
Anatomy Of A Model Cell mapasgmaes
Structure and Composition of the Cell Membrane. The cell membrane is an extremely pliable structure composed primarily of two layers of phospholipids (a "bilayer"). Cholesterol and various proteins are also embedded within the membrane giving the membrane a variety of functions described below.
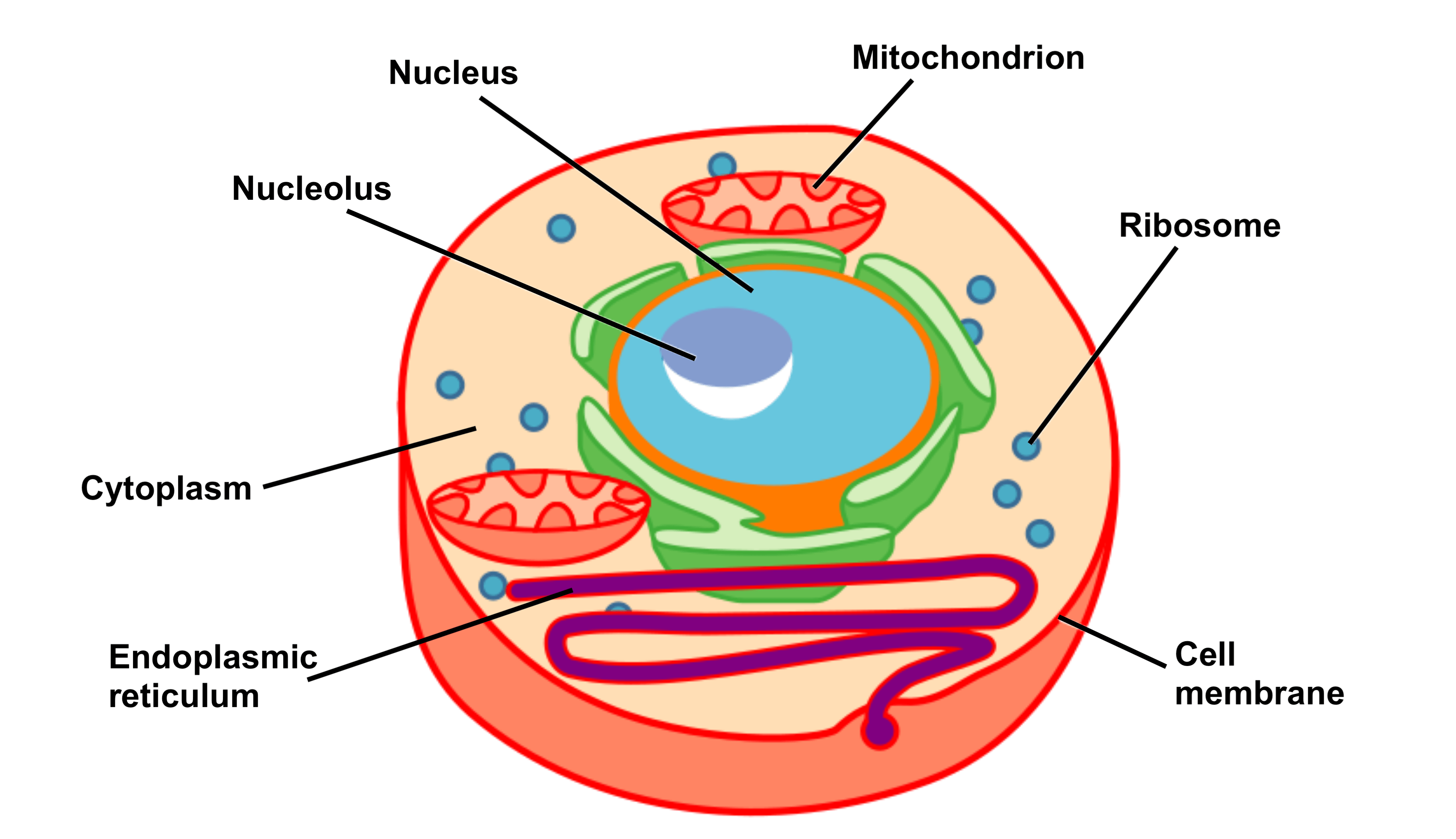
Labelled Diagram Of Ribosomes
Cell diagram labeled Cell diagram unlabeled Learn faster with interactive cell quizzes Sources + Show all What are the parts of a cell? There exist two general classes of cells: Prokaryotic cells: Simple, self-sustaining cells (bacteria and archaea) Eukaryotic cells: Complex, non self-sustaining cells (found in animals, plants, algae and fungi)

anatomy of the cell
Cell Parts ID Game. Test your knowledge by identifying the parts of the cell. Choose cell type (s): Animal Plant Fungus Bacterium. Choose difficulty: Beginner Advanced Expert. Choose to display: Part name Clue. Play.

Printable Plant Cell Diagram Labeled Printable Diagram Cell diagram
Cell organelles are specialized entities present inside a particular type of cell that performs a specific function. There are various cell organelles, out of which, some are common in most types of cells like cell membranes, nucleus, and cytoplasm. However, some organelles are specific to one particular type of cell-like plastids and cell.

Biology 101 Cells Owlcation
Animal cells are eukaryotic cells, meaning they possess a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Unlike plant cells, animal cells do not have cell walls, allowing for more flexibility in shape and movement. A plasma membrane encloses the cell contents of both plant and animal cells, but it is the outer coating of an animal cell.

Microtubule Animal Cell
Cell diagrams showing a typical animal cell and plant cell. Image created with Biorender.com. Questions Tips & Thanks Want to join the conversation? Sort by: Top Voted lillianjohnson a year ago has there ever been anything that had both animal and plant cells? • 12 comments ( 67 votes) Barrs Julianna a year ago

What is a cell? Facts
A membrane-bound nucleus, a central cavity surrounded by membrane that houses the cell's genetic material. A number of membrane-bound organelles, compartments with specialized functions that float in the cytosol.
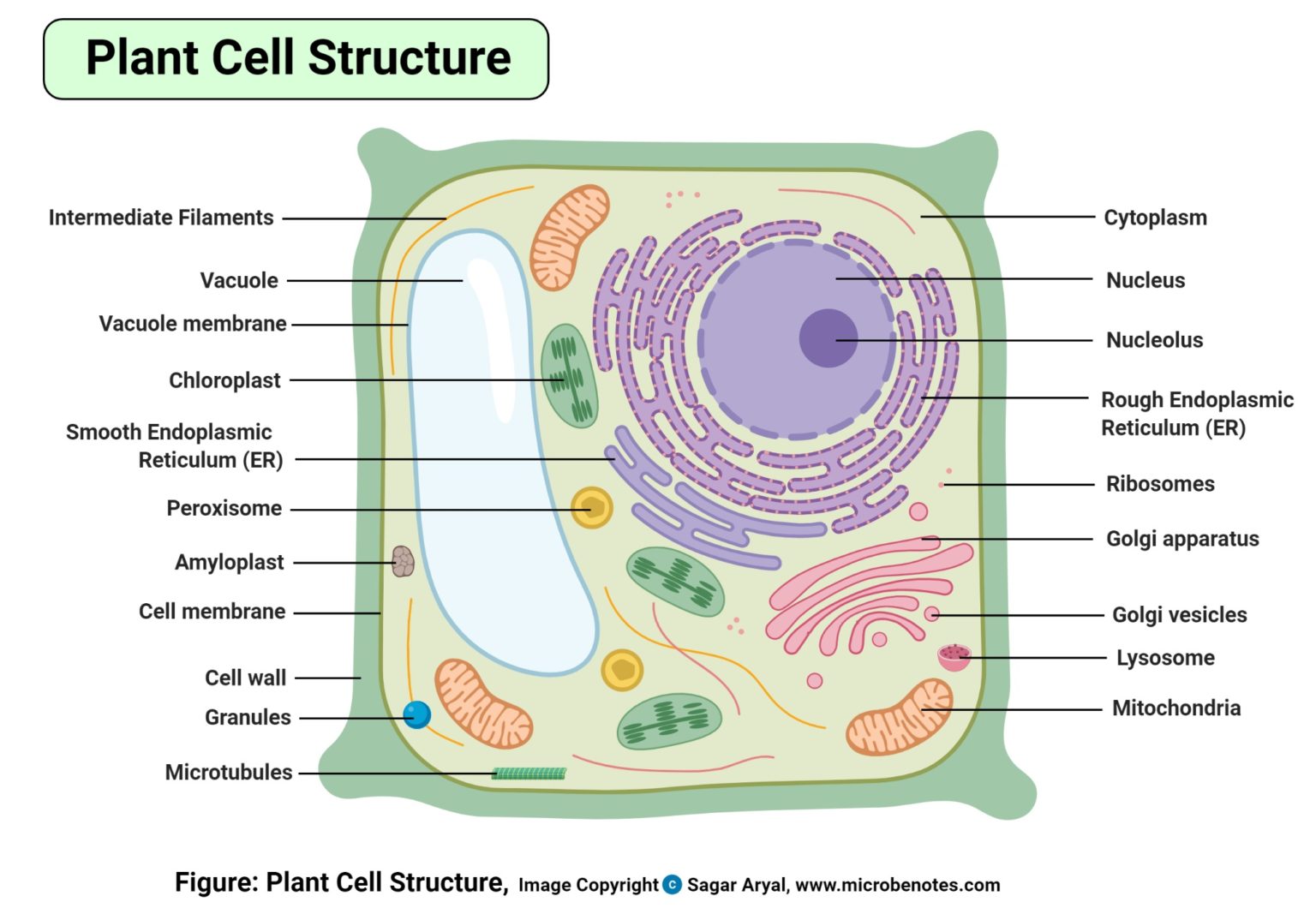
Plant Cell Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram
A brief explanation of the different parts of an animal cell along with a well-labelled diagram is mentioned below for reference. Also Read Different between Plant Cell and Animal Cell Well-Labelled Diagram of Animal Cell The Cell Organelles are membrane-bound, present within the cells.
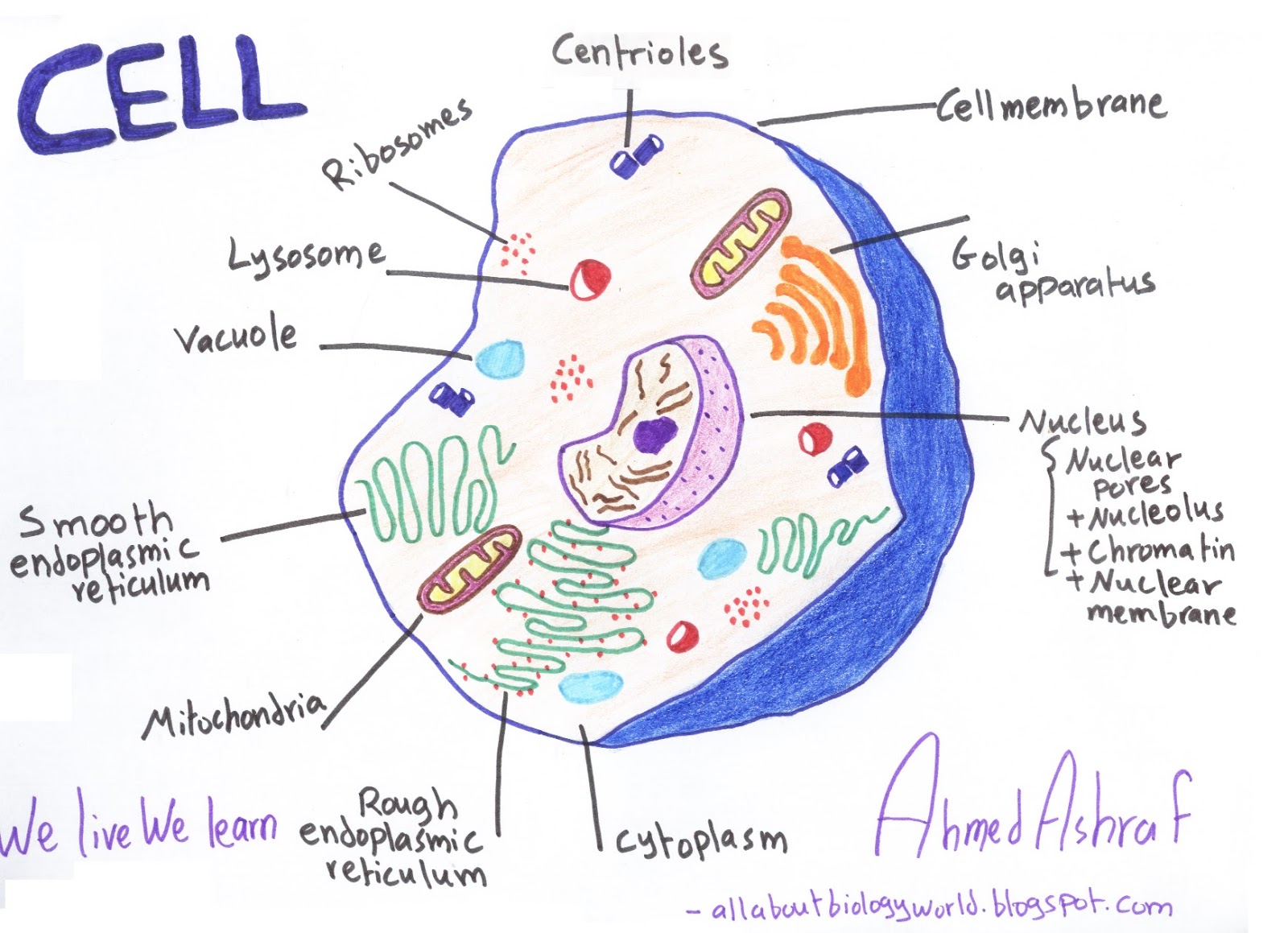
Biology Club Our cells 1 ( structure, function, division, disorder
1. Plasma membrane (Cell membrane) 2. Nucleus 3. Cytoplasm 4. Mitochondria 5. Ribosomes 6. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) 7. Golgi apparatus (Golgi bodies/Golgi complex) 8. Lysosomes 9. Cytoskeleton Functions of Cytoskeleton 10. Microtubules 11. Centrioles 12. Peroxisomes 13. Cilia and Flagella

Plant Cell Diagram Labeled Class 9 Labeled Functions and Diagram
Cell Diagrams with Labelling Activity. I've created two interactive diagrams for an upcoming open textbook for high-school level biology. The cell structure illustrations for these diagrams were generated in BioRender. Both diagrams feature a drag-and-drop labelling activity created with H5P here on Learnful.

Characteristics Of Eukaryotic Cellular Structures ALevel Biology
They're one of two major classifications of cells - eukaryotic and prokaryotic. They're also the more complex of the two. Eukaryotic cells include animal cells - including human cells - plant cells, fungal cells and algae. Eukaryotic cells are characterized by a membrane-bound nucleus.

Explain the nucleus of a cell with a neat labeled diagram Science
What exactly is its job? The plasma membrane not only defines the borders of the cell, but also allows the cell to interact with its environment in a controlled way. Cells must be able to exclude, take in, and excrete various substances, all in specific amounts.

Cell Structure
A cell is the smallest living thing in the human organism, and all living structures in the human body are made of cells. There are hundreds of different types of cells in the human body, which vary in shape (e.g. round, flat, long and thin, short and thick) and size (e.g. small granule cells of the cerebellum in the brain (4 micrometers), up to the huge oocytes (eggs) produced in the female.
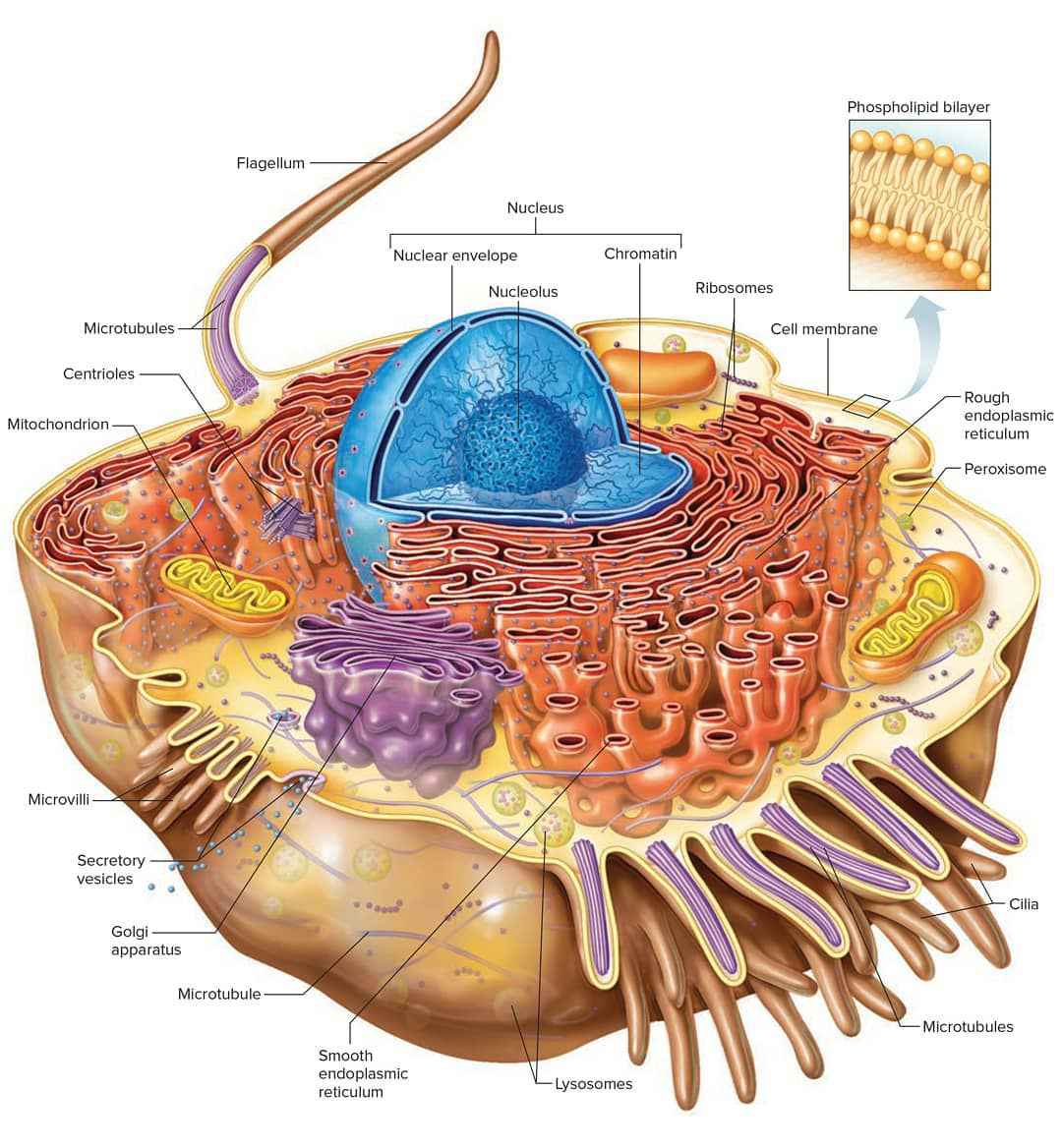
Cell Biology, Cell Structure
cell, in biology, the basic membrane-bound unit that contains the fundamental molecules of life and of which all living things are composed.A single cell is often a complete organism in itself, such as a bacterium or yeast.Other cells acquire specialized functions as they mature. These cells cooperate with other specialized cells and become the building blocks of large multicellular organisms.

Cells
Label the cell parts you can distinguish. The movement of the cytoplasm is detected by the movement of the chloroplasts which are suspended in cytoplasm. The chloroplasts are carried along in the cytoplasm as if in a current. This movement is known as cyclosis or cytoplasmic streaming. With arrows, indicate the directions of streaming (cyclosis.

Eukaryotic cell structure diagrams Biological Science Picture
A diagram of an animal cell is useful for understanding the structure and functioning of an animal. This article includes a well-labeled diagram and a brief description of each component of an animal cell. Animal cells are eukaryotic cells with a membrane-bound nucleus. Since they do not have cell walls and chloroplasts, they are distinct from.