
Bacillus Subtilis petri dishes, the top two are frozen and the bottom
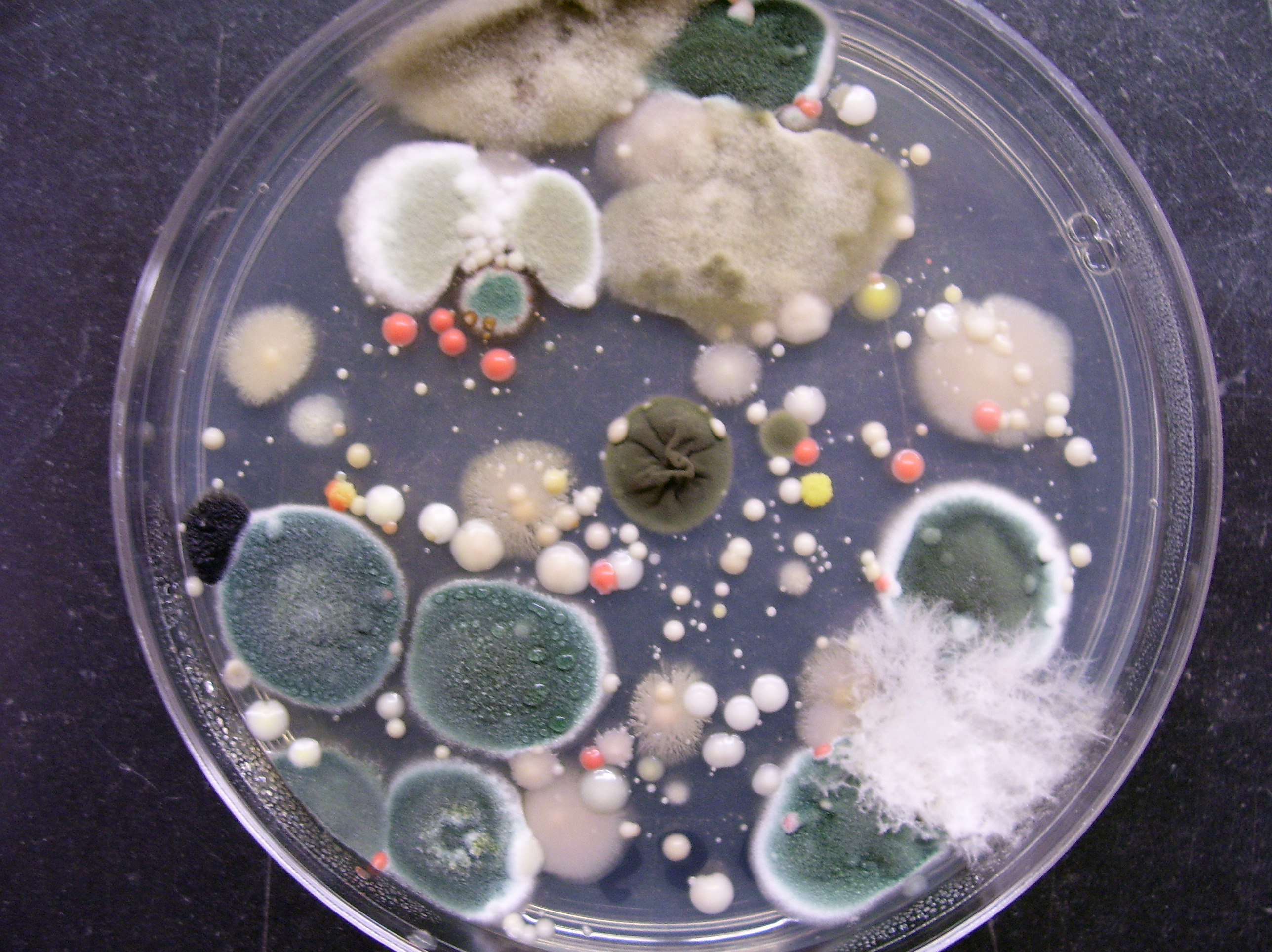
Colony morphology is a method that scientists use to describe the characteristics of an individual colony of bacteria growing on agar in a Petri dish. It can be used to help to identify them. Colony morphology A swab from a bin spread directly onto nutrient agar. Colonies differ in their shape, size, colour and texture.
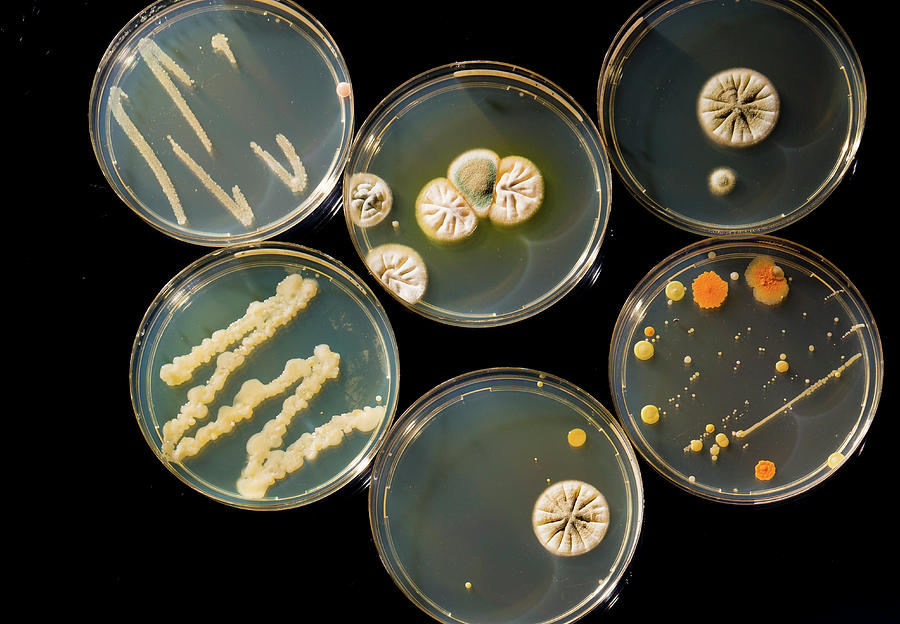
Petri Dishes With Bacteria Photograph by Wladimir Bulgar/science Photo
A petri dish is a small shallow transparent dish with a lid that is mainly used in biological experiments for the culture of cells. For instance, in microbiological experiments, a Petri dish is used as a container to grow microbes with growth media in it. It is derived from the name of its inventor, German bacteriologist Julius Richard Petri.
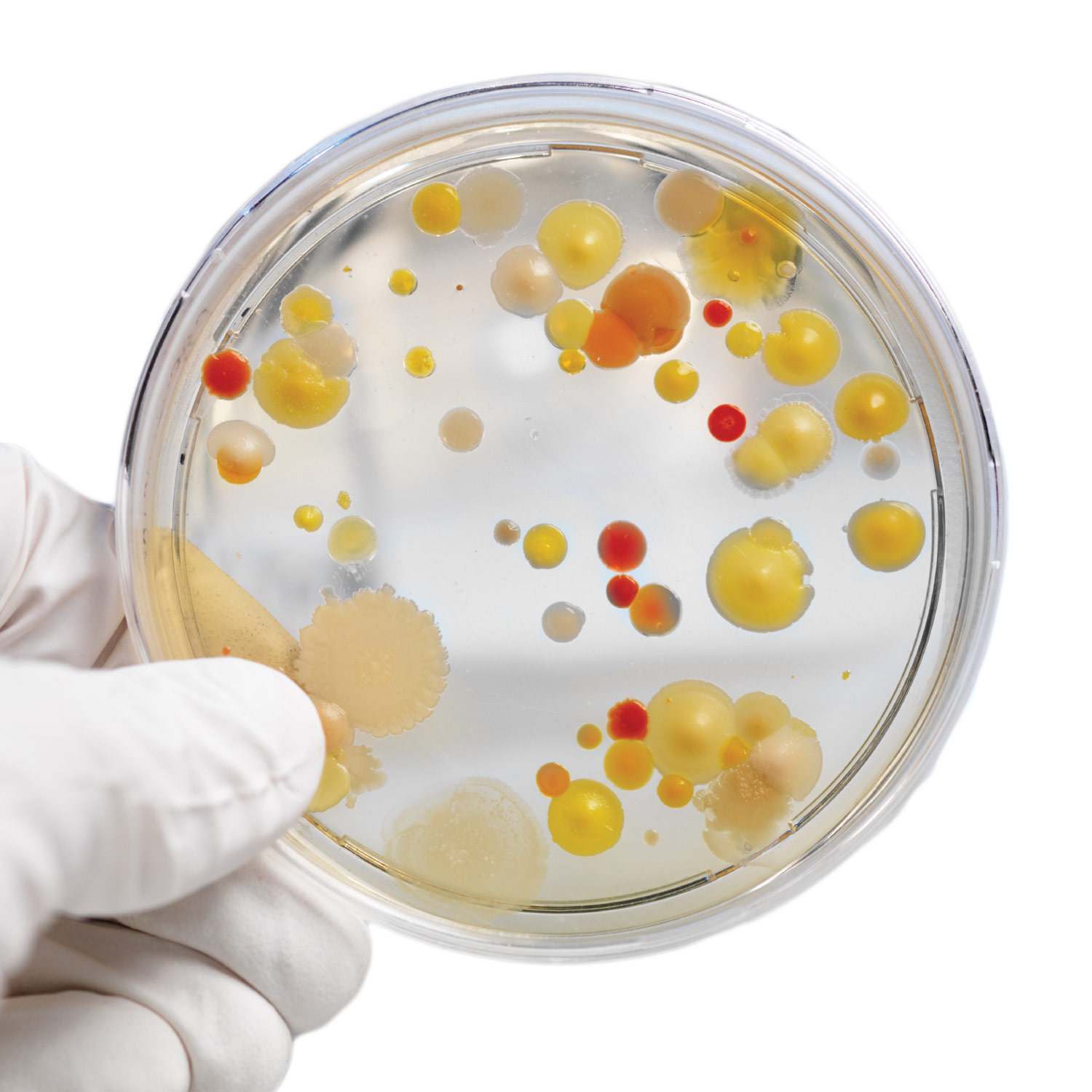
Growing Bacteria in Petri Dishes Biology Experiment
A Petri dish is essential laboratory equipment for the growth of microorganisms in the artificial solid culture media. A Petri dish consists of two parts: the smaller one is a container, and the larger is a lid. The larger dish fits over, the smaller dish and forms a cap. The commonly used Petri dish in a laboratory has a diameter of 90 mm.

Petri Dish Bacteria Identification
Using Bacillus cereus as a test organism and untreated plastic Petri dishes as a representative non-porous surface, the efficacy is experimentally validated. B. cereus is an aerobic, rod-shaped, gram-positive bacteria that can quickly multiply at room temperature.

Petri Dish With Bacteria Colonies Isolated On White Stock Photo
A Petri dish (alternatively known as a Petri plate or cell-culture dish) is a shallow transparent lidded dish that biologists use to hold growth medium in which cells can be cultured, [1] [2] originally, cells of bacteria, fungi and small mosses. [3] The container is named after its inventor, German bacteriologist Julius Richard Petri.
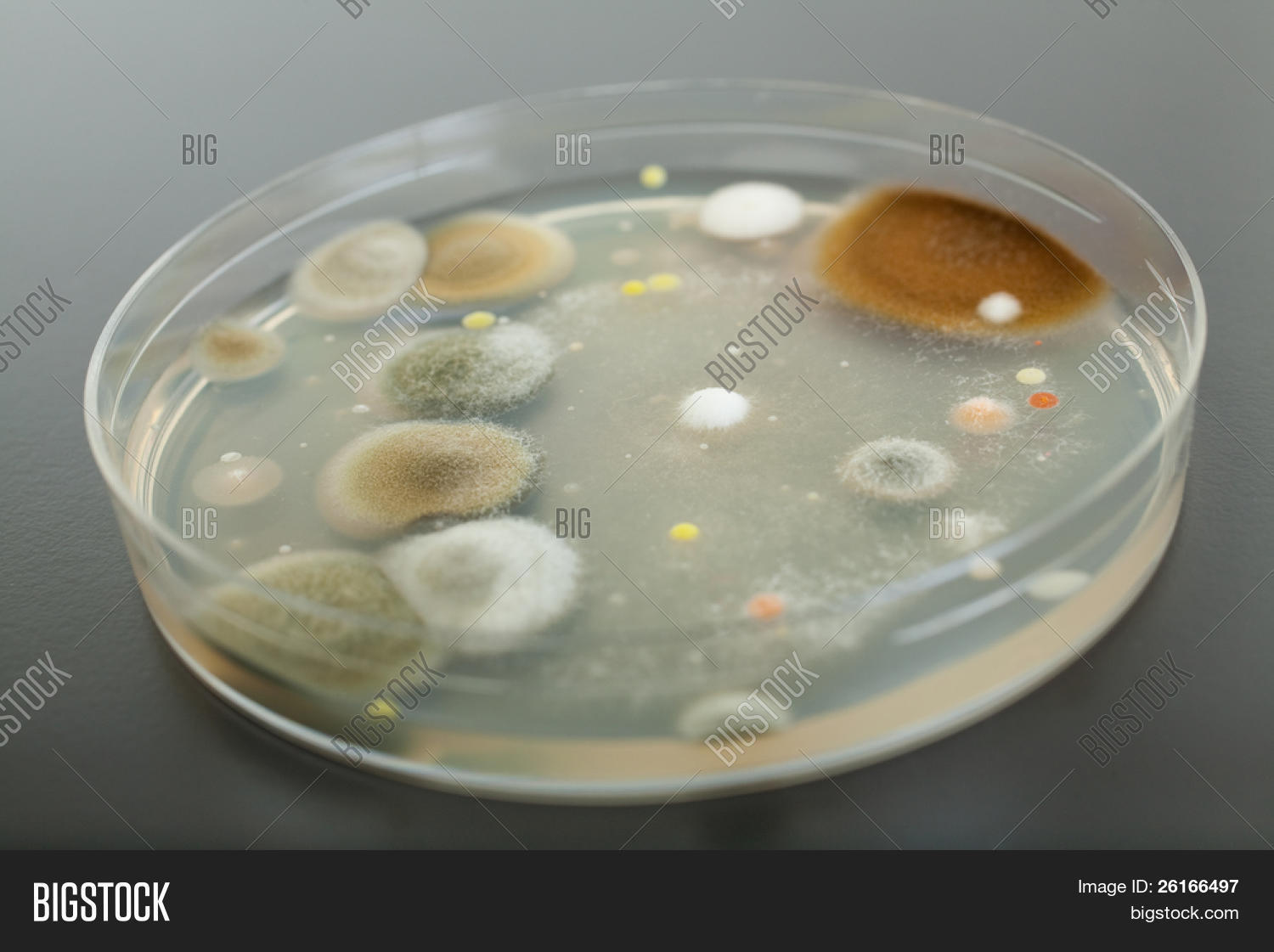
Petri Dish Agar Image & Photo (Free Trial) Bigstock
Science The big story: the petri dish 30 March 2017 How did the Petri dish first come into being and was Richard Julius Petri really the man responsible for its creation? Stephen Mortlock delves into the annals of microbiology. Scientists use them every day and discard them without a second thought.
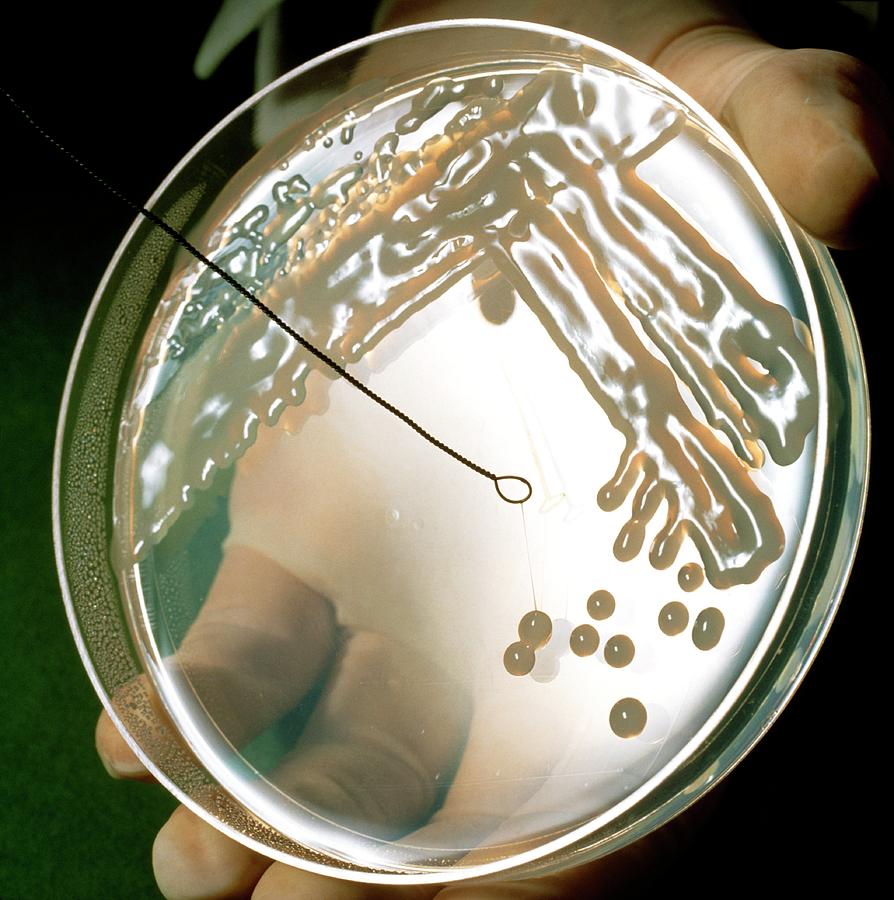
Petri Dish Culture Of A Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria Photograph by Dr
In a creative stroke inspired by Hollywood wizardry, scientists from the Kishony Lab at HMS and Technion (www.technion.ac.il/en/) have designed a simple way to observe how bacteria move as they.
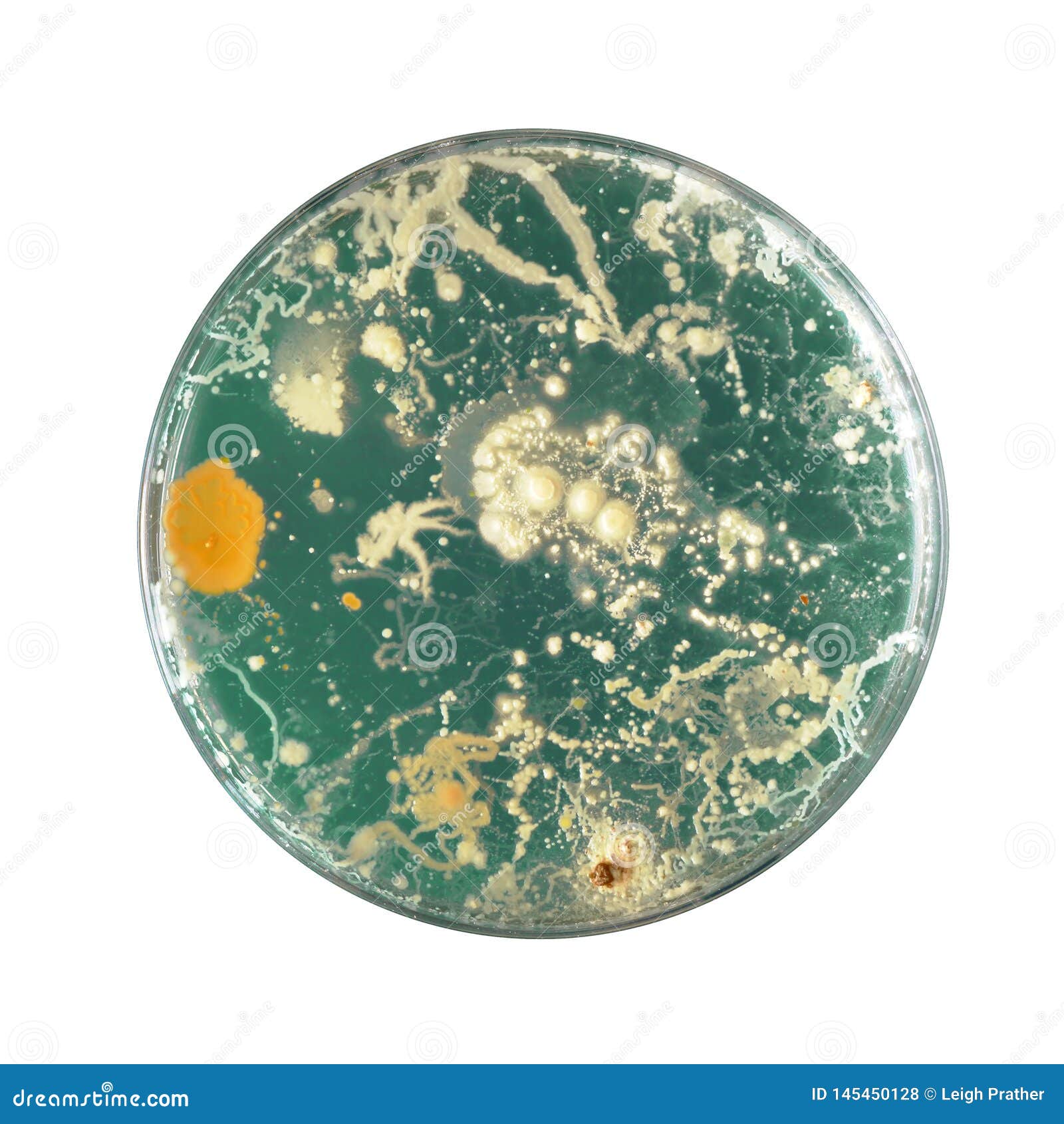
Bacteria Growing in a Petri Dish Stock Photo Image of culture
Bacteria are grown in Petri dishes upon a solid medium known as bacterial agar, where raised, circular colonies form. Unlike an individual bacterial cell, a colony is a group of bacteria large enough to be visible to the naked eye.
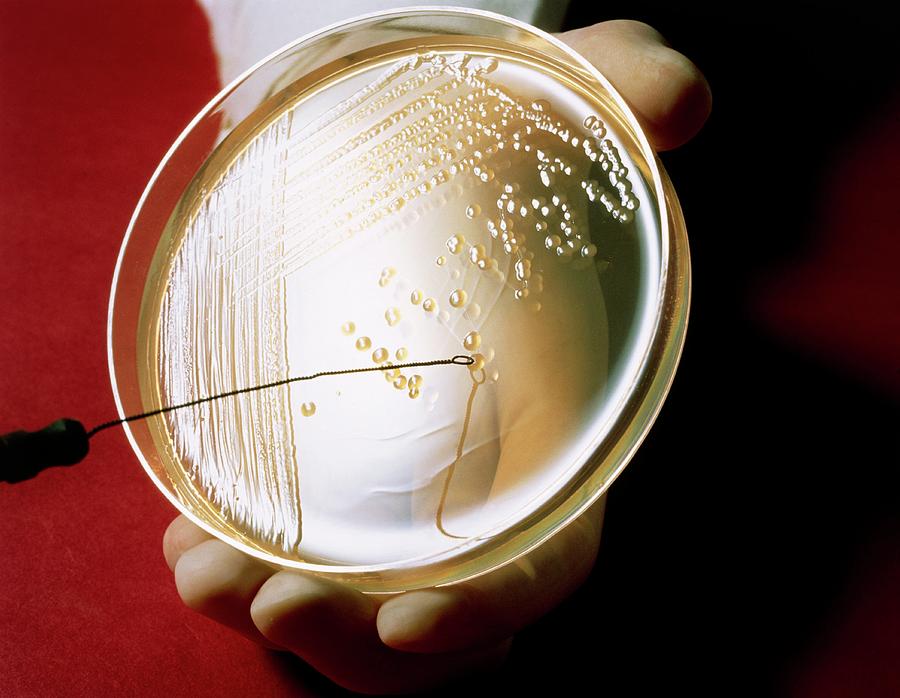
Petri Dish Culture Of Bacterium Escherichia Coli Photograph by Dr
Biology Agar, Petri Dishes, and Bacteria Filters category Agar, Petri Dishes, and Bacteria Sort By: 43 Results Best Seller Best Seller Bacteria Growing Kit $35.95 Add to Cart Quick View Best Seller Best Seller Petri Dishes, polystyrene, 90 x 15 mm, 20 pack $7.95 Add to Cart Quick View Best Seller Best Seller Science Buddies Bacteria Discovery Kit
Bacteria In A Petri Dish Wallpapers High Quality Download Free
Thus, to measure bacteria in a petri dish, you want to be sure you have agar plates, not just petri dishes. To measure bacteria growth, follow these steps. Sterilize all of your equipment in ethanol to be sure you are only measuring the bacterial culture of your choosing. Add 10 microliters of your bacterial culture to 90 microliters of your.
Time Lapse of Bacteria Bacillus Cereus Growing in Petri Dish YouTube
Dip the loop into the E. coli culture and then remove it. Open the agar plate and gently glide the loop back and forth across the surface of one section of the agar. Take care to not scratch through the agar with the loop. The agar provides the nutrients the E. coli need to grow. Place the loop in the Bunsen burner flame again to sterilize it.

What is a Petri Dish? (with pictures)
After a day or two, billions of bacteria have colonized the outer lanes of the large petri dish. Each time a bacterium divides, it must copy its genome. In doing so, mistakes—known as mutations—are inevitable. Collectively, the bacteria on this dish have experienced billions of mutations.
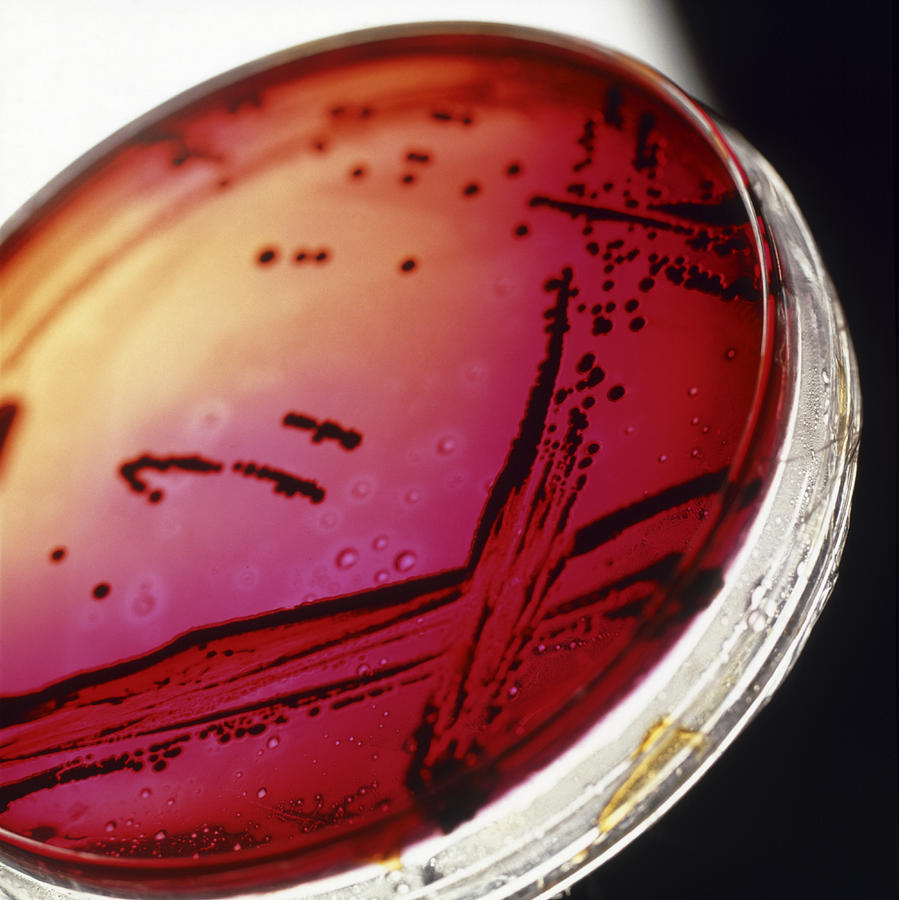
View Of A Petri Dish With Bacterial Cultures Photograph by Tek Image
Ever wanted to grow bacteria for a science project or just for fun? It's surprisingly simple! All you need is some nutrient agar (a special gelatinous growing material), a number of sterilized Petri dishes, and some disgustingly good sources of bacteria! Part 1 Preparing the Petri Dishes Download Article 1 Prepare the agar.

Bacillus Bacteria on a Petri Plate Stock Image Image of petri, dish
Feb. 7, 2020 We may not see them, but microbes are all around. This fact is revealed to microbiology students who are tasked with a classic project: to identify bacteria and fungi from their environment. Armed with cotton swabs and Petri dishes full of nutient agar, students head out of the lab to see what lives on surfaces they encounter everyday.

Petri dish with bacteria colonies, isolated on white Microbiome Hub
Spread Plate Technique for Bacteria and Fungi. The spread plate technique is used to grow a continuous lawn of bacteria or fungi on an agar plate. To get started, you will need: A clean, sterile work area. Agar plates appropriate for growing the bacteria or fungi you are trying to grow. A sterile spreader or sterile glass beads.

Petri dishes with bacteria Stock Image F018/3375 Science Photo
Order now at http://www.stevespanglerscience.com/search?sSearch=agar&sClass=Product&sType=&submit.x=0&submit.y=0 You can smell a good science project a block.