FDM 3D Printing of Polymers Containing Natural Fillers Encyclopedia MDPI
Stereolithography (SLA) Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) Digital Light Process (DLP) Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) PolyJet Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) Electron Beam Melting (EBM)

NEW INFOGRAPHIC on The basics of 3D printing features 3Drag printer! Open Electronics Open
3D Printing is the process of creating objects by depositing layers of material on top of one another. 3D Printing is called additive manufacturing (AM) instead of traditional subtractive methods like CNC milling when used for industrial production. This technology has been around for about four decades, invented in the early 1980s.

A schematic illustration of the PolyJet 3D printing mechanism Download Scientific Diagram
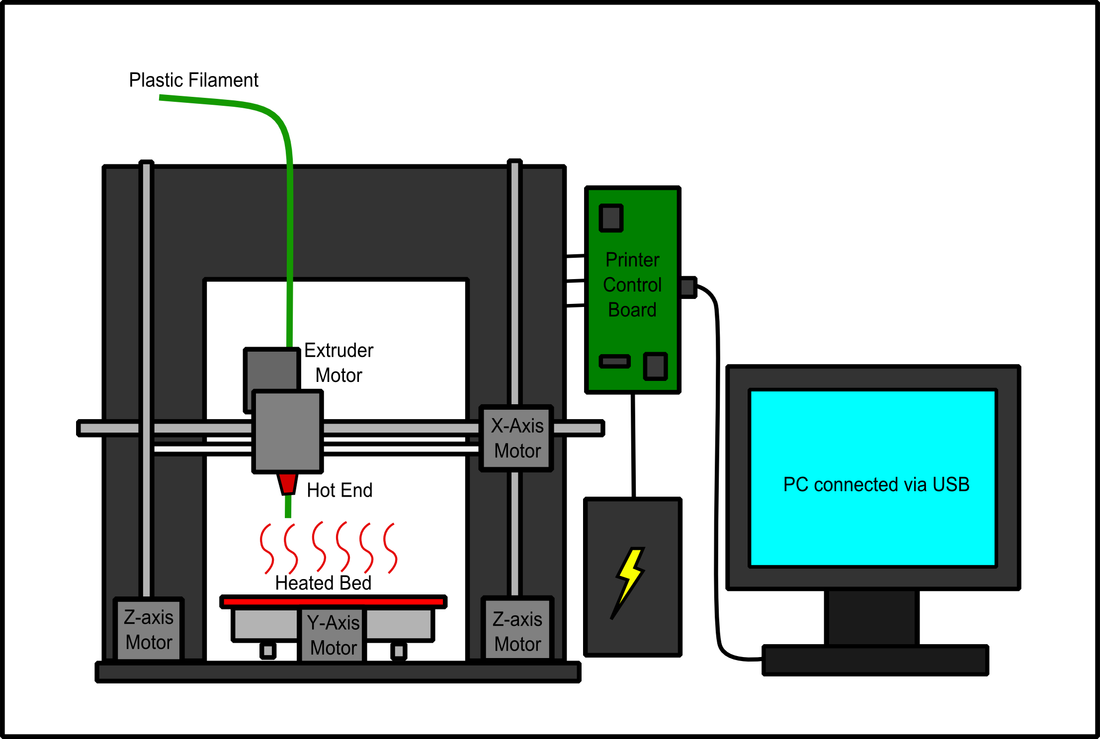
3D printing, the process of making a solid object from a digital model, is a form of additive manufacturing. Here's a diagram of how 3D printers work.

(a) Schematic of 3D printer in spray configuration. (b) Printer Download Scientific Diagram
3D printing diagram is a visual representation that illustrates the process, components, and steps involved in 3D printing. It provides a clear overview of how the technology works and helps users understand the different stages of the printing process. A typical 3D printing diagram includes several key elements, such as the printer, filament.
Anatomy of a 3D Printer How 3D Printers Work Made Simple 3D Printer Power
3D printing or additive manufacturing is a process of making three dimensional objects from a digital file. The creation of a 3D printed object is achieved using additive processes. In an additive process an object is created by laying down successive layers of material until the object is created.
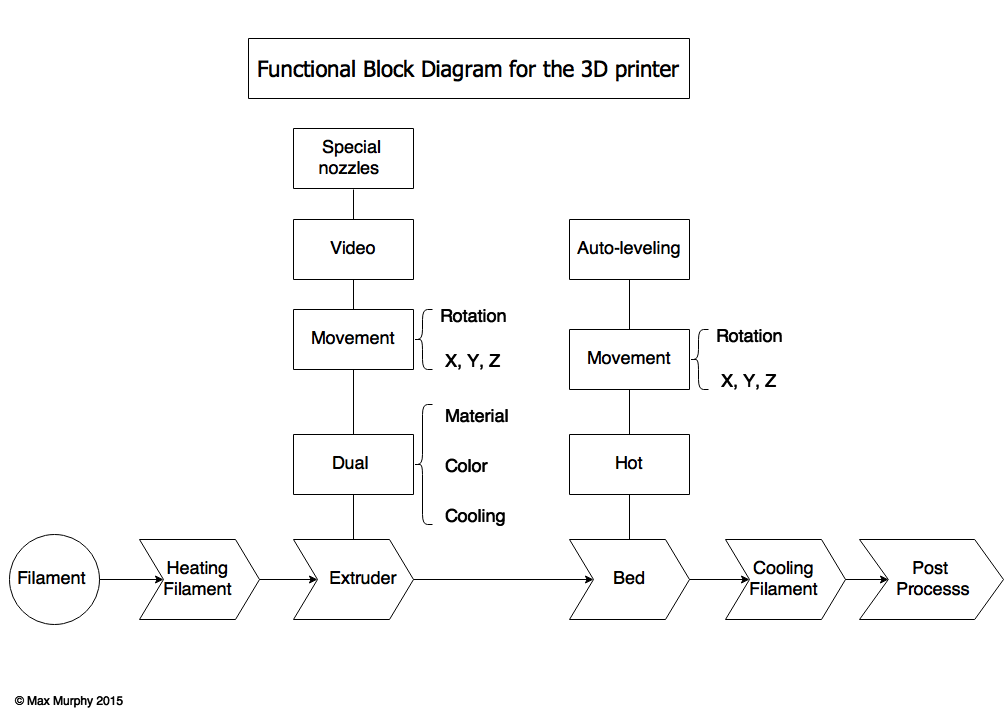
SKMurphy, Inc. 3D Printing Evolution Functional Block Diagram
This 3D Printing Evolution Functional Block Diagram shows the process flow of 3D printing in the X direction and the evolution of the functional blocks in the Y direction. Extruder Dual/Multi extruder The first improvement to the extruder, that several 3D printers have now, is the dual extruder capability.
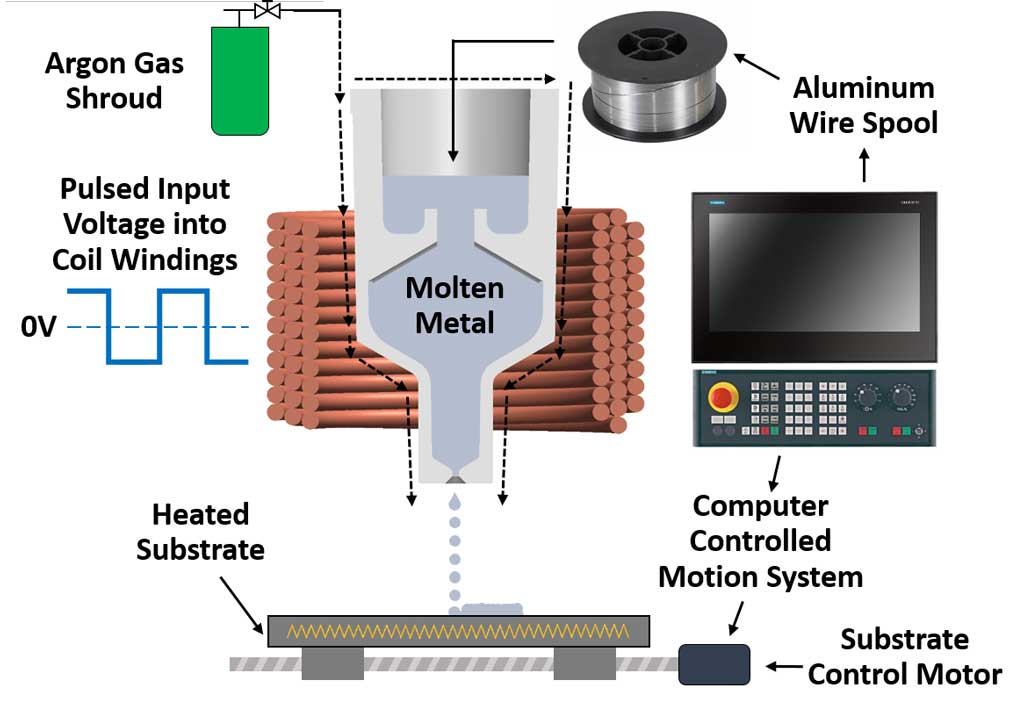
Liquid Metal 3D Printing Additive Manufacturing FLOW3D
Tinkercad is a free web app for 3D design, electronics, and coding, trusted by over 50 million people around the world. Build STEM confidence by bringing project-based learning to the classroom. Start Tinkering Join Class Free for everyone No downloads. No strings attached. Start creating from the first click. Start Tinkering › Learn by doing

Block diagram of the developed 3D printer. Download Scientific Diagram
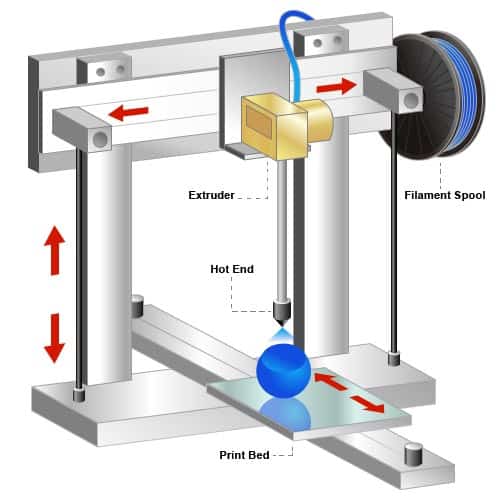
3D Printer Parts Section 1: Parts Directly Involved in Printing Process Extruder The 3D printer extruder is the central hub of the printing process, and covers both the cold end and the hot end. The extruder's cold end channels filament to the hot end, ensuring a smooth transition from solid to melted filament onto the print surface.

Introduction to SLA 3D Printing 3D Hubs
Beginner's Guide To 3D Printing. The aim of this guide is to teach you the fundamental concepts of how to 3D print, and provide you with the tools and resources you need to get started and make an informed choice about buying your first 3D printer. You will learn the basic history of 3D printing, the software that powers it, how the hardware.
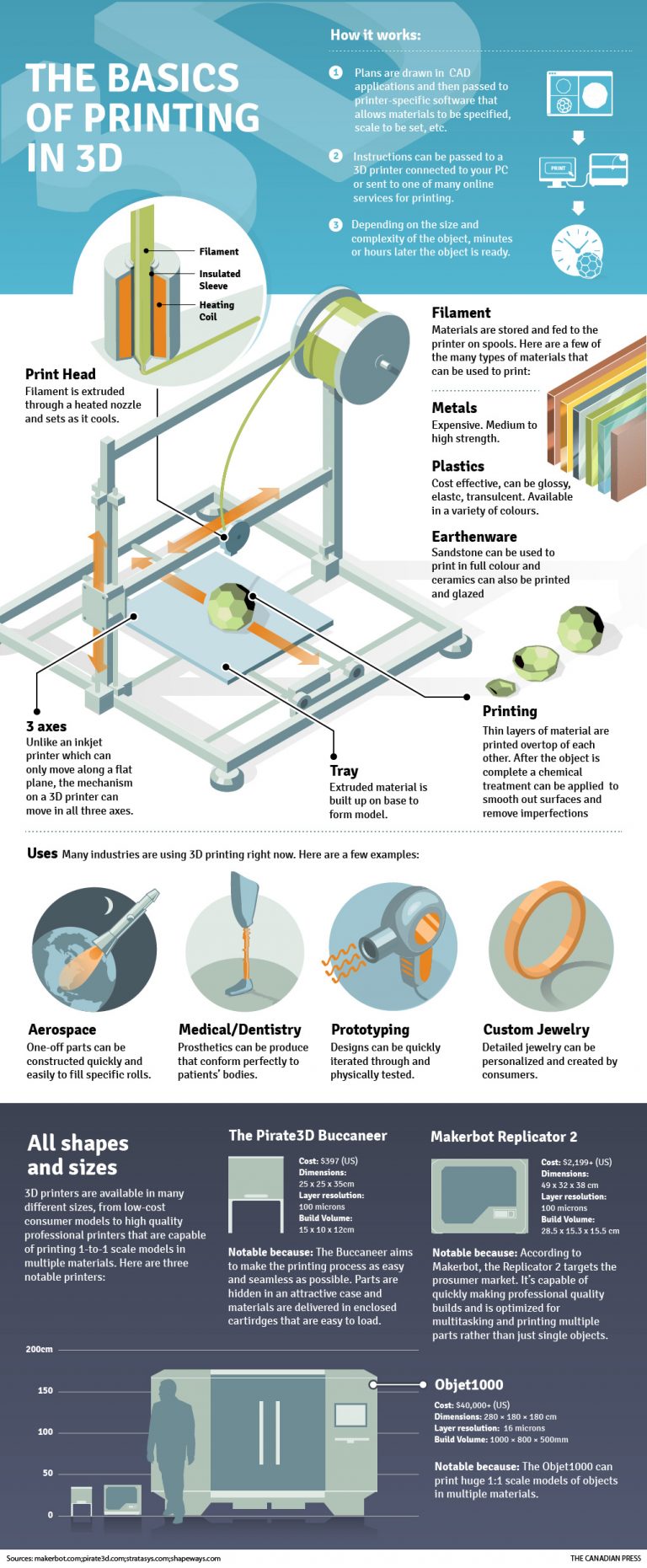
The Basics of 3D Printing {Infographic} Best Infographics
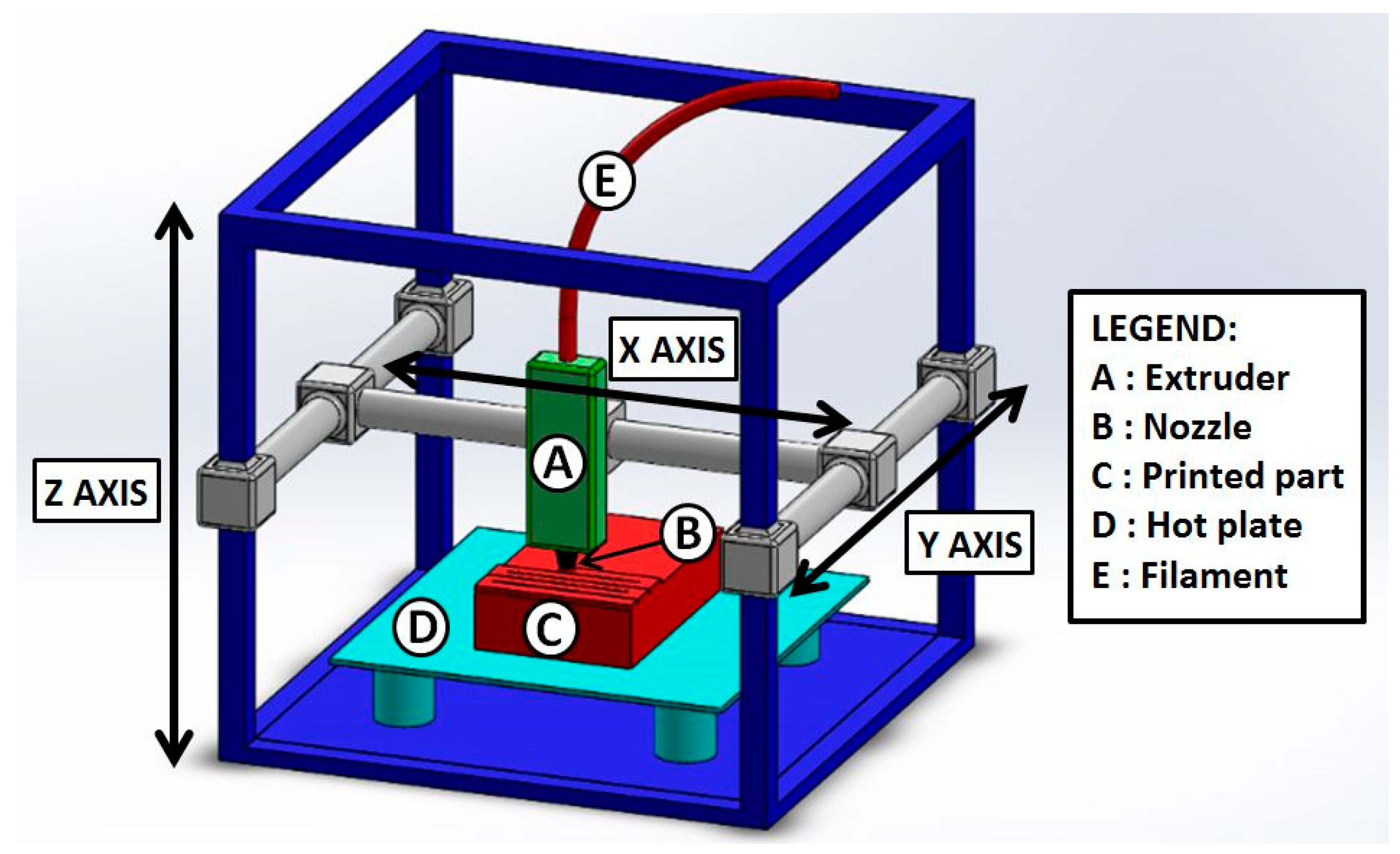
Updated Dec 16, 2023 A 3D printer must move in three-dimensional space to create 3D objects. Read on to learn all about how 3D printer axis systems work.
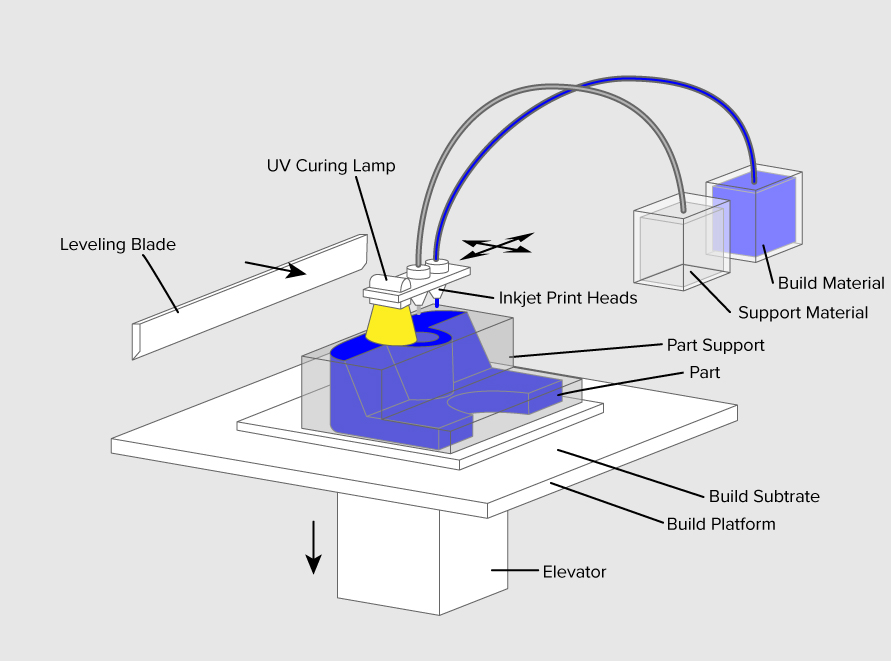
What is 3D printing? How does a 3D printer work? Learn 3D printing
The concept of 3D Printing was laid out by David E.H. Jones in 1974. However, methods and materials for fabricating models weren't developed until the early 1980s. The term '3D printing' covers numerous processes and techniques that offer a wide spectrum of capabilities for the production of parts and products in different materials.

Four 3D printing configurations. (a, b) SLA type 3D printer and DLP... Download Scientific Diagram
Stereolithography (SLA) 3D printing is the most common resin 3D printing process that has become vastly popular for its ability to produce high-accuracy, isotropic, and watertight prototypes and end-use parts in a range of advanced materials with fine features and smooth surface finish. In this comprehensive guide, learn how (SLA) resin 3D printers work, why thousands of professionals use this.
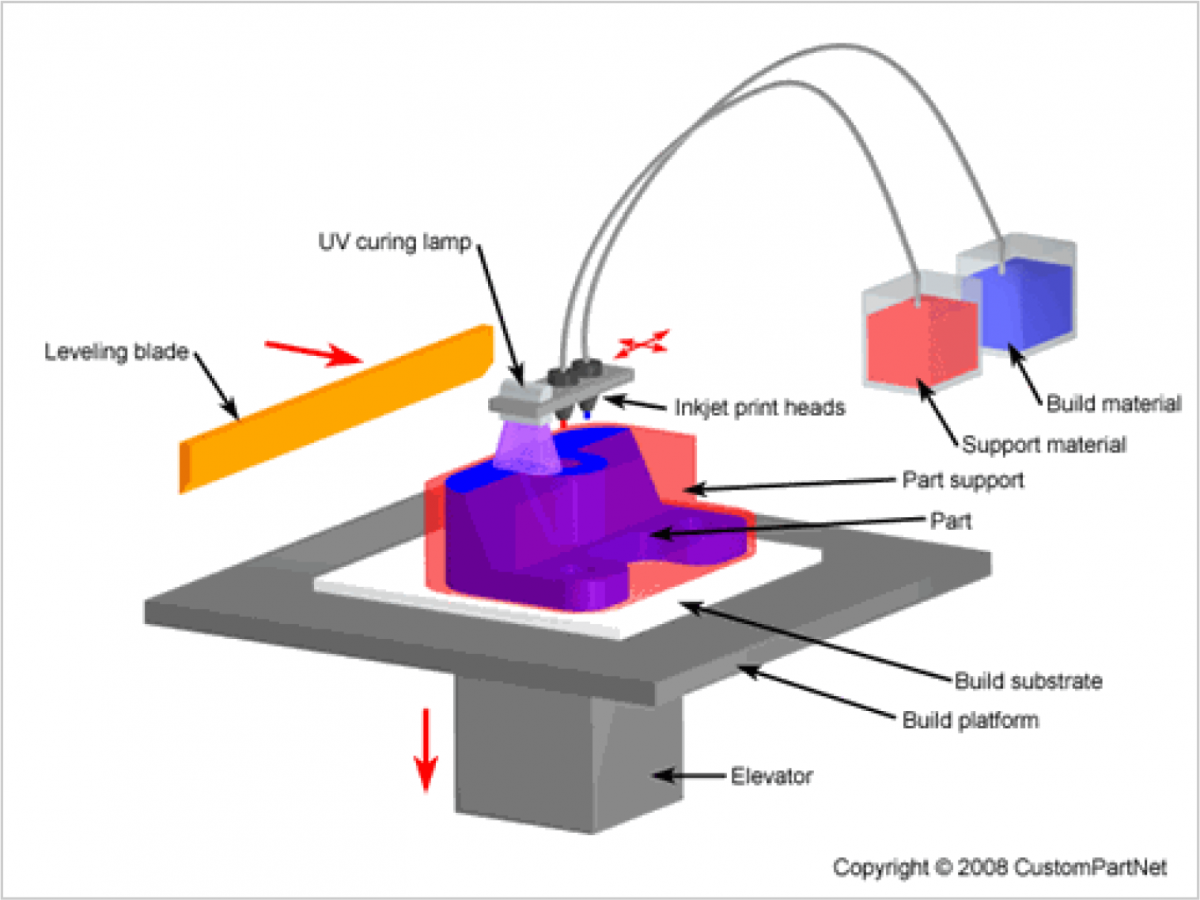
3D Printing Processes Material Jetting (Part 7/8)
3D printing is an additive technology used to manufacture parts. It is 'additive' in that it doesn't require a block of material or a mold to manufacture physical objects, it simply stacks and fuses layers of material. It's typically fast, with low fixed setup costs, and can create more complex geometries than 'traditional.
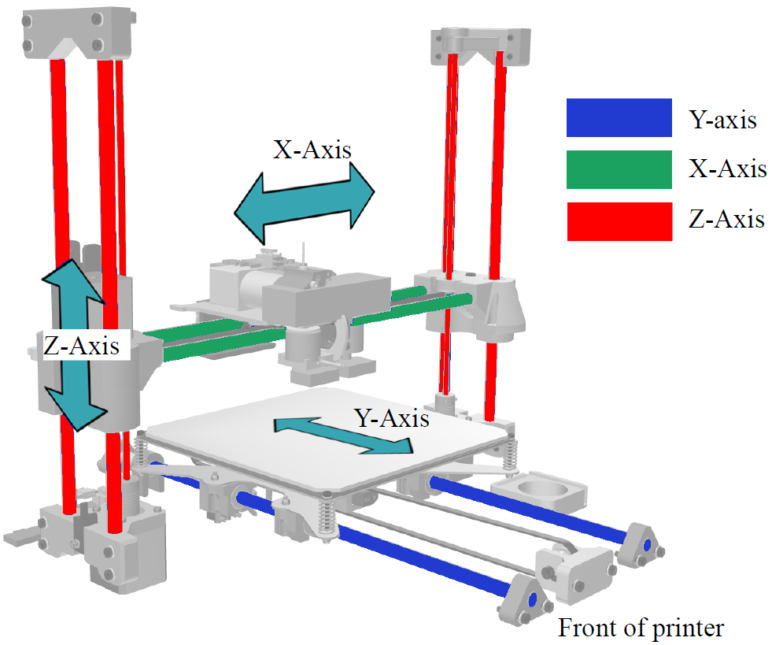
3D Printed Lithophanes Prototype Hubs
How exactly do they work? Let's take a closer look! Photo: 3D printing in action: this is the printhead of an Invent3D printer, slowly building up an object, layer by layer, by squirting molten blue plastic out of its precisely moving nozzle. Photo by Cpl. Justin Updegraff courtesy of US Marine Corps. Sponsored links Contents Medicine
3D Printing for Beginners 2014 ISt Blog
Tech Breakdown Open Source 3D Design Anatomy of a 3D Printer: How Does a 3D Printer Work? Get an understanding of how 3D printing works, from the inside and out. This guide will walk you through each of the critical components of a 3D Printer, answering the question: "How does a 3D printer work?" Posted on February 24, 2016 by Tyler Anderson

A schematic diagram of a 3D printer Download Scientific Diagram
FFF (Fused Filament Fabrication) is a 3D printing technology using PLA, ABS and other thermoplastic filaments, which will be heated and extruded by an extrusion head, and then stacked layer by layer under the control of a computer to finally construct a shaped three-dimensional model.