The Carpal Tunnel Borders Contents TeachMeAnatomy
Anatomy of the flexor retinaculum For an accurate definition of the anatomic limits of the carpal tunnel, 26 cadaver upper extremities were studied by gross (lo), histologic (3), and radiographic (13) methods.. ture is the transverse carpal ligament.4-6 Flexor reti- nuculum and transverse carpal ligament are considered
The flexor retinaculum of Hand Gross anatomy , Attachments and
Definition The TCL is the middle portion of the flexor retinaculum (FR). 1 The proximal portion of the FR is the distal continuation of the antebrachial fascia. 2 The transition from the antebrachial fascia to the TCL can be identified based on gross inspection, predominantly marked by the abrupt increase in thickness.

15 The Forearm Fascia and Retinacula Musculoskeletal Key
The terms transverse carpal ligament and flexor retinaculum have commonly been used to describe the fibrous structure running between the ulnar-sided hamate and pisiform bones and the radial-sided scaphoid and trapezium bones. However, the flexor retinaculum is composed of three parts. The most proximal part is continuous with the volar antebrachial fascia, the intermediate part is recognized.

View of the wrist showing the flexor retinaculum at the wrist and the
1/4 Synonyms: none Intercarpal joints are all classified as synovial plane joints, meaning that the articular surfaces are functionally considered as nearly flat and lined with fibrocartilage. The joints are enclosed by the thin fibrous capsules whose internal surfaces are lined by the synovial membranes.

Flexor Retinaculum of Hand Anatomy l Surface marking l Structures
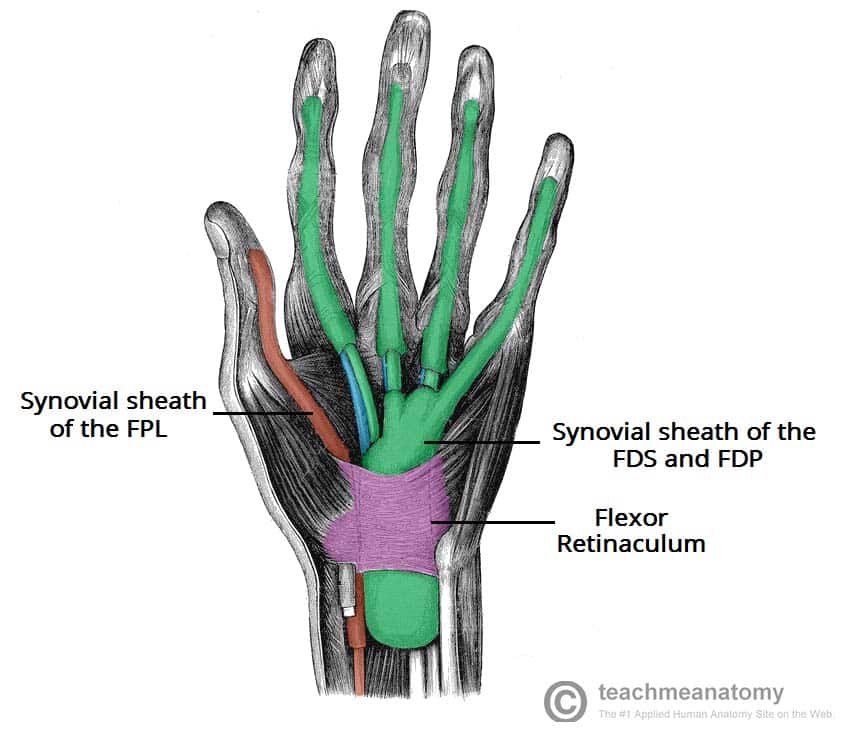
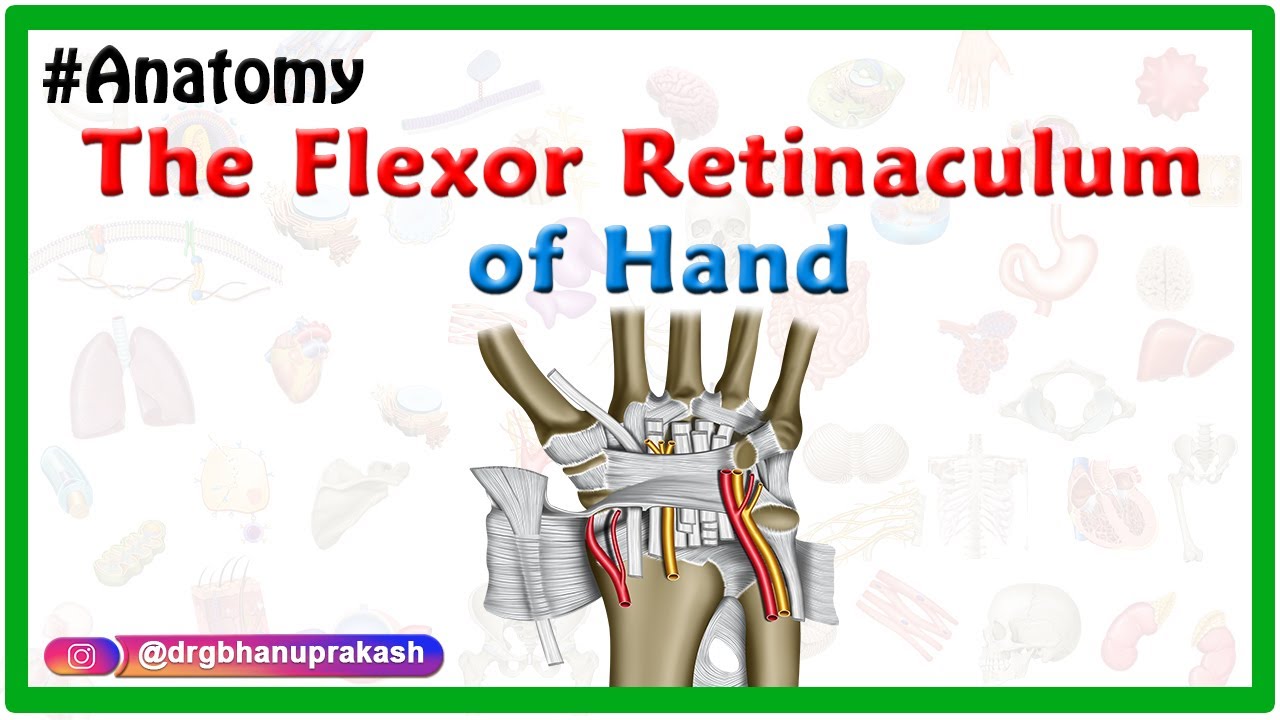
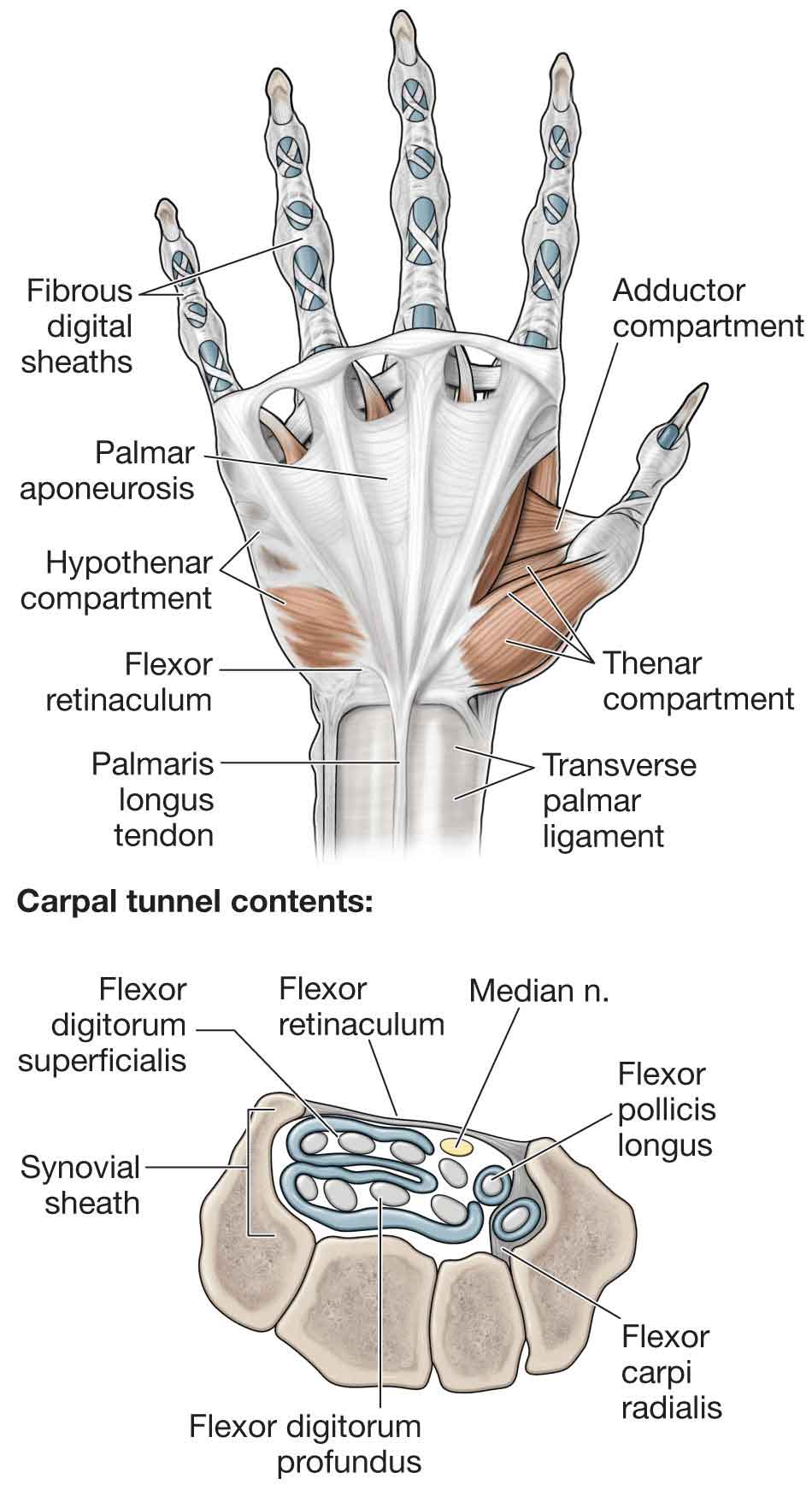
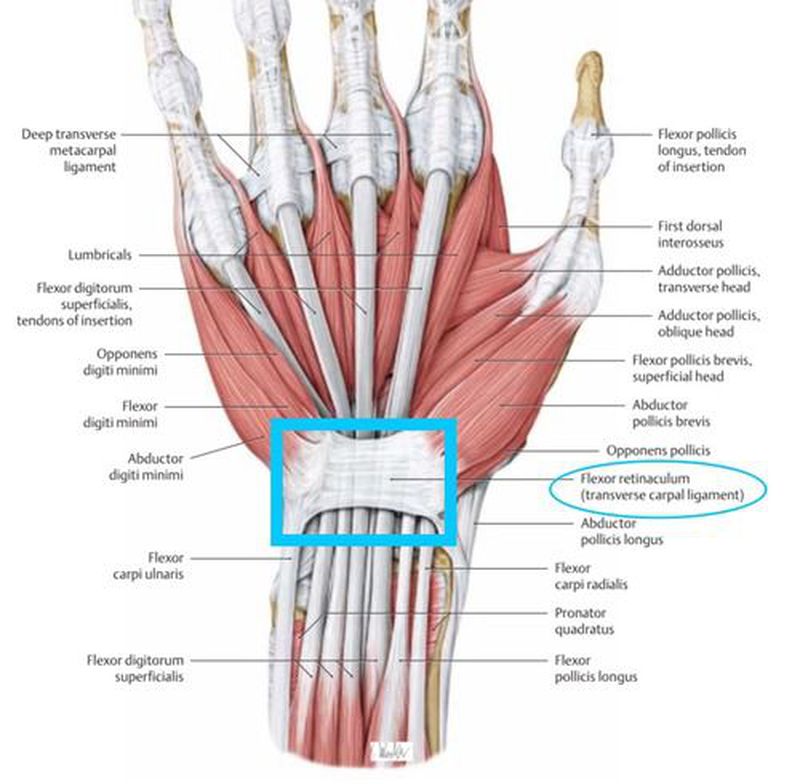
Flexor retinaculum is a strong fibrous band which bridges the anterior concavity of the carpal bones thus converts it into a tunnel, the carpal tunnel [1]. Attachments Medially, To the pisiform bone To the hook of the hamate Laterally, To the tubercle of the scaphoid To the crest of the trapezium [1]

Strained Flexor Retinaculum of the Foot
The carpal tunnel is a relatively small space and contains the median nerve and nine tendons that also pass from the forearm into the fingers. Most commonly, CTS results when the tendons or their lining (the synovium) thicken or the ligament tightens. The space available for the median nerve is reduced, and the median nerve becomes compressed.

View of the wrist showing the flexor retinaculum at the wrist and the
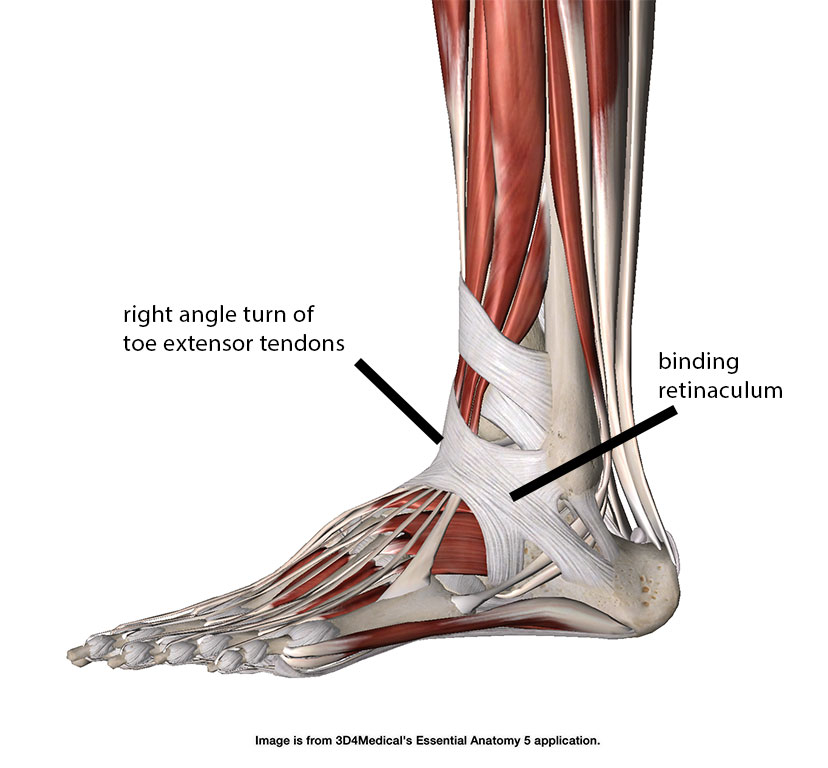
The flexor retinaculum of the foot is a strong fibrous band that covers the tendons of the muscles that flex the foot such as walking on the toes like a ballerina.
The Mechanical Function of Retinacula Academy of Clinical Massage
The flexor retinaculum of foot ( laciniate ligament, internal annular ligament) is a strong fibrous band in the foot . Structure The flexor retinaculum of the foot extends from the medial malleolus above, to the calcaneus below. [1]

Superior Extensor Retinaculum Anatomy, Musculoskeletal system
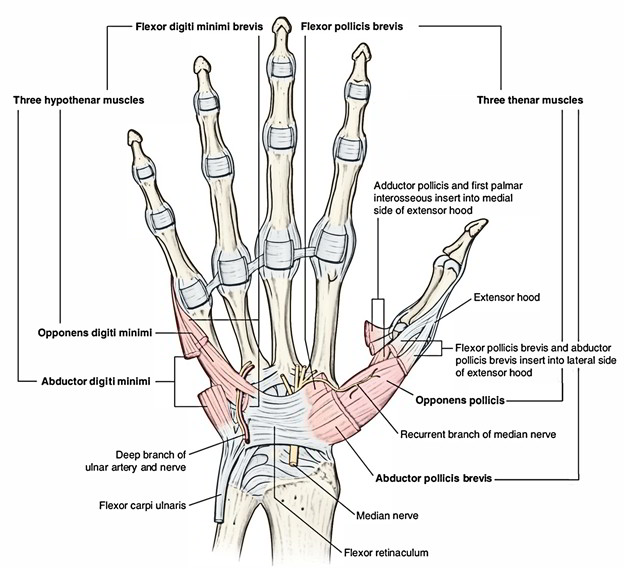
The flexor retinaculum branches off in two places, here and here, to enclose two small, separate tunnels. This one, on the radial side, encloses the tendon of flexor carpi radialis. This one, superficial and on the ulnar side, encloses the ulnar artery and nerve. We'll be returning to the flexor retinaculum later, to look at some important.

Pin em Musculoskeletal System
First Online: 15 December 2022 20 Accesses Abstract The complex anatomy of the hand and wrist joints permits the intricate movements and high function of the upper limb. This chapter provides an overview of the bony anatomy of the hand and wrist, their articulations, and muscular and tendinous attachments. Keywords Hand Wrist Carpal

The flexor retinaculum in the carpal tunnel consists of three segments
The roof of the carpal tunnel is formed by the flexor retinaculum (also known as transverse carpal ligament), a thick connective tissue ligament. This ligament bridges the space between the medial and lateral ends of the carpal arch, converting the arch into a tunnel. Contents Tendons of flexor digitorum profundus muscle
The Forearm, Wrist, and Hand Musculoskeletal Key
The flexor tendon sheaths of the remaining three fingers are separate. The radial bursa extends for the entire length of the flexor pollicis longus tendon and ends just proximal to the flexor retinaculum. The radial & ulnar bursa communicate at the level of the wrist joint in almost 50% of individuals. Dorsal carpal tendinous sheaths
Flexor Retinaculum MEDizzy
Flexor Retinaculum Thick connective tissue which forms the roof of the carpal tunnel. Turns the carpal arch into the carpal tunnel by bridging the space between the medial and lateral parts of the arch. Spans between the hook of hamate and pisiform (medially) to the scaphoid and trapezium (laterally).
Flexor Retinaculum (Hand) Earth's Lab
The Palmar carpal ligament (PCL) is a distinct component of the antebrachial fascia. The distal part and the true covering of the carpal tunnel is the flexor retinaculum. There is an area in the distal part of the flexor retinaculum that consists of crisscrossing of muscle aponeurosis of the thenar and hypothenar muscles ( Fig. 18.9a,b ).
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/retinaculum-flexorum/UfDcRtsSwVXr5QZEpzZZSQ_MtMxTgGEQj_Retinaculum_flexorum_1.png)
Flexor retinaculum (Retinaculum flexorum) Kenhub
The hamulus also serves as the attachment point for a number of different muscles and ligaments of the hand and forearm, including the flexor retinaculum. Articulations The hamate bone articulates with several adjacent bones: The proximal surface articulates with the lunate bone;

Anatomy and Functional Anatomy of the Hand Plastic Surgery Key
The flexor retinaculum is a fibrous connective tissue band that forms the anterior roof of the carpal tunnel (see Image. Flexor Retinaculum of the Wrist). Many experts consider the flexor retinaculum synonymous with the transverse carpal and annular ligaments.