
AN ILLUSTRATED DICTIONARY Gods, Demons and Symbols of Ancient Mesopotamia Ancient mesopotamia
Mesopotamia was an ancient civilization positioned between the Tigris River and the Euphrates River. Today, this area is known as Iraq.The Mesopotamian core mythology was a mixture of magic and entertainment, with words of wisdom, praise for individual heroes or kings, and magical tales.Scholars believe that the first writing of Mesopotamian myths and epics were mnemonic aids to help the.

Mesopotamian deities could also be represented by symbols or emblems. Some divine symbols, such
Mesopotamia (from the Greek, meaning 'between two rivers') was an ancient region located in the eastern Mediterranean bounded in the northeast by the Zagros Mountains and in the southeast by the Arabian Plateau, corresponding to modern-day Iraq and parts of Iran, Syria, Kuwait, and Turkey and known as the Fertile Crescent and the cradle of civilization.

The tree of life, omphalos and Nimrud « Cradle of Civilization Ancient sumerian, Sumerian
Lilith Sculpture was used to adorn temples and promote worship of local deities in each city-state of Sumer. A popular Mesopotamian sculpture features a goddess is depicted as a beautiful, winged woman with bird's talons. She holds the sacred rod-and-ring symbol and wears a horned headdress.
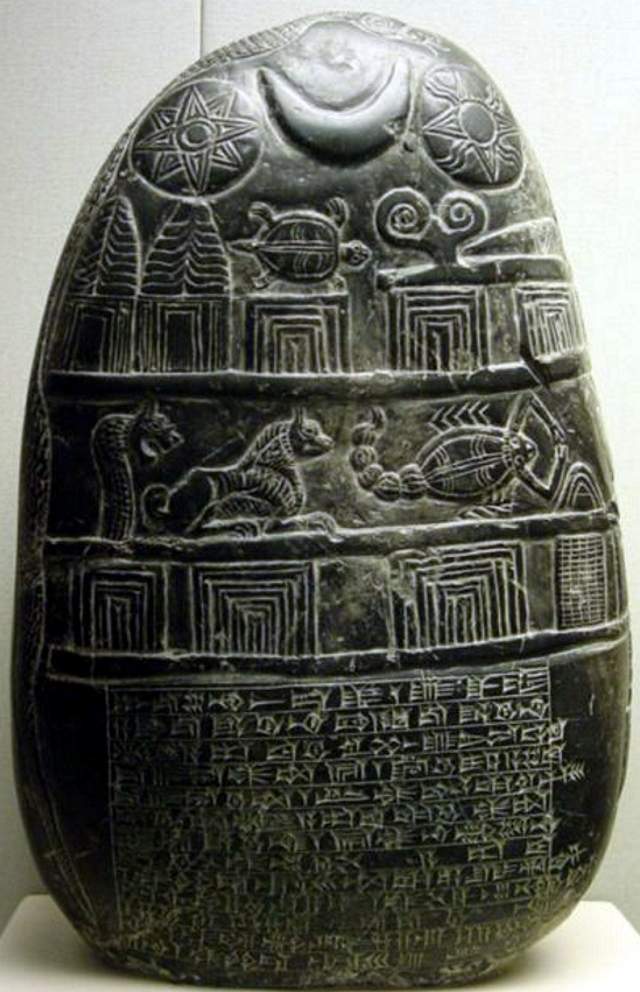

The Deities of Ancient Mesopotamia, an overview e n e n u r u
ripheral Mesopotamia. While a shen visual and symbolic parallel is possible, however, the meaning behind the Mesopotamian rod and ring would have already been in place centu-ries before the existence of the Alalakh seal. 11. Jean Chevalier and Alain Gheerbrant, A Dictionary of Symbols, trans. John

Related image Symboles anciens, Histoire du monde, Mésopotamie
Other meanings might well have been Mesopotamia, it has often been interpreted in isolation. A associated with function, both of the vessel and the way it range of interpretations have been put forward for different was used, and were possibly reinforced by variables such examples.. explicit meanings could be the world. 18. Understanding.

Writing Sumerian, Cuneiform, Pictographs Britannica
Animals were ubiquitous in Mesopotamian art, symbolizing the power of kings and gods, offering protection from enemies, or working for humans pulling plows in the fields or chariots into wars. Mar 16, 2023 • By Daniella Garran, PGCert Archaeology & Heritage, MA Education, BA Art History

The Deities of Ancient Mesopotamia, an overview e n e n u r u
― Leonardo da Vinci Mesopotamian symbols and meanings that remind us of creativity, wisdom, respect, courage, unity, and solidarity are hidden in world's earliest cities, and the place where writing was invented. For exploring more, please visit our "Mesopotamia: The Cradle of Civilizations" blog post.
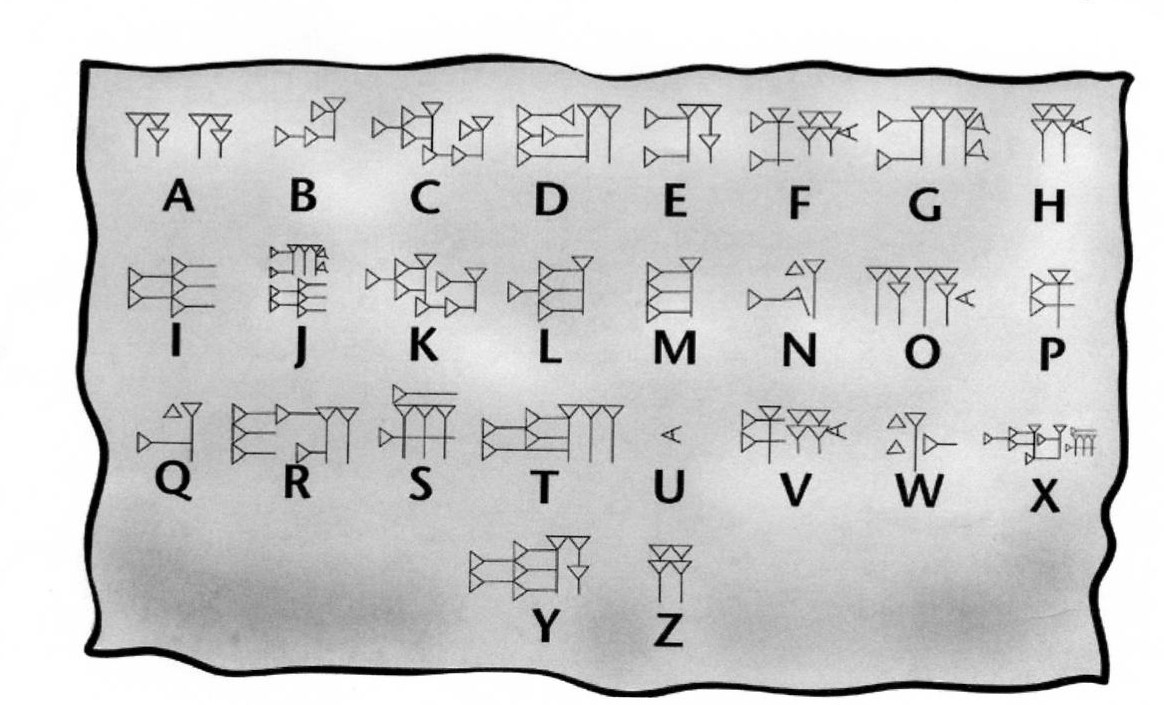
ALL MESOPOTAMIA — Cuneiform alphabets
Ancient Middle East Mesopotamia Mesopotamia By: History.com Editors Updated: April 24, 2023 | Original: November 30, 2017 copy page link Prisma/UIG/Getty Images Mesopotamia is a region of.

7 Most Important Mesopotamian Gods
Century B.C. Inanna was known as the goddess of " love, procreation, and war ." Sometimes she has a quiver and a bow for weapons, as well as a lion escort. Her place in Mesopotamian mythology is complete with a story of her descent into the underworld.

Pin by Galina Oxiouta on Anunnaki And WhoElse Bloodline Ancient symbols, Ancient aliens
Sumerian is the first known written language. Its script, called cuneiform, meaning wedge-shaped. The Cuneiform script is one of the earliest known forms of written expression.
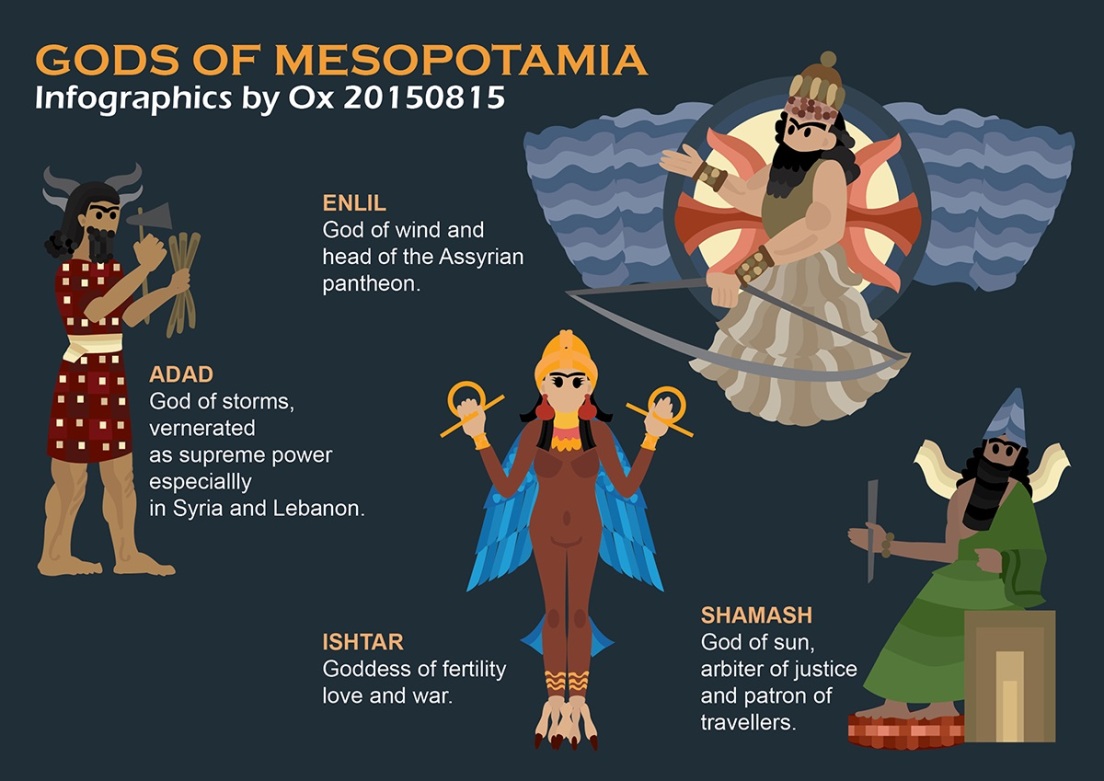
Infographics Gods of Mesopotamia
Early Imagery Nude female figurines are among the earliest artifacts to which a religious significance can be attached. Among the prehistoric figurines of Mesopotamia are the tall, thin, clay "lizard" figures with elongated heads, coffee-bean eyes, slit mouths, and clay pellets decorating the shoulders.

The Mythical Lamassu Impressive Symbols for Mesopotamian Protection Ancient mesopotamia
Mesopotamian mythology, the myths, epics, hymns, lamentations, penitential psalms, incantations, wisdom literature, and handbooks dealing with rituals and omens of ancient Mesopotamia.. A brief treatment of Mesopotamian mythology follows. For full treatment, see Mesopotamian religion. The literature that has survived from Mesopotamia was written primarily on stone or clay tablets.

Black Symbols Mesopotamia HighRes Vector Graphic Getty Images
Symbols representing animals, plants, celestial bodies, and natural phenomena played a significant role in their religious beliefs and rituals. 3) Religious Significance: Religion played a central role in ancient Mesopotamian society. Symbolism was heavily intertwined with religious practices and beliefs.

Pin by MASTER THERION on Symbols Sumerian, Ancient writing, Ancient sumerian
This script is known as the cuneiform which is a combination of two Latin words meaning wedge and shape. This pictorial script over a period of time eventually developed in the first of alphabets. In Sumer all the writing was done by pictorial representation.

Mesopotamia Sumer Inanna Star Of Ishtar Symbol, PNG, 768x768px, Mesopotamia, Akkadian, Area
The Cross (Garza) The next symbol is one that everyone probably already knows, though the meaning tends to change depending on the culture. The Sumerian cross is one of the earliest and most popular symbols of the modern day, but most people have no idea that it has its roots in Mesopotamian culture.

Reckoning before writing Ancient writing, Ancient mesopotamia, Ancient alphabets
Mesopotamian Religion was central to the people's lives. Humans were created as co-laborers with their gods to hold off the forces of chaos and to keep the world running smoothly. As in ancient Egypt, the gods were honored daily for providing humanity with life and sustenance, and people were expected to give back through works that honored the.