
babylonian number system worksheet
The Babylonian Numerals - Astronomy and Base 60. The Babylonians developed a system for writing down numbers, using symbols for singles, tens, and hundreds, showing that they probably used a decimal system for everyday life. This system allowed them to handle large numbers comfortably and perform all of the major arithmetical functions.
Babylonian numerals converter seedmain
Updated on July 03, 2019 Babylonian mathematics used a sexagesimal (base 60) system that was so functional it remains in effect, albeit with some tweaks, in the 21 st century. Whenever people tell time or make reference to the degrees of a circle, they rely on the base 60 system. Base 10 or Base 60
Babylonian Numeration A MiniPrimary Source Project for Preservice
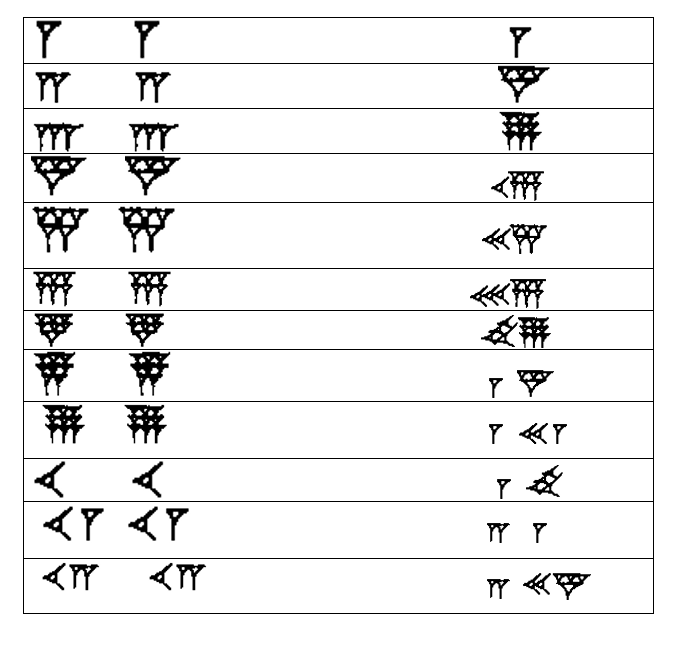
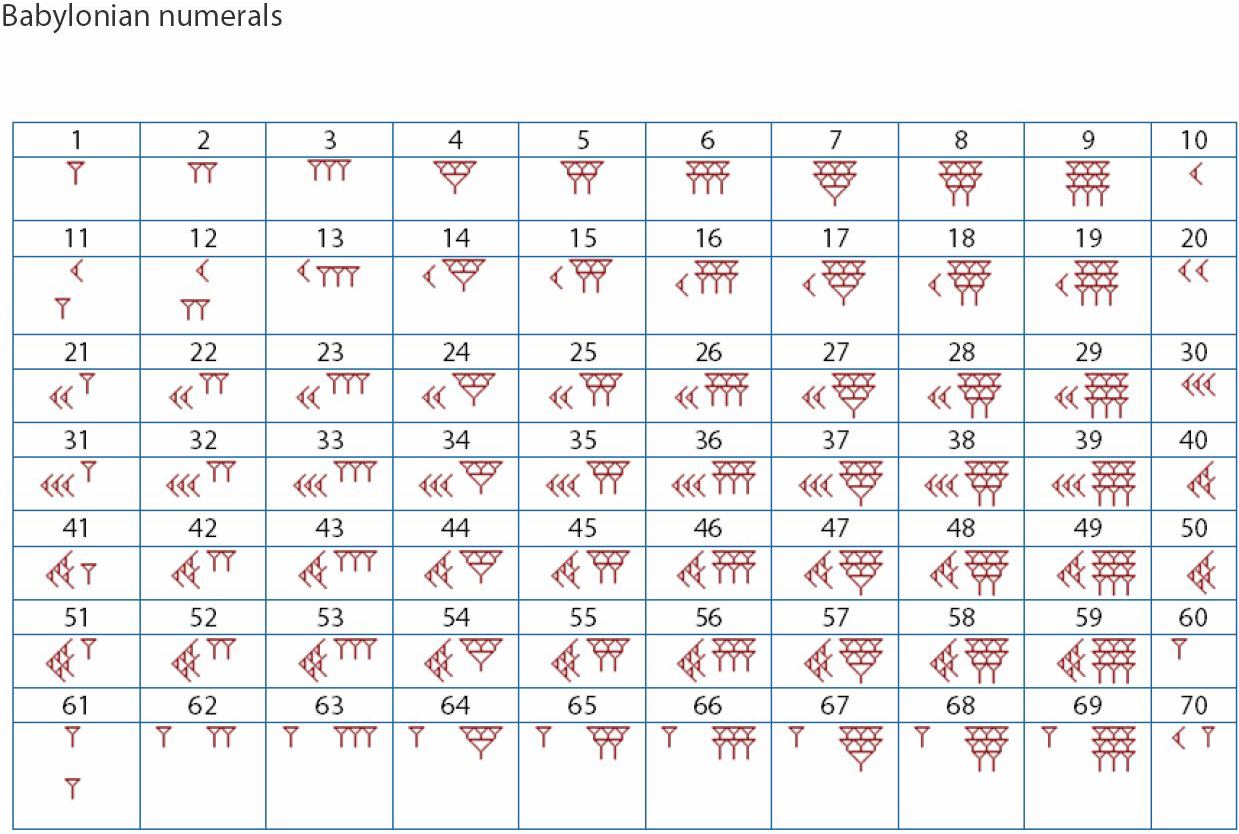
The complete list of the Babylonian numerals up to 59 is in Table 4.1. Table 4.1 Babylonian Numerals. You can see how Babylonians repeated the symbols to indicate multiples of a value. The number 6 is 6 of the symbol for 1 grouped together. The symbol for 30 is three of the symbols for 10 grouped together.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/plate018-56aab2fa5f9b58b7d008deb1.jpg)
Babylonian Mathematics Number Systems and Terms
Understand and Convert Babylonian Numerals to Hindu-Arabic Numerals. The Babylonians used a mix of an additive system of numbers and a positional system of numbers.An additive system is a number system where the value of repeated instances of a symbol is added the number of times the symbol appears.

Babylonian numerals YouTube
The Babylonian system is credited as being the first known positional numeral system, in which the value of a particular digit depends both on the digit itself and its position within the number. This was an extremely important development, because non-place-value systems require unique symbols to represent each power of a base (ten, one hundred, one thousand, and so forth), which can make.

Babylonian Numeration A MiniPrimary Source Project for Preservice
The Babylonians numerals are shown in Table 1. They were probably created using a stylus against a wet clay tablet. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33

Subtracting babylonian numerals nodelopez
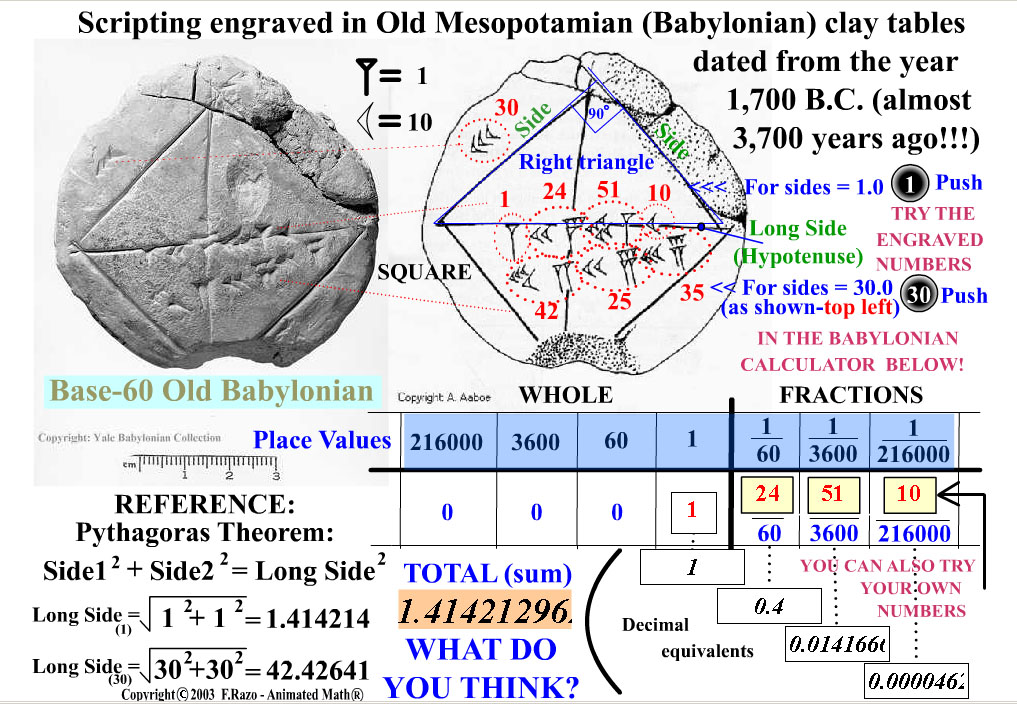
Babylonian Numbers Senkareh Table of Squares (Plate 18). Here is an example of Babylonian mathematics, written in cuneiform. With this table of squares you can see how to put Base 60 put into practice. http://www.gutenberg.org/files/16161/16161-h/16161-h.htm - The Seven Great Monarchies, G. Rawlinson Three Main Areas of Difference From Our Numbers
Ancient Numerals and Numbers History Dictionary
The Babylonian sexagesimal positional system places numbers with the same convention, so the right most position is for the units up to 59, the position one to the left is for 60 \times n 60×n where 1 ≤ n ≤ 59 1≤ n≤ 59, etc.

Bookish 2 Project Hail Mary Aditya Srinivasan
The Babylonian numeral system was described in Section 3 as 'remarkable'. It is worth spelling out the reasons for this judgement. Although what we notice first is that it was a place-value system (see Box 1), what is perhaps more striking is the coupling of this feature with a 'floating sexagesimal point'; that is, the lack of any.

"Babylonian Numerals" Spiral Notebook for Sale by coolmathposters
The Babylonian Number System. Perhaps the most widely known fact about Babylonian mathematics is that it used an artificial sexagesimal number system. That is, the place values corresponded to postive and negative powers of 60. For example, the number 4000 would be expressed as 1,6,40 = 1 x 60^2 + 6 x 60 + 40 x 1 in sexagesimal notation.
PPT Ancient Babylonian Science PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Babylonian numeration is a numbering system used by the ancient Babylonians/Sumerians in Mesopotamia to represent numbers. In mesopotamian/babylonian/sumerian number system, our current number system, called hindu-arabic (0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9) did not exist.

How to write numbers in babylonian cuneiform
Babylonian Numerals. A base-60, or sexagesimal, number system, used by the ancient Babylonians. See also Numeral, Sexagesimal Explore with Wolfram|Alpha. More things to try: golden ratio (1+e)/2; FT sinc t; References O'Connor, J. J. and Robertson, E. F. "Babylonian numerals."
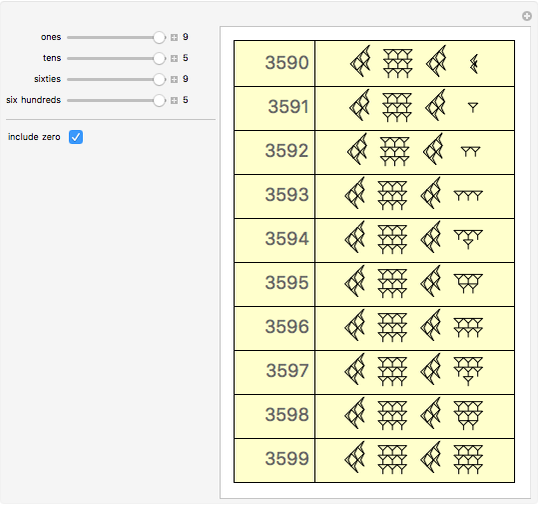
Babylonian Numerals Wolfram Demonstrations Project
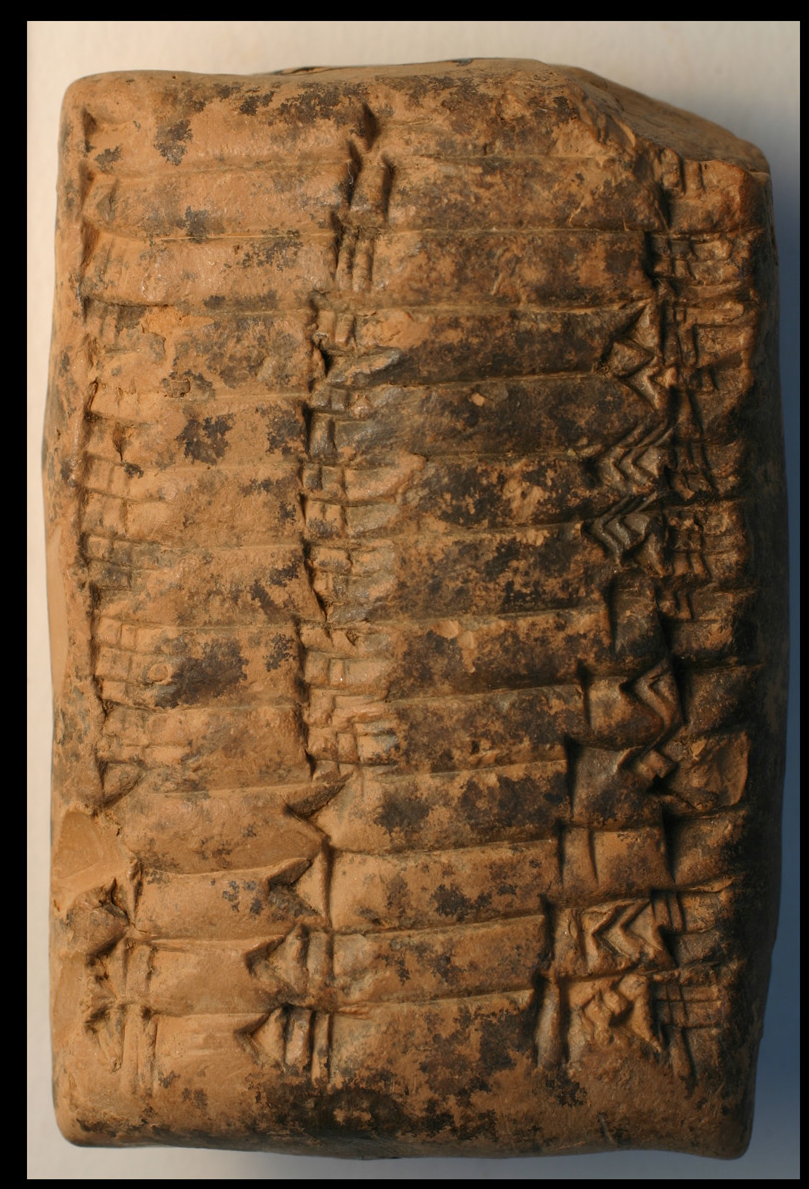
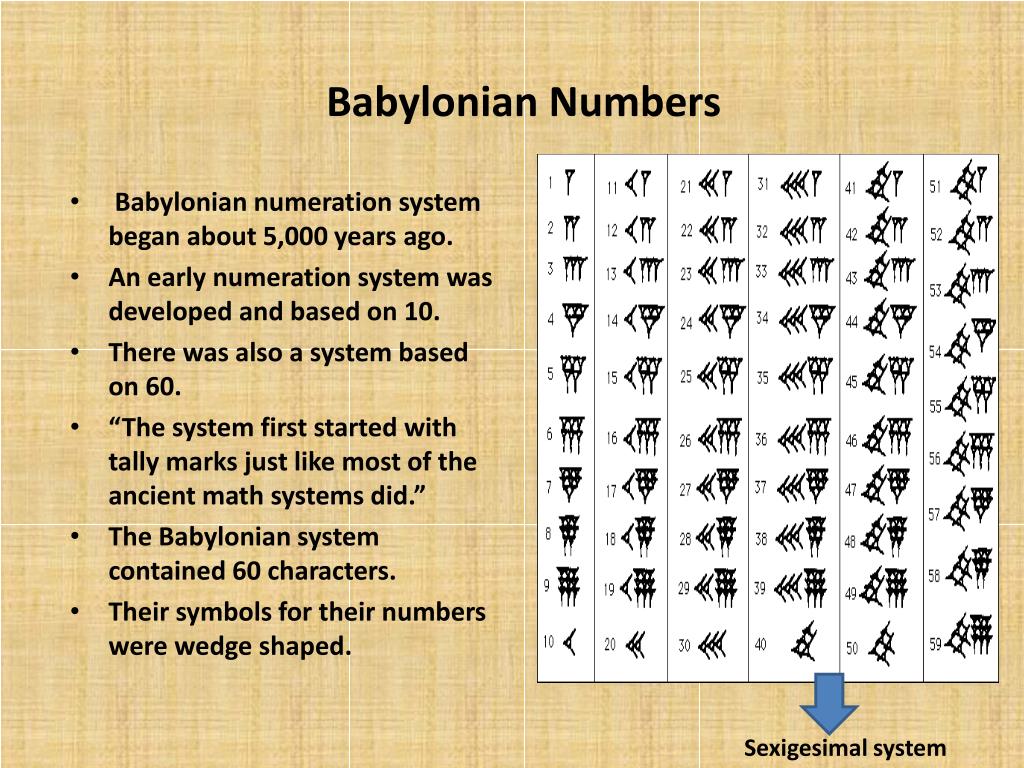
Babylonian cuneiform numerals Babylonian cuneiform numerals, also used in Assyria and Chaldea, were written in cuneiform, using a wedge-tipped reed stylus to print a mark on a soft clay tablet which would be exposed in the sun to harden to create a permanent record.
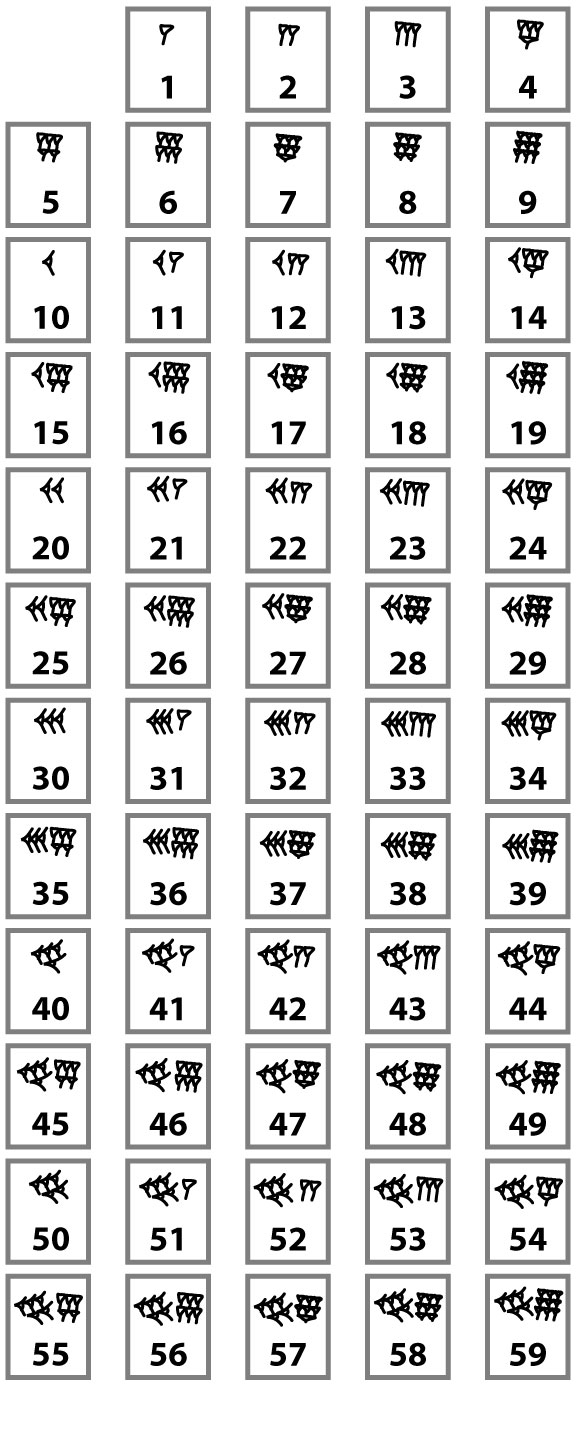
Babylonian Numbers mathMastery Blog
They give squares of the numbers up to 59 and cubes of the numbers up to 32. The table gives 8^ {2} = 1,4 82 = 1,4 which stands for 8^ {2} = 1, 4 = 1 \times 60 + 4 = 64 82 = 1,4 = 1×60+4= 64 and so on up to 59^ {2} = 58, 1 (= 58 \times 60 +1 = 3481) 592 = 58,1(= 58×60+1 = 3481). The Babylonians used the formula

"Babylonian Numerals" Poster by coolmathposters Redbubble
Babylonian mathematics is a range of numeric and more advanced mathematical practices in the ancient Near East, written in cuneiform script. Study has historically focused on the Old Babylonian period in the early second millennium BC due to the wealth of data available.
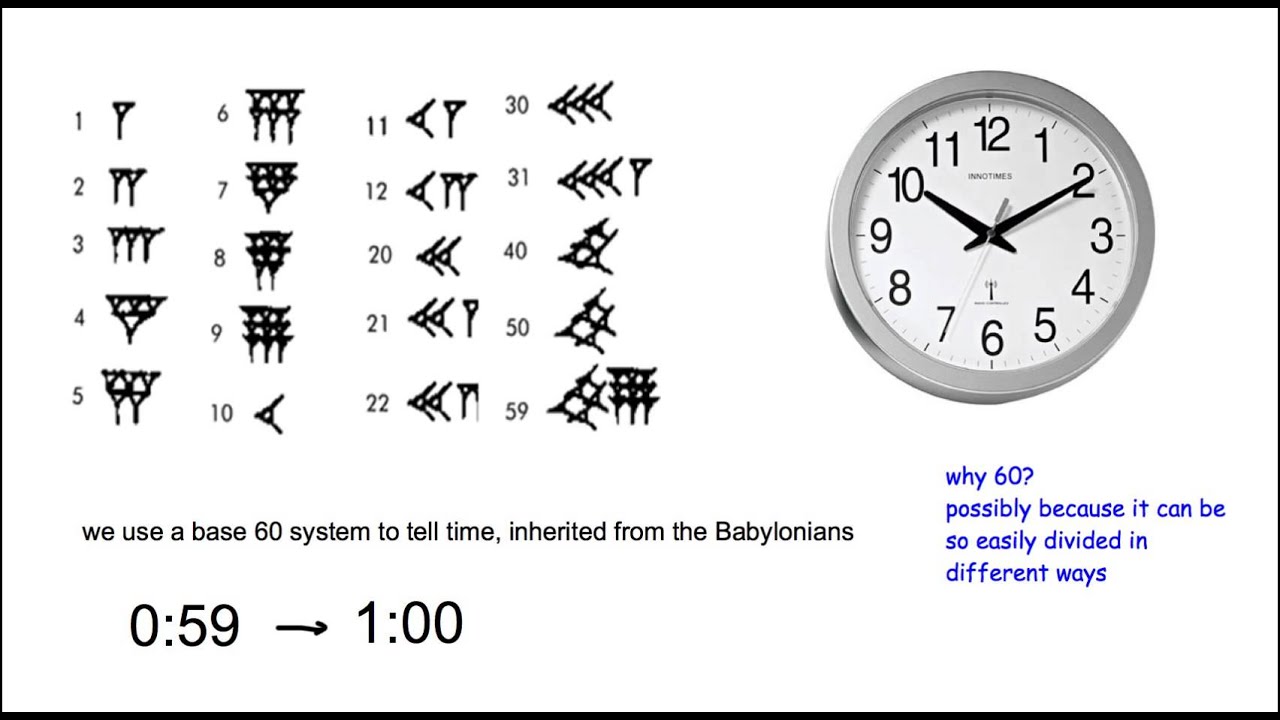
ancient babylonian numbers YouTube
Take a clay tablet and stylus in hand, and dive in with us on a journey in time to the four thousand years old civilization where it (almost) all began. Here you will learn about: Mesopotamian math; Babylonian numbers; and How to convert from decimal numbers to Babylonian, and vice-versa. And much more!