
Fosse craniche Medicina247
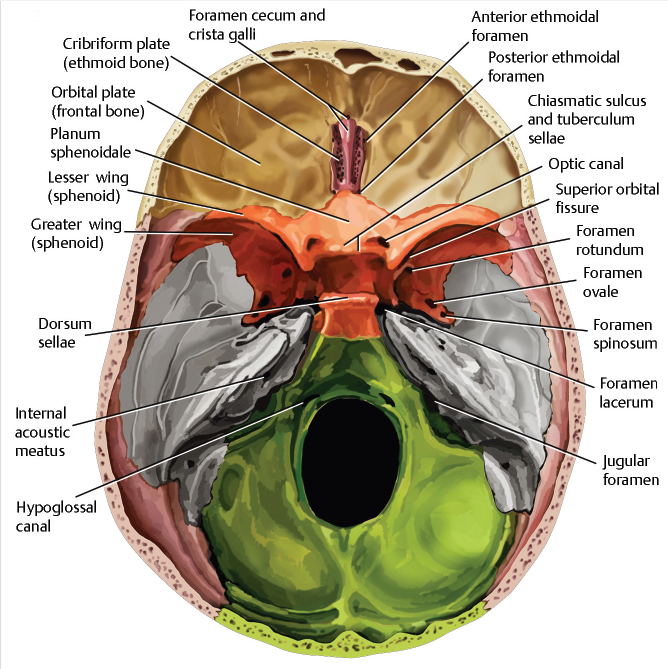
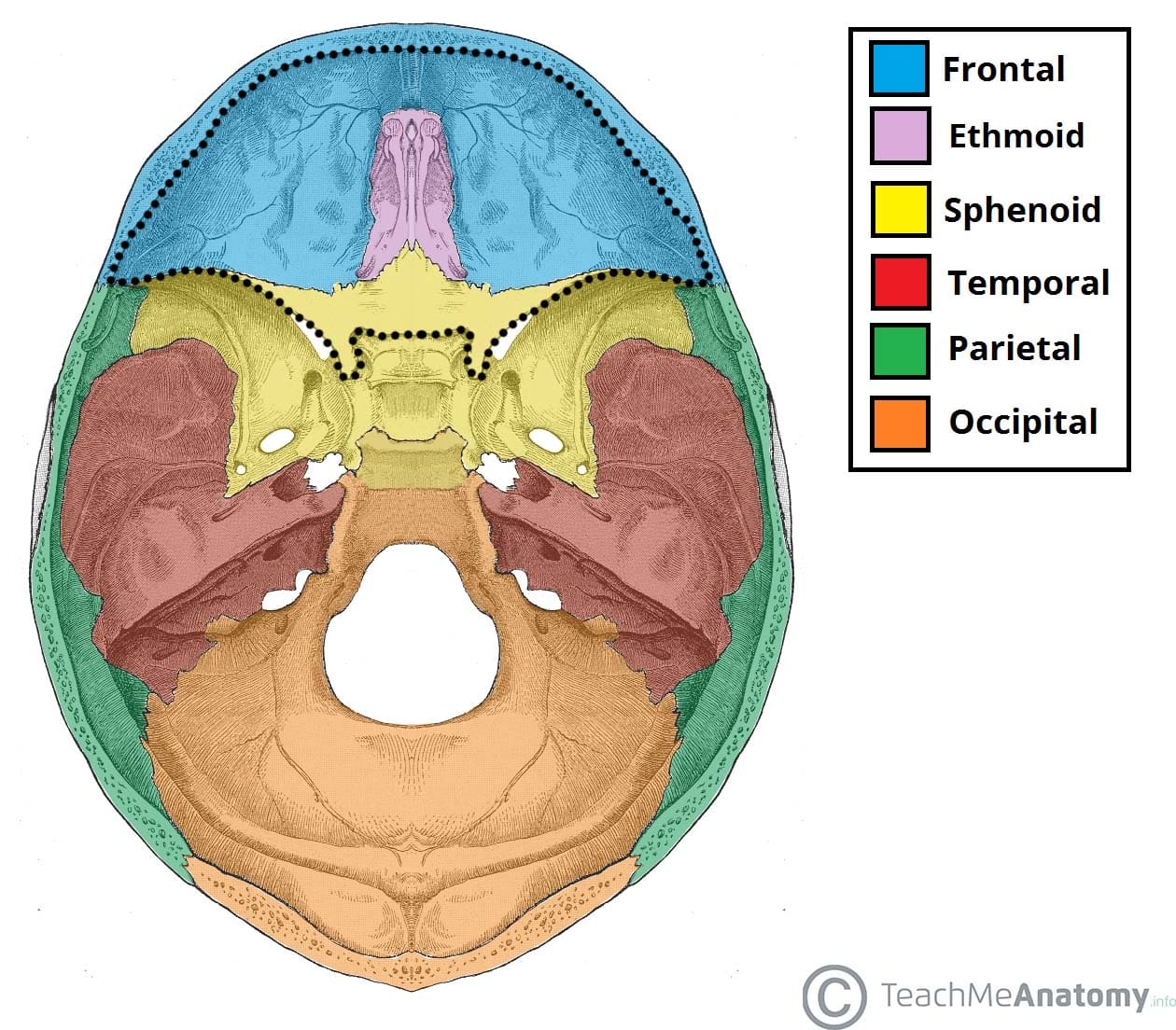
The anterior cranial fossa (Latin: fossa cranii anterior) lies at the highest level of the internal cranial base and is formed by the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone, orbital plate of the frontal bone, and lesser wings of the sphenoid. Anterior cranial fossa by Anatomy Next Borders of anterior cranial fossa

Skull Anatomy Geoffrey E. Reed life
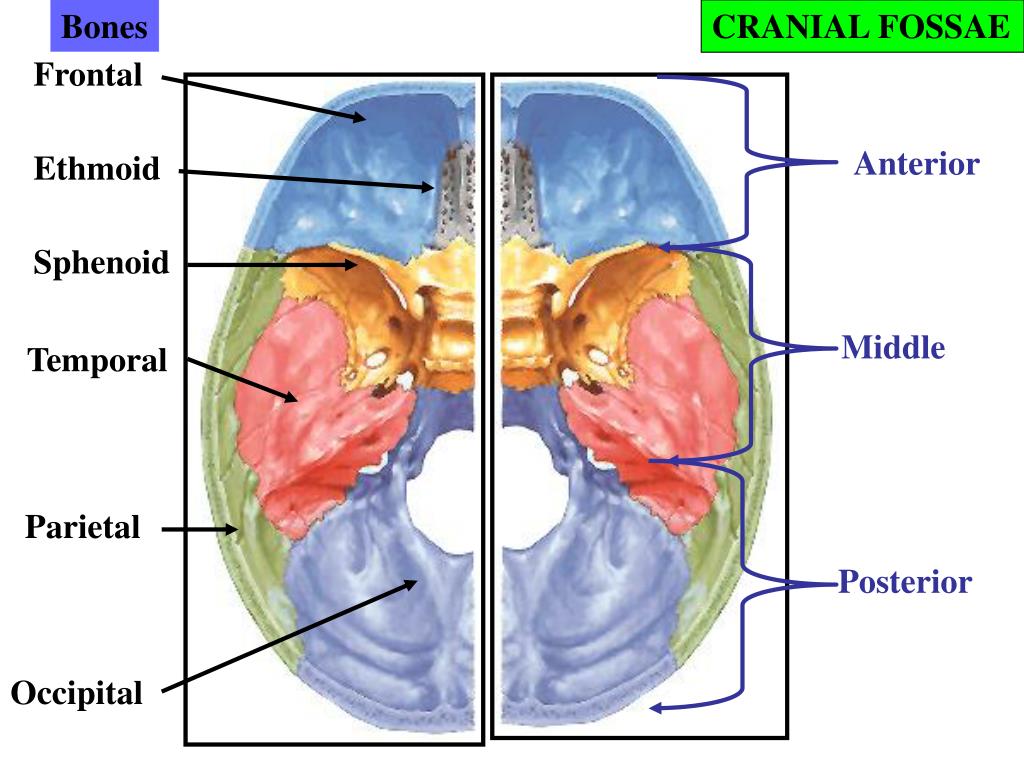
Top view. Calvaria is removed. The image demonstrates cerebral surfaces of bones of the skull that forms the anterior, middle, and posterior cranial fossas. The list of terms: The detailed view of the cranial base's inner surface with emphasis on openings and connections to other topographical areas of the skull.
Anterior Cranial Fossa, Nasal Cavity, and Paranasal Sinuses Radiology Key
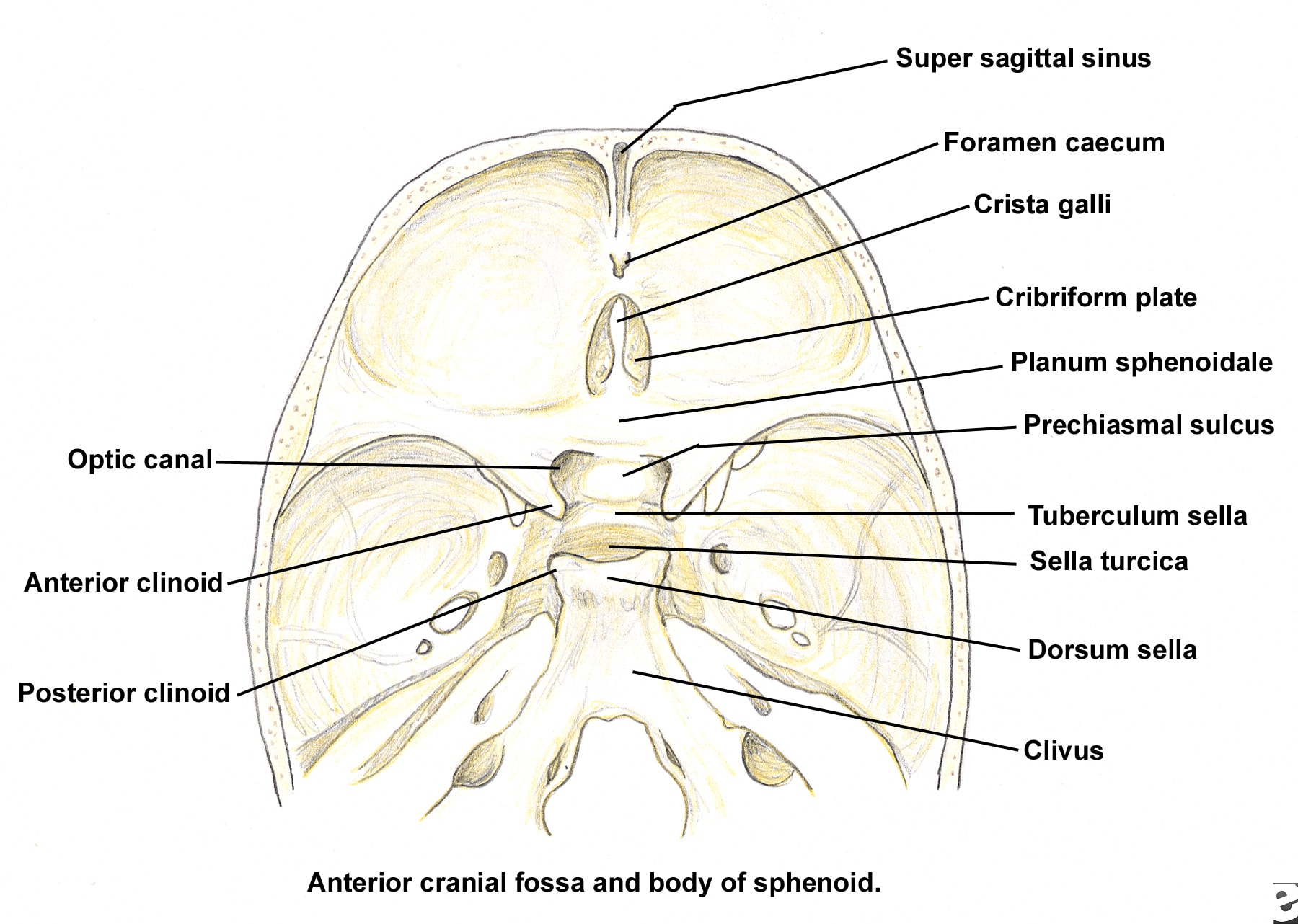
The anterior cranial fossa constitutes the floor of the cranial vault which houses the frontal lobes of the brain. Gross anatomy Structures present in the midline of the anterior cranial fossa from anterior to posterior are: groove for superior sagittal sinus groove for anterior meningeal vessels foramen cecum crista galli
Anterior Cranial Fossa Boundaries Contents TeachMeAnatomy
The anterior cranial fossa contains the following parts of the brain: frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex, olfactory bulb, olfactory tract, orbital gyri. [1] Openings There are several openings connecting the anterior cranial fossa with other parts of the skull, and these are the following: anterior ethmoidal foramen, cribriform foramina.
Anterior Cranial Fossa, Nasal Cavity, and Paranasal Sinuses Radiology Key
The middle cranial fossa consists of three bones - the sphenoid bone and the two temporal bones. Its boundaries are as follows: Anteriorly and laterally it is bounded by the lesser wings of the sphenoid bone. These are two triangular projections of bone that arise from the central sphenoid body.

Middle cranial fossa Encyclopedia Anatomy.app Learn anatomy 3D
Introduction Skull base fractures are of high importance in neurotrauma. They occur in 3.5 - 24% of head injuries and are often related to brain injury (in 50% of the cases). 70% of the skull base fractures occur in the anterior fossa, 20% in the middle central skull base and 5% in the middle and posterior fossa. Traumatic (CSF) leakage
Fossa cranii anterior
The authors report their results on patients showing anterior cranial fossa fractures; clinical data, surgical indications, and results are reported and critically analyzed. Methods From 1991 to 2010, 223 patients were admitted in our institution with diagnosis of anterior cranial fossa fracture. Fractures were classified as type A—fracture.

Anterior Cranial Fossa فرهنگ تفصیلی دندان پزشکی
📌 𝐅𝐨𝐥𝐥𝐨𝐰 𝐨𝐧 𝐈𝐧𝐬𝐭𝐚𝐠𝐫𝐚𝐦:- https://www.instagram.com/drgbhanuprakash📌𝗝𝗼𝗶𝗻 𝗢𝘂𝗿.
Fossa cranii anterior DocCheck Flexikon
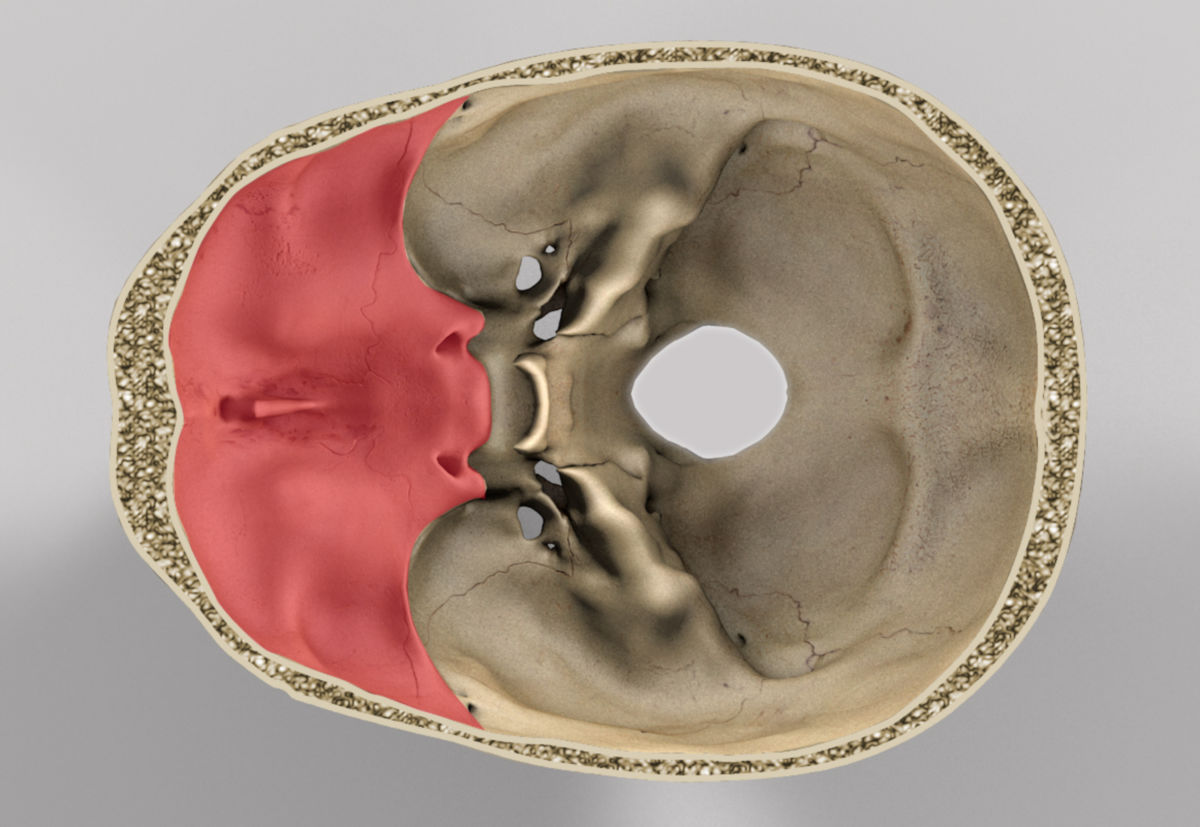
The anterior cranial fossa is a depression in the cranial base, which primarily supports the large frontal lobes of the cerebral hemispheres. However, in the center of the anterior cranial fossa are small depressions, the olfactory fossae, which support the olfactory bulbs (Figs. 2.1, 2.6, and 2.7).The bulbs represent the first part of the olfactory system within the brain itself.
PPT Cranial Cavity PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3995014
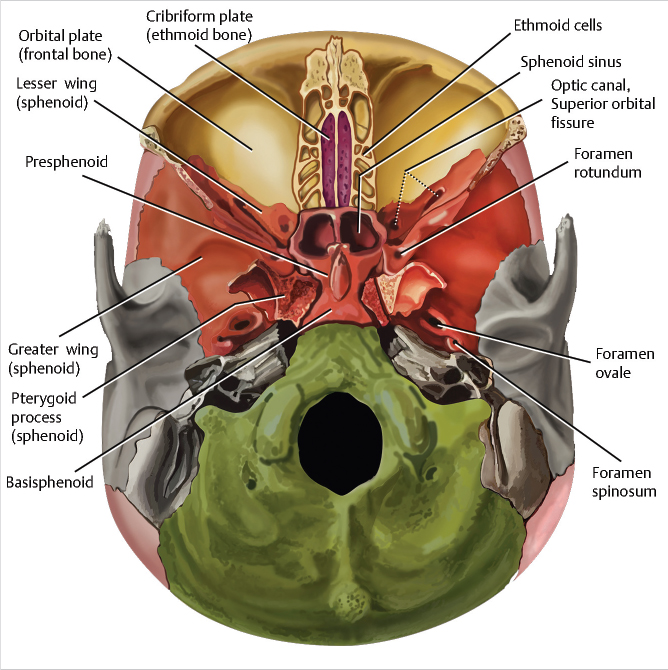
The anterior cranial fossa comprises a holey plate at the center, the so called cribriform plate (lamina cribrosa). The approximately 20 cribriform foramina serve as a passageway for the olfactory nerves to the olfactory mucosa in the nasal cavity.. Both the optic nerve and the ophthalmic artery pass through the optic canal which is centrally located on the sphenoid bone.
Anterior cranial fossa and body of the sphenoid.
The anterior cranial fossa is a depression in the floor of the cranial base which houses the projecting frontal lobes of the brain. It is formed by the orbital plates of the frontal, the cribriform plate of the ethmoid, and the small wings and front part of the body of the sphenoid; it is limited behind by the posterior borders of the small wings of the sphenoid and by the anterior margin of.

Skull Encyclopedia Anatomy.app Learn anatomy 3D models
Anterior cranial fossa - e-Anatomy - IMAIOS Human anatomy 2 Human body Parts of human body Regions of human body Musculoskeletal systems Skeletal system Axial skeleton Appendicular skeleton Bones Cranium Frontal aspect of cranium Superior aspect of cranium Occipital aspect of cranium Lateral aspect of cranium Inferior aspect of cranium Pericranium

Anterior Cranial Fossa Anatomy Tutorial YouTube
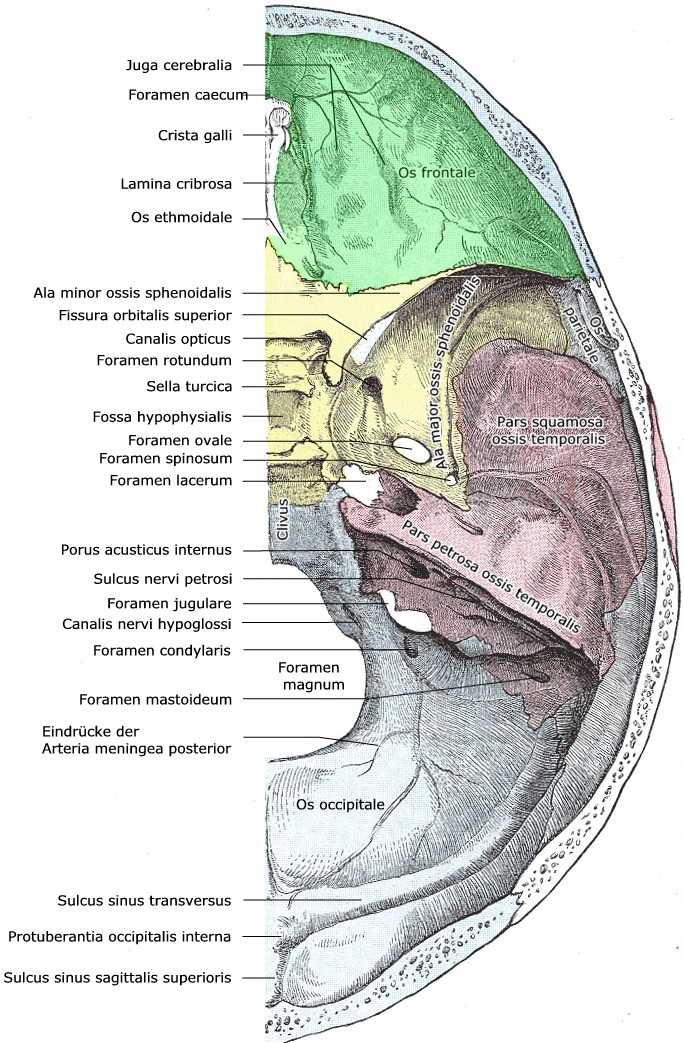
Definitions. The word foramen comes from the Latin word meaning "hole.". Essentially, all of the foramen (singular), or the foramina (plural of foramen), in the skull are holes. They are passageways through the bones of the skull that allow different structures of the nervous and circulatory system to enter and exit the skull.

Foramina and fissures of the skull Skull anatomy, Oral anatomy
Fossa cranii anterior 1/3 Synonyms: none The sella turcica is a saddle shaped cavity which is within the body of the sphenoid and contains the pituitary gland. Its name is from the 'Turkish saddle' which was used by soldiers during the times of the Ottoman Empire and was famous for having four corners.

Internal surface of the cranial base Medical anatomy, Human skeleton
The anterior cranial fossa is the most shallow and superior of the three cranial fossae. It lies superiorly over the nasal and orbital cavities. The fossa accommodates the anteroinferior portions of the frontal lobes of the brain. In this article, we shall look at the borders, contents and clinical correlations of the anterior cranial fossa.

Anatomy of Anterior cranial Fossa YouTube
The middle cranial fossa is formed by the sphenoid bones, and the temporal bones. It lodges the temporal lobes, and the pituitary gland. [1] [2] It is deeper than the anterior cranial fossa, is narrow medially and widens laterally to the sides of the skull. It is separated from the posterior cranial fossa by the clivus and the petrous crest .