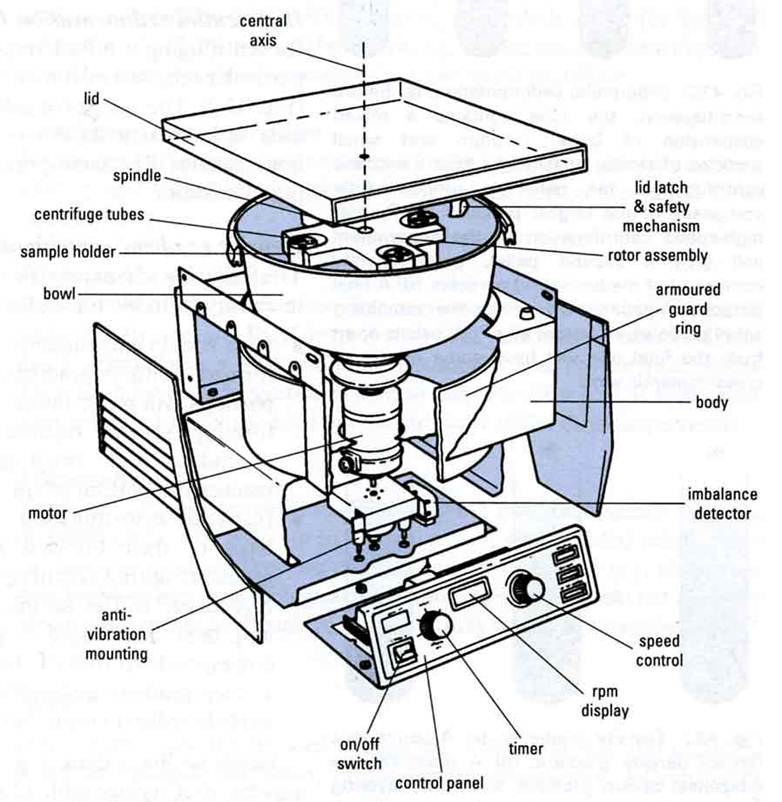
General Information The most basic laboratory centrifuge is a test-tube centrifuge. Test tubes are placed in a holder, the lid is closed and the tubes are spun. The resulting centrifugal force causes the denser components to move to the bottom of the tube, with the less dense components above them.

Bagian Bagian Centrifuge
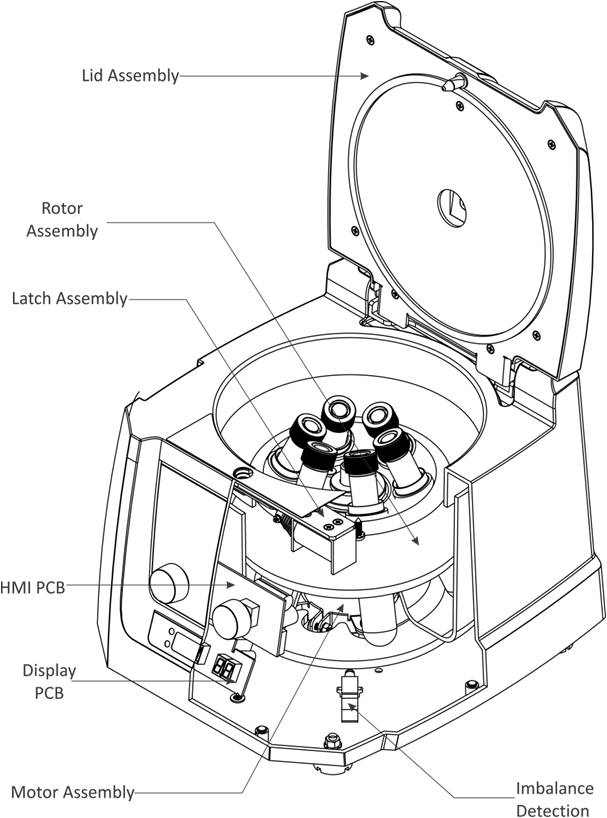
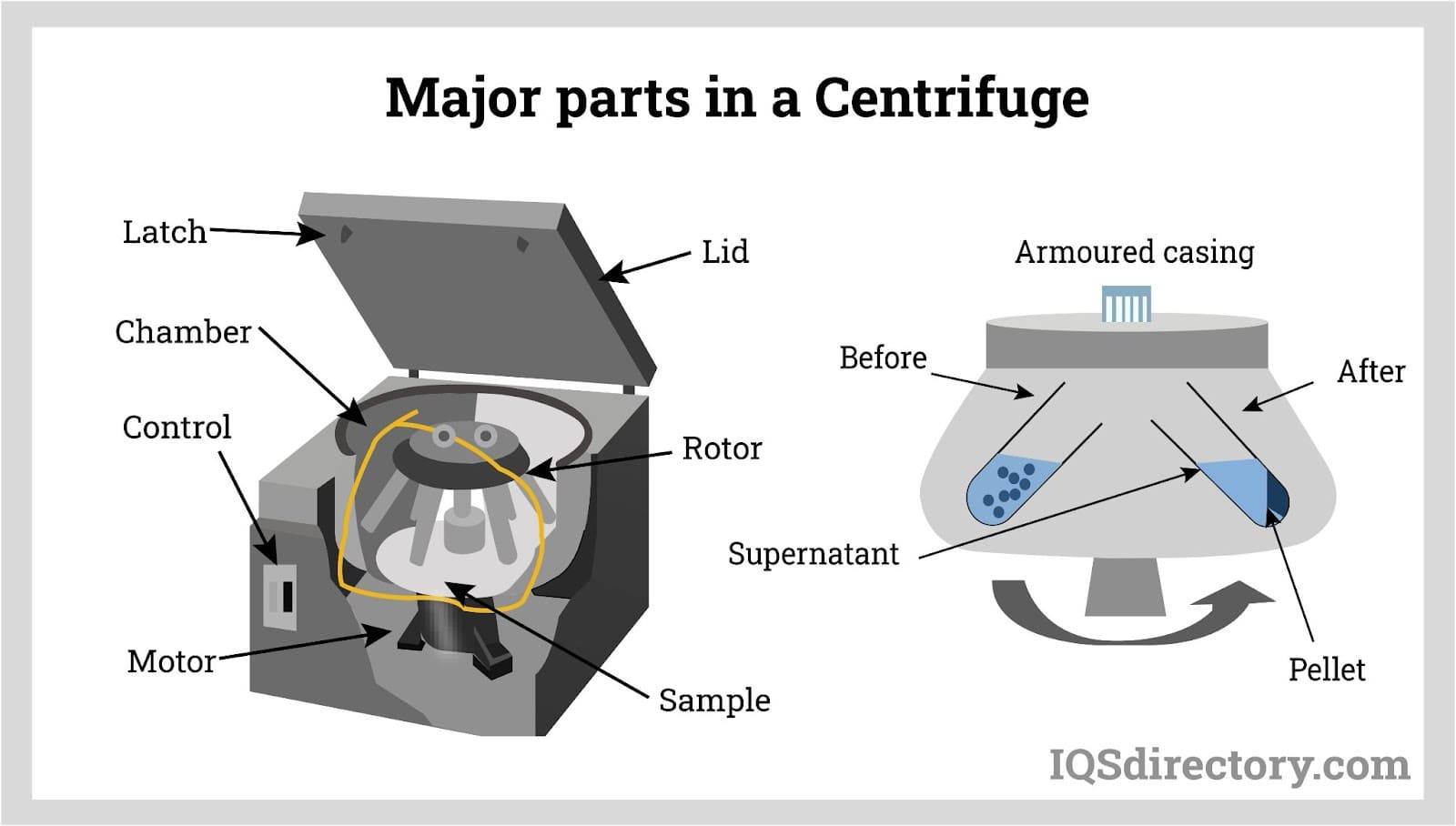
Front view of an open tabletop centrifuge with labels for the core parts that would be found on almost any centrifuge. Types and Parts. There are several types of centrifuges: Mini or Tabletop Centrifuges sit on your benchtop and typically hold the common 1.5 mL microfuge tubes used in labs, though some larger models can hold larger conical.

Centrifuges
A centrifuge is used to separate particles suspended in a liquid according to particle size and density, viscosity of the medium, and rotor speed. Within a solution, gravitational force will cause particles of higher density than the solvent to sink, and those less dense than the solvent to float to the top.

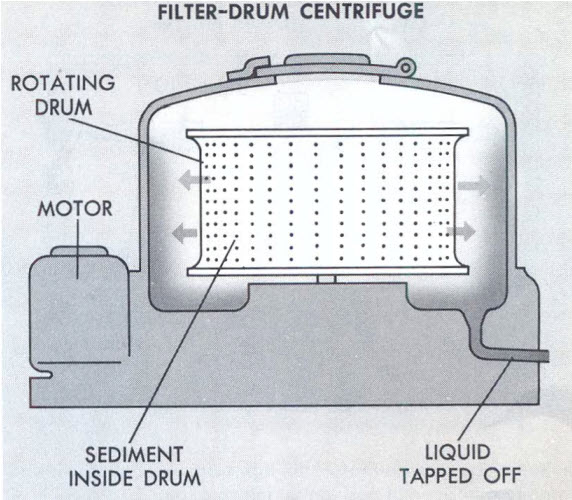
Schematic diagram of centrifuge tests Download Scientific Diagram
A centrifuge is a device that uses centrifugal force to subject a specimen to a specified constant force, for example to separate various components of a fluid. This is achieved by spinning the fluid at high speed within a container, thereby separating fluids of different densities (e.g. cream from milk) or liquids from solids. It works by.

Process of Separating Cream from Milk Centrifugation Teachoo
1. Benchtop centrifuge 2. Continuous flow centrifuge 3. Gas centrifuge 4. Hematocrit centrifuge 5. High-speed centrifuge 6. Low-speed centrifuge 7. Microcentrifuge 8. Refrigerated centrifuges 9. Ultracentrifuges 10. Vacuum centrifuge/ Concentrators Reference

Hematocrit Centrifuge 12000 rpm. Compact, transportable
The term centrifuge can refer to a machine that houses a rapidly rotating container to separate its contents by density (noun) or to the act of using the machine (verb). Centrifuges are most often used to separate different liquids and solid particulates from liquids, but they may be used for gases. They are also used for purposes other than.