
What are secondary growth in dicot stem? Definition, Types and
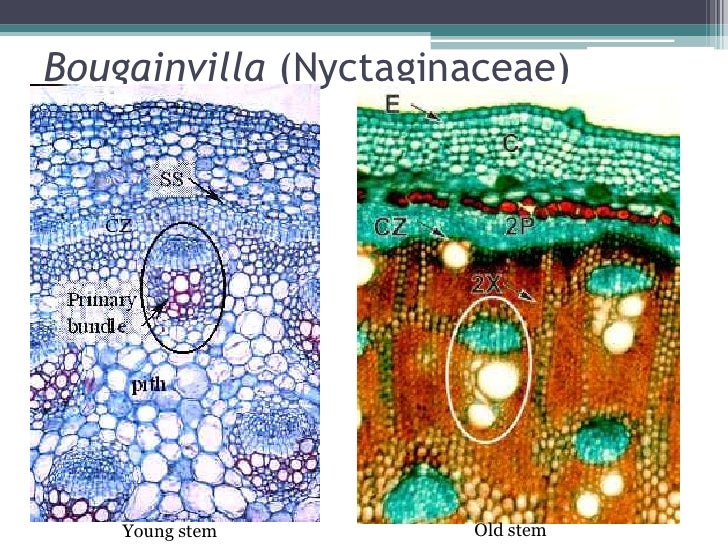
Part ll, , Prof. (Dr.) Punam Jeswal, Head, Department of Botany, , Anomalous Secondary Growth In Boerhaavia, Boerhaavia is a member of family, Nyctaginaceae. They are generally, herbaceous plant., , Boerhaavia Stem Transverse section through the young stem of Boerhaavia show following, tissues : -, , Epidermis 1) Epidermis is single layered and.

zoom BOERHAAVIA STEM T,S. , BOUGAINBIIEA STEM T.S. ANOMALOUS SECONDARY
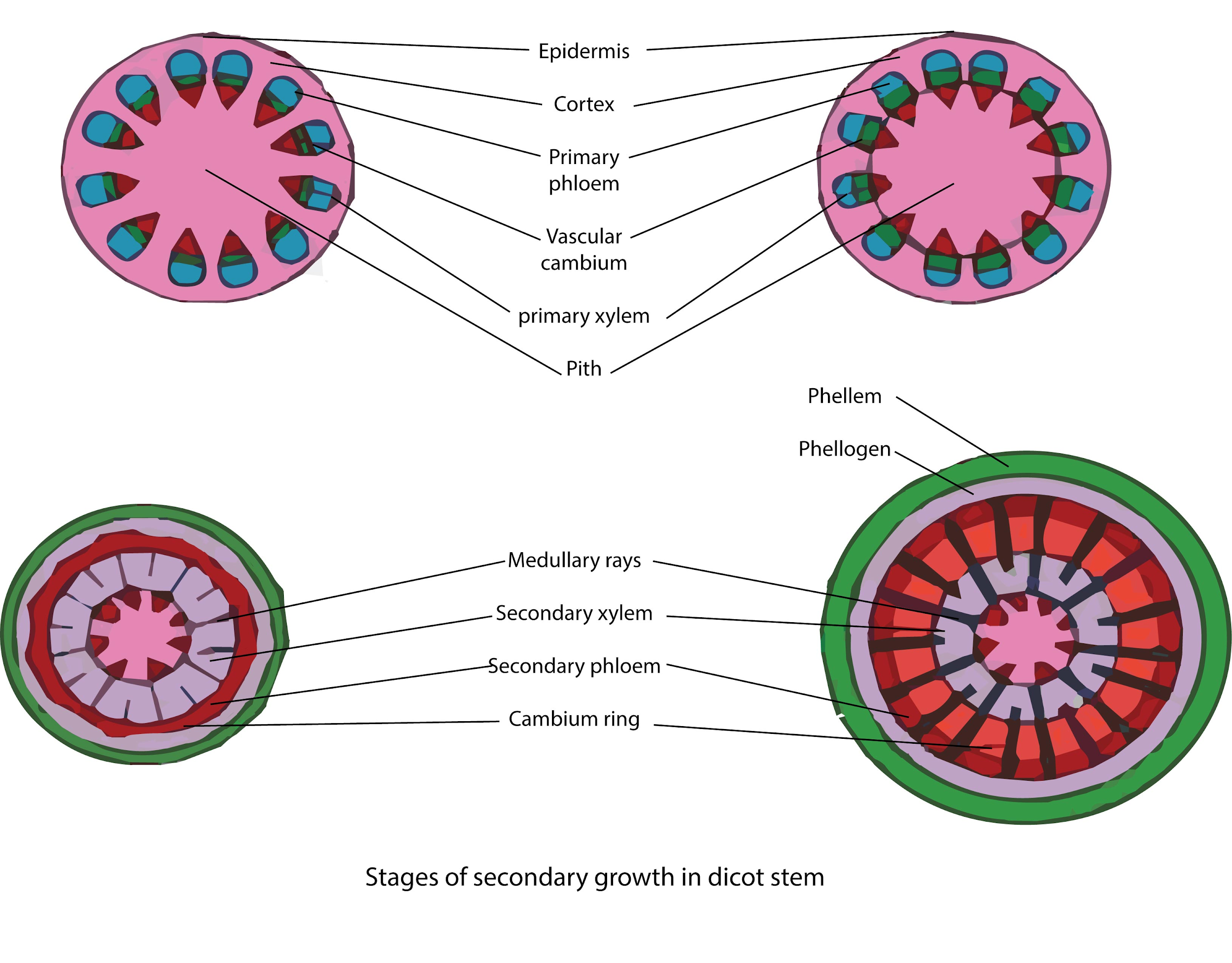
Anomalous secondary growth " is the term under which have been grouped cambial conformations, cambial products, and cambial numbers which differ from the most common " normal " condition, namely, a single cylindrical cambium that produces phloem externally and xylem internally.

Anomalous Secondary Growth
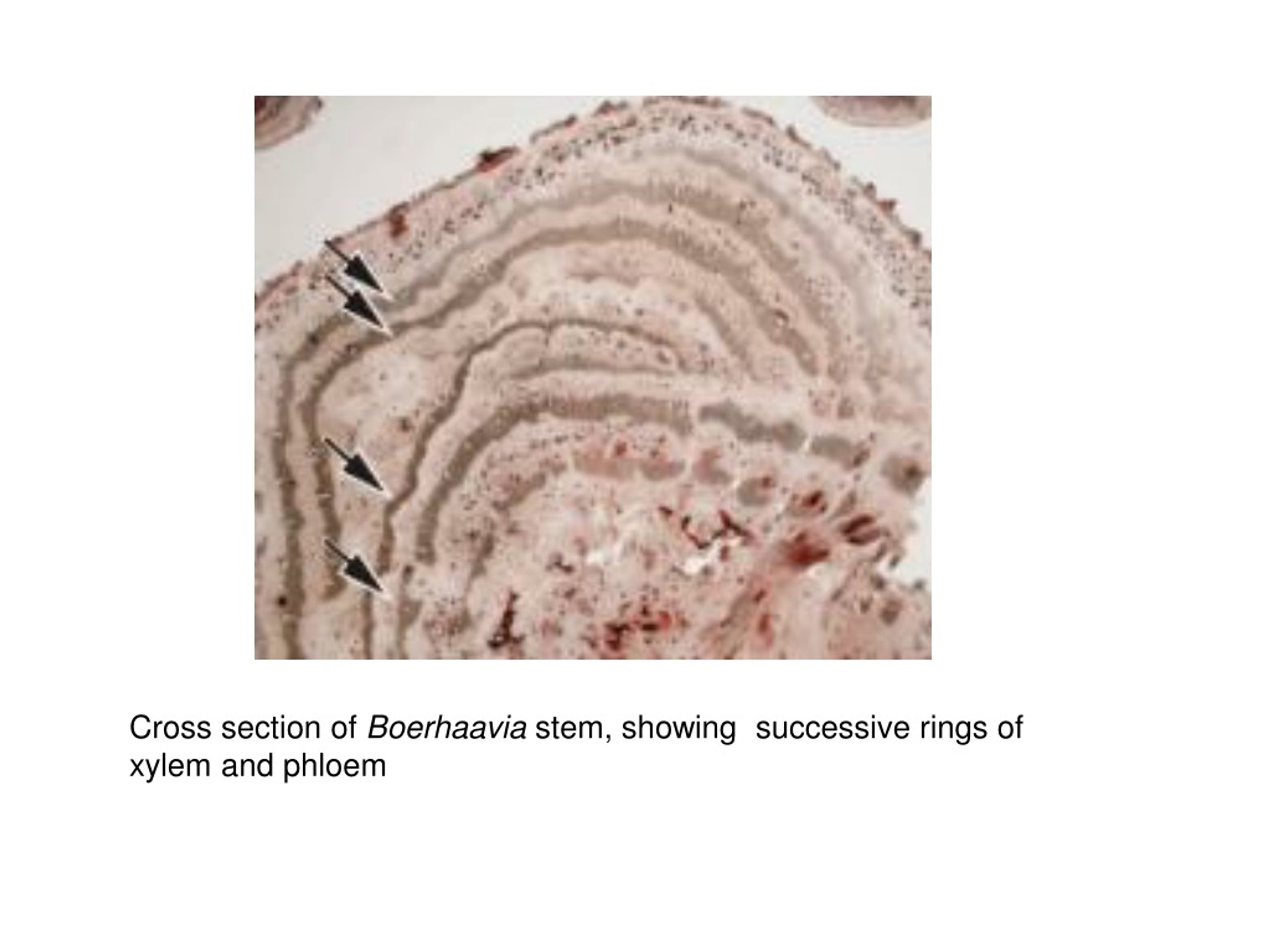
The stem of Boerhaavia contain well defined anomalous secondary growth which is characterized by the presence of successive rings of xylem and phloem (vascular bundles). After primary growth, the secondary growth is limited in the inner (Two medullary vascular bundles) and the middle ring of vascular bundles (6 to 14) by a fascicular cambium .

Anomalous Secondary Growth In Boerhaavia Plant Anatomy And
Botany ,II Semester

Anomalous secondary growth in bignonia YouTube
In this article we will discuss about the anatomy of various anomalous dicot stems: 1. Bougainvillea - Stem 2. Salvadora - Stem 3. Achyranthes- Stem 4. Chenopodium - Stem 5. Boerhaavia - Stem 6. Leptadenia - Stem7. Mirabilis- Stem 8. Amaranthus - Stem 9. Nyctanthes - Stem10. Bignonia - Stem. 1.
Anomalous Secondary Growth
The stem of Boerhaavia shows anomalous second-ary thickening via formation of successive rings of cambium (Maheshwari 1930). The cambium. Anomalous secondary growth re-sults, in some groups at least, from loss of normal cambial activity during evolution toward an herba-ceous mode of structure. It is considered that suc-
Explain the process of secondary growth in the stems of woody
Stage A Vascular bundles of dicot stems are conjoint (xylem and phloem in one bundle), collateral (laterally placed on the same radius) and open (fascicular cambium present between xylem and pholem), arranged in a ring.

Punam Jaiswal UGII Anomalous Secondary Growth in Boerhaavia PDF
Anomalous Secondary Growth In many plants, the pattern of the secondary thickening shows deviation from the normal type. The term "Anomalous Secondary Growth" is given for this deviation or variation. The anomalous secondary growth is more common in tropical plants.

DBOT 15 Nyctanthes & Boerhavia Sec. Growth in stem Dbios Charts
The reasons are: 1. The Activity of Normal Cambium is Abnormal 2. Abnormally Situated Cambium Forms Normal Secondary Vascular Tissues 3. Formation of Secondary Tissues by Accessory Cambium 4. Formation of Interxylary Phloem 5. Formation of Intra-Xylary Phloem. Reason # 1. The Activity of Normal Cambium is Abnormal:
PPT Anomalous secondary growth in stems PowerPoint Presentation, free
Anomalous secondary growth in Plants with special reference to Bignonia, Boerhavia, Aristolochia & Dracaena Dec 15, 2020 • 6 likes • 9,370 views N Nistarini College, Purulia (W.B) India Associate Professor Science This PPT intends to explore the most exception of nature-anomalous secondary growth in plants.

Anomalous Secondary growth in Boerhaavia Stem YouTube
Anomalous Secondary Grwoth in Boerhaavia Stem Boerhavia diffusa, commonly known as 'punarnava' (meaning that rejuvenates the body) is a highly medicinal plant belongs to the family Nyctaginaceae. It is a prostrate herbaceous plant.
Anomalous Secondary Growth
Punam Jaiswal UG-II Anomalous Secondary Growth in Boerhaavia | PDF | Plant Stem | Tissue (Biology) Punam Jaiswal UG-II Anomalous Secondary Growth in Boerhaavia (1) - Read online for free. Anomalous secondary growth

Learningbotanist.in Anomalous secondary growth
The woody climbers or lianes and the storage organs exhibit anomalous structure and abnormal secondary increase in thickness, as they are constructed differently from the normal ones both from morphological and physiological points of view.

Anomalous Secondary Growth Plantlet
. Multicellular epidermal hairs arise from some cells. Cortex: It is well differentiated and consists of few layered collenchymatous hypodermis followed by chlorenchyma. Collenchyma is 3 to 4 cells deep, but generally near stomata it is only one layered. Chlorenchyma is present inner to collenchyma in the form of 3 to 7 layers.
3.2 Secondary growth Biology LibreTexts
NEET UG - Anomalous Secondary Growth in Boerhavia Stem Offered by Unacademy Please Login To Continue NEET UG Free courses Strategy & College Overview Strategy Anomalous Secondary Growth in Boerhavia Stem Lesson 9 of 13 • 29 upvotes • 12:28mins Juhi Mishra Anatomy of Boerhavia Stem (Hindi) Learn Biology With Diagrams 13 lessons • 2h 34m 1

Anomalous secondary growth in Boerhaavia Dicot plants,primary structure
This video is about anomalous secondary growth in boerhaavia stem. If you like the video then " SUBSCRIBE " our channel and Press the BELL ICON for f Show chat replay Anomalous secondary.