Bat ear diagram [IMAGE] EurekAlert! Science News Releases
A new paper in Nature is the world's first study to compare the inner ear structures of the two main groups of bats. By examining the microscopic inner ears of bats from 19 of the 21 known bat.

Bat Anatomy Worksheet for 4th 5th Grade Lesson
CT scans of the bats' brains revealed huge differences in these tiny structures. The yin bats' ears were a lot like ours, including a thick bony canal wall packed with nerve endings to protect the.

Bat Anatomy Stock Image C024/4377 Science Photo Library
The ears and brain cells in bats are especially tuned to the frequencies of the sounds they emit and the echoes that result. A concentration of receptor cells in their inner ear makes bats.

The general anatomy of a bat. Download Scientific Diagram
Other animals. The tragus is a key feature in many bat species. As a piece of skin in front of the ear canal, it plays an important role in directing sounds into the ear for prey location and navigation via echolocation. Because the tragus tends to be prominent in bats, it is an important feature in identifying bat species. The tragus allows echolocating bat species to vertically discriminate.
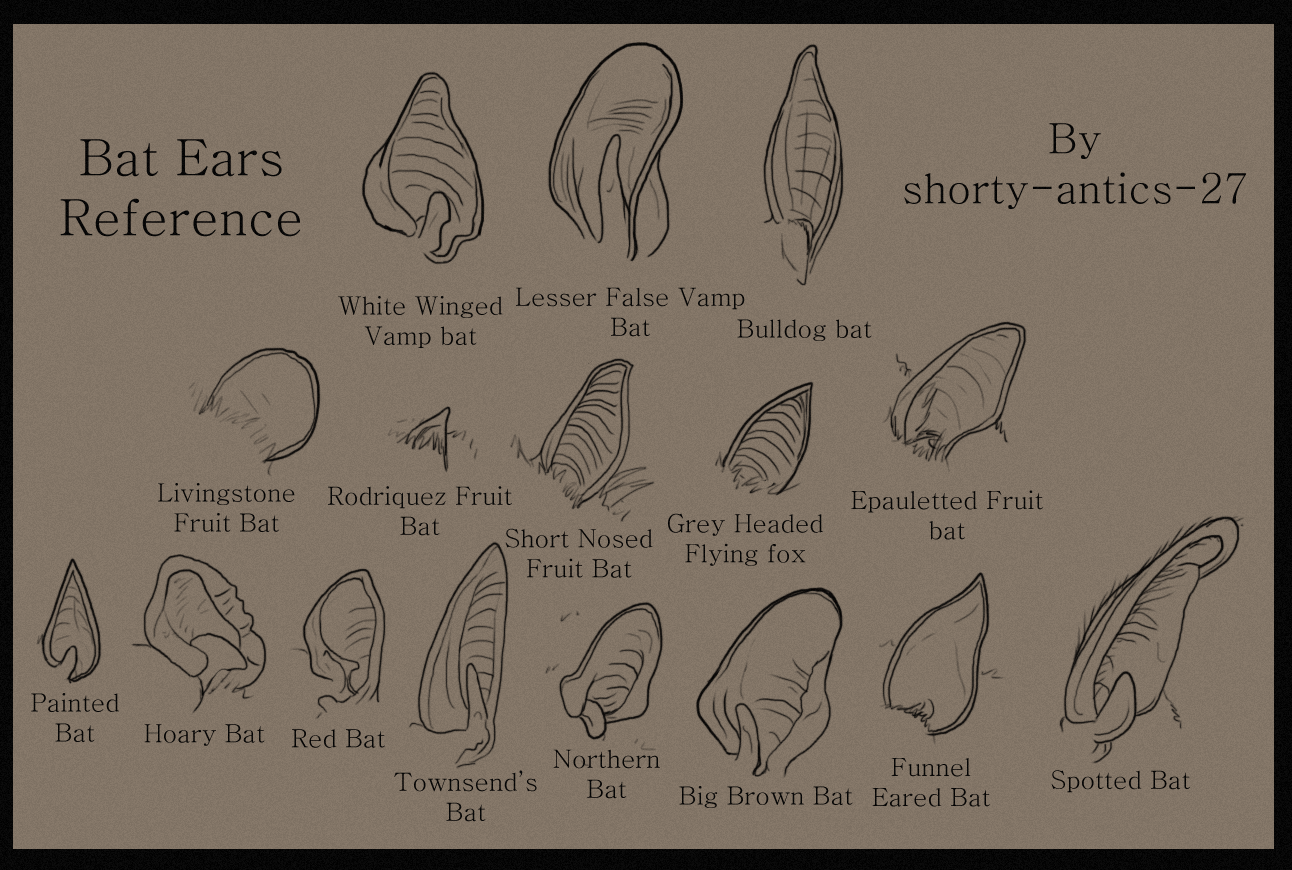
Bat Ear Reference by shortyantics27 on DeviantArt
The little brown bat ( Myotis lucifugus) is one of a group of bats with ear anatomy unlike almost all other mammals, scientists have learned. Michael Durham/Minden Pictures. Bats use sound to hunt a dizzying array of prey. Some zero in on flowers to sip nectar, whereas others find cattle and suck their blood. Many nab insects midflight.
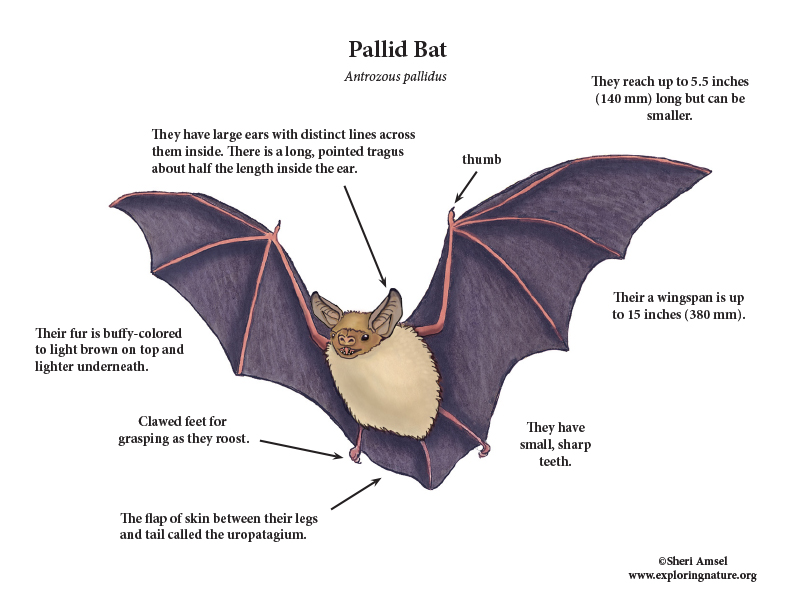
Bat Anatomy
A new article compares the inner ear structures of the two main groups of bats. By examining the microscopic inner ears of bats from 19 of the 21 known bat families, the researchers were able to.

Anatomy of a Bat Free Get Brainy Box
Echolocation also provides evidence of bats' evolutionary history, as portrayed by their family tree. Writing in Nature, Sulser et al. 1 present neuroanatomical evidence from an examination of.
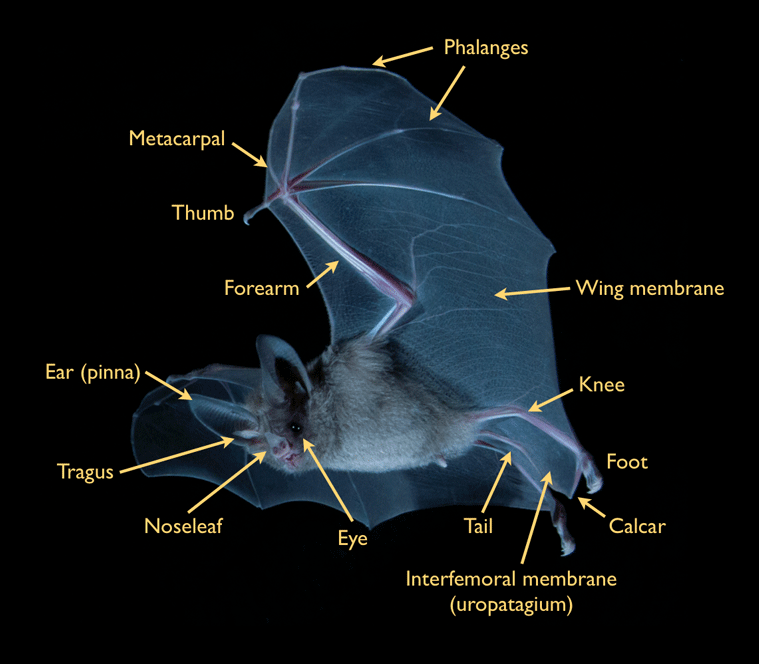
anatomy of bat
The inner ear of bats consists of a snail-shaped tube, known as the cochlea, that is lined with sensory hair cells and is filled with fluid.. The researchers are interested in continuing their studies on the evolution of bat echolocation by comparing the anatomy involved in hearing echoed sounds among bats and other mammals. "There is this.
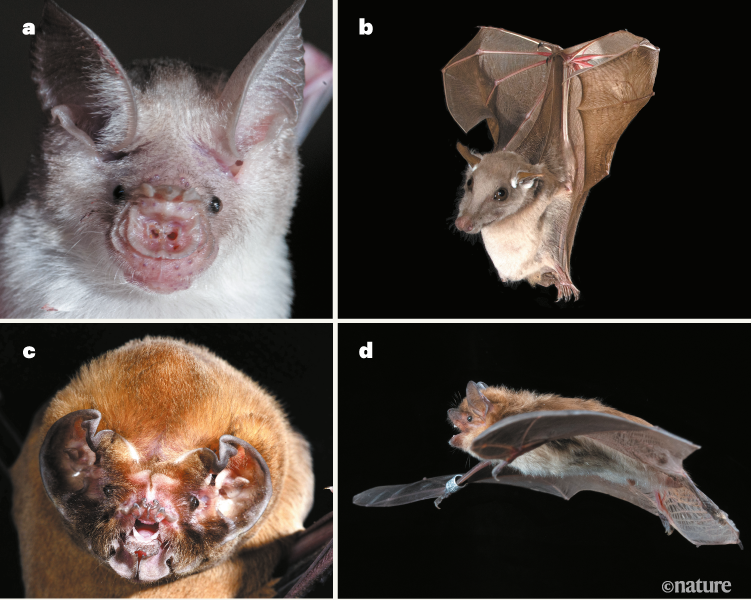
Ear anatomy traces a family tree for bats
Phylogenomics of bats suggests that their echolocation either evolved separately in the bat suborders Yinpterochiroptera and Yangochiroptera, or had a single origin in bat ancestors and was later lost in some yinpterochiropterans 1-6.Hearing for echolocation behaviour depends on the inner ear, of which the spiral ganglion is an essential structure.

Inner Ear Drawing at GetDrawings Free download
Anatomy and physiology Skull and dentition A preserved megabat showing how the skeleton fits inside its skin. The head and teeth shape of bats can vary by species.. Six species have been recorded to live over thirty years in the wild: the brown long-eared bat (Plecotus auritus), the little brown bat (Myotis lucifugus),.

Animal drawings, Animals, Animal illustration
Abstract. The first steps in frequency analysis by the mammalian auditory system are performed in the cochlea. Hair cells are tuned to a restricted frequency range and the orderly pattern of frequency representation found at all levels of the ascending auditory pathway is laid out in the frequency place code along basilar membrane (BM) length.

Image result for bat anatomy Bat anatomy, Scientific illustration, Animal sketches
January: Ear anatomy traces a family tree for bats. Bats were previously classified into one of two suborders — Megachiroptera and Microchiroptera. But a study published in 2000 used DNA.

Bat's Ears and Nose Infogram
Bats are mammals belonging to the order Chiroptera, a name of Greek origin meaning "hand-wing," which accurately describes the animal's most unusual anatomical feature.. Also, recognition of mothers and babies involves both audible and ultrasonic sound. The bat's ear is extremely mobile and sensitive to sound. The tragus, a lobe projecting.
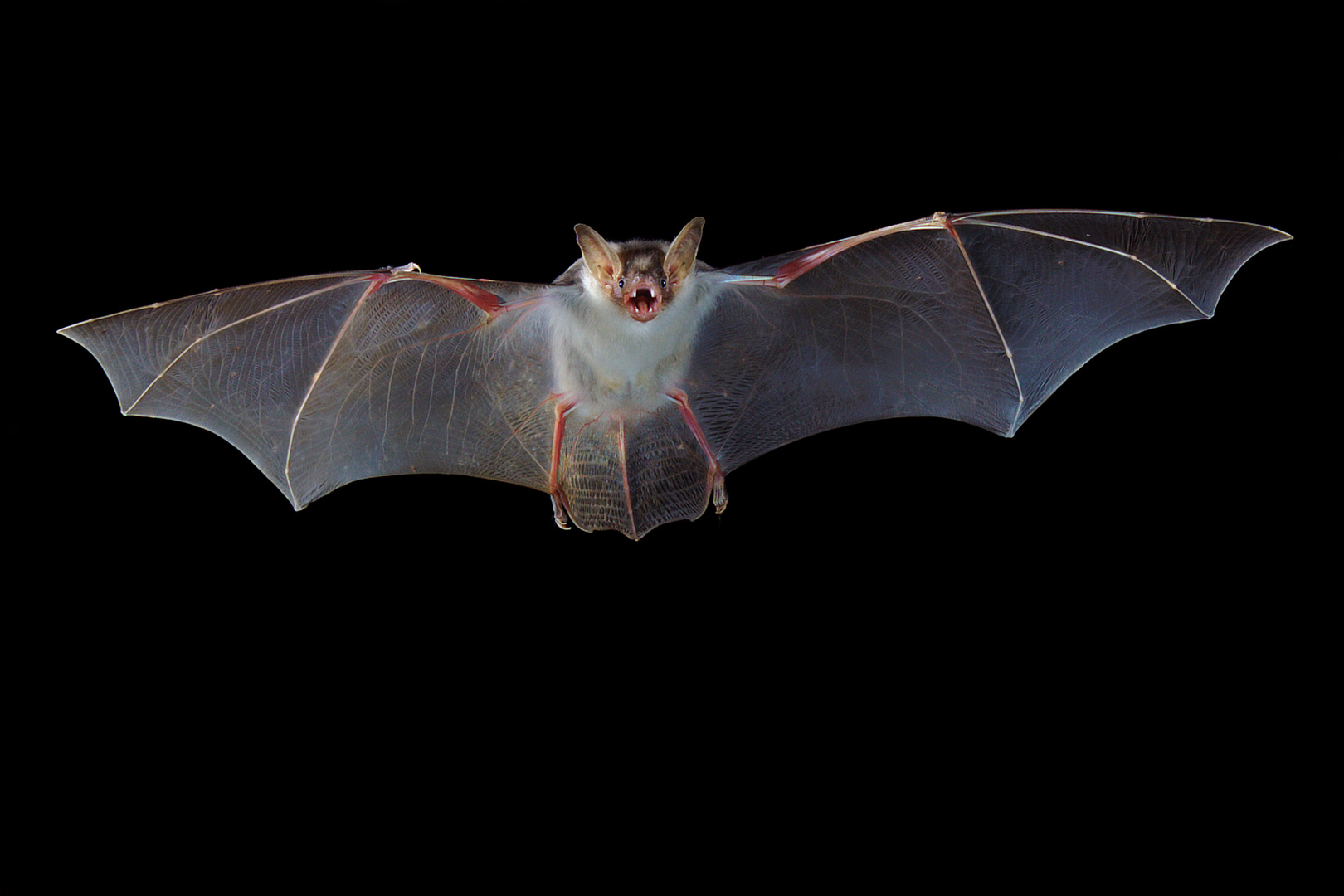

Bat Anatomy Foto & Bild tiere, wildlife, säugetiere Bilder auf
"This is the first time we found different neuroanatomies in the inner ear, which give these bats different ways of processing the echolocating signal.". PhD, Professor of Organismal Biology and Anatomy at UChicago and senior author of the new study. He found that the inner ear ganglion, a major structure of neurons that connects the.

Parts of A Bat (General) Bat anatomy, Bat mammal, Bat species
Inner ear of bats were decalcified in EDTA solution and then were sliced into sections at 8 µm or 12 µm thickness.. Ear anatomy traces a family tree for bats. M. Brock Fenton; Nature News.
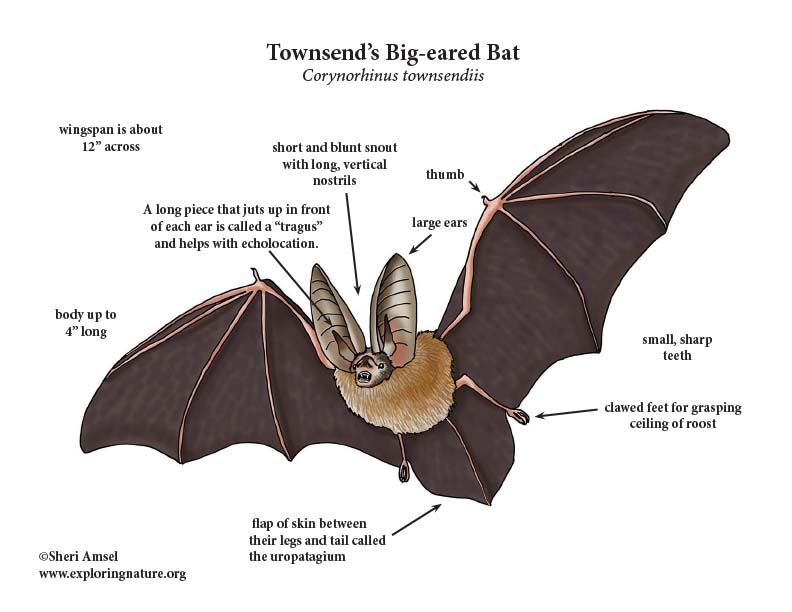
Bat (Townsend’s Bigeared) Diagram
Many bats, on catching large prey in flight, bring the membrane forward and, by flexing the neck and back, tuck the prey against and into the membrane. With this maneuver the bat takes hold of the victim headfirst and is able to kill or disable it promptly. At rest a bat's head, especially the ears, is its most striking feature.