
Normal ankle Image
Normal plantar fascia. A schematic representation (a) and lateral plain radiograph (b) show the normal PF (arrows). On sagittal ultrasound scan, the normal PF (arrows) appears as a fibrillar ligamentous structure (c). On MRI, the normal PF (arrows) is seen as a thin band of low signal intensity on both T1-weighted (d) and fluid-sensitive (e) images

Normal Foot X Ray Normal foot series Image Check you have the right
Diagnostics & Testing / Foot X-Ray Foot X-Ray A foot X-ray is a test that produces an image of the anatomy of your foot. Your healthcare provider may use foot X-rays to diagnose and treat health conditions in your foot or feet. Foot X-rays are quick, easy and painless procedures.

Image
A foot x-ray, also known as foot series or foot radiograph, is a set of two x-rays of the foot. It is performed to look for evidence of injury (or pathology) affecting the foot, often after trauma. Reference article This is a summary article. For more information, you can read a more in-depth reference article: foot series. Summary indications

footxray Family Foot and Ankle
Overview Along with questions of your medical history, your doctor may need to take x-rays of your foot to help aid in making a diagnosis to determine the cause of your foot pain. If the foot is broken it will be put into a cast. Toes that are broken are taped.
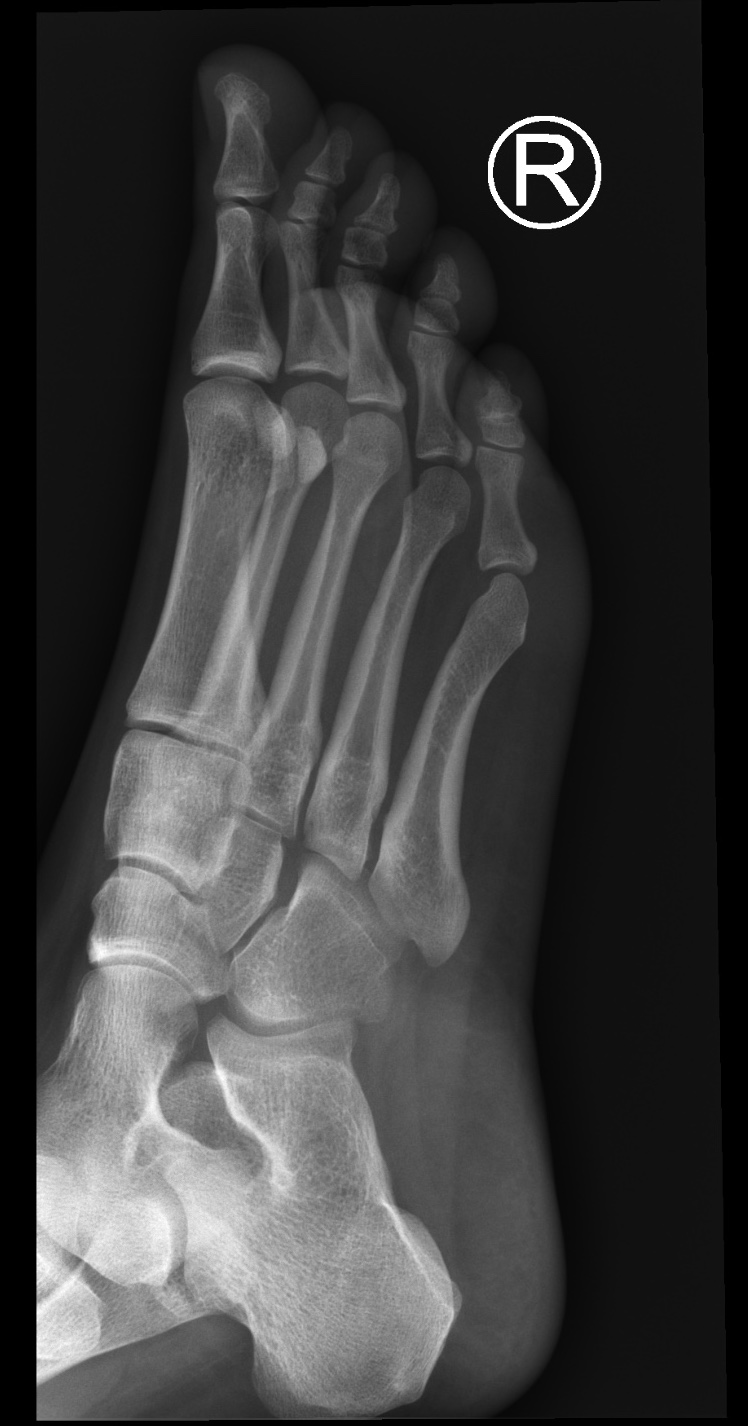
Normal foot xrays Image
Fig. 5A —Children with medial foot pain, one with history of cerebral palsy. Weightbearing anteroposterior view of left foot in 9-year-old boy with medial foot pain shows hindfoot and forefoot alignment abnormalities. Mid talar line passes far medial to base of first metatarsal, and there is lateral subluxation of navicular on talus.
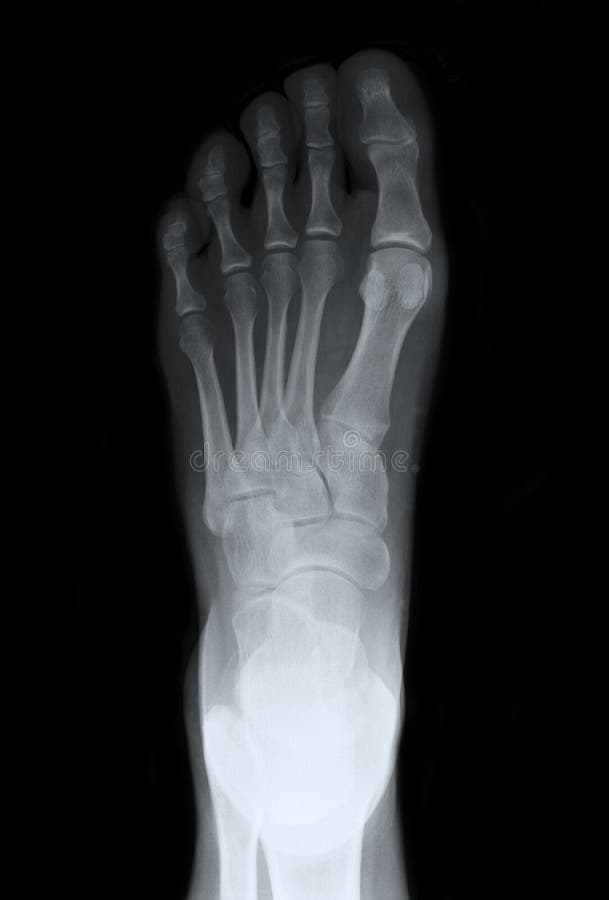
Left Foot Top Xray stock photo. Image of office, bones 23546186
Presentation Pain. ?fracture Patient Data Age: 20 years. Gender: Female x-ray Frontal Oblique Lateral Normal right foot radiographs in a young adult female for reference. Case Discussion Normal right foot radiographs in a young adult female for reference. 1 article features images from this case 11 public playlists include this case
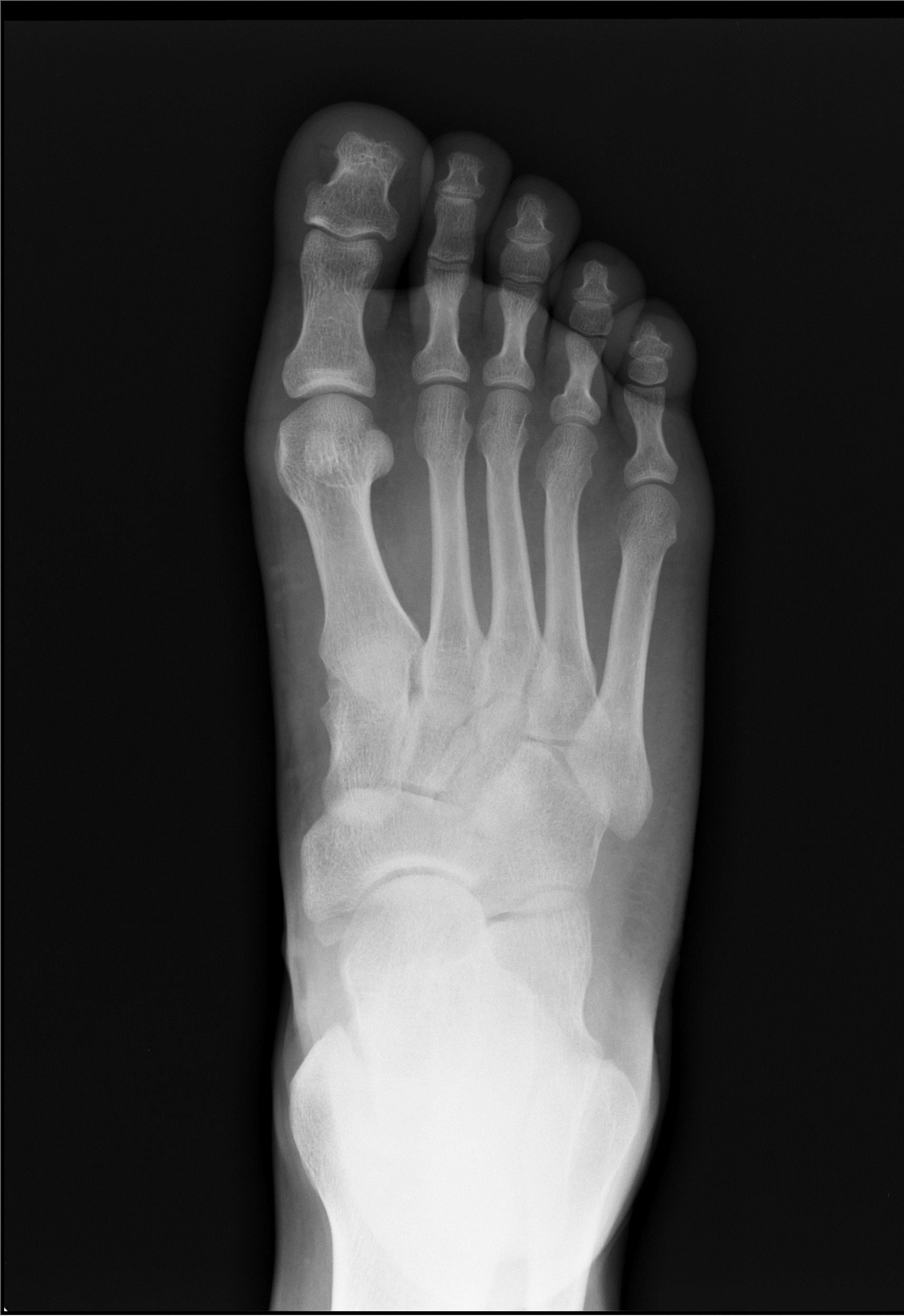
footxray RCEMLearning
No fracture is seen. Bones show normal alignment and architecture. Joint spaces and articular margins are intact. Soft tissues show normal appearance. FREE download PDF Word format X rays Left Foot AP/OBL . Also available other updated Radiology MRI, CT Scan, Xray, Sonography, USG, Mammography, PET CT, EEG and ECG Report templates.

Xray left foot Fig. 4 Xray left foot Download Scientific Diagram
A normal left foot X-ray should show clear and well-defined structures without any signs of fractures, dislocations, or abnormalities. Understanding the anatomy and function of a normal left foot can help healthcare professionals diagnose and treat various foot conditions effectively. If you have any concerns about your left foot, it is.

Oblique and anteriorposterior view Xrays of a normal foot showing... Download Scientific Diagram
An approach to the traumatic foot x-ray. 1. Adequacy. This view is best used in the evaluation of midfoot and forefoot [5]. Lateral: should include projection of ankle in addition to foot [5]. The base of 1st, 2nd, and 3rd metatarsals should align with three cuneiform bones [5].

EMRad Radiologic Approach to the Traumatic Ankle MEDTAC International Corp.
Technical factors AP projection centering point x-ray beam centered to the base of the 3 rd metatarsal the beam must be angled approximately 10° posteriorly towards the calcaneum to mimic the arch of the foot, this may change if the arch is high or flat collimation lateral to the skin margins anterior to the skin margins of the distal phalanges
Podiatrist in Akron Hallux Rigidus in Akron Green Foot & Ankle Care, LLC
1. Check you have the right views. There are two views in foot x-rays DP (dorsal-plantar) and oblique. Both should ideally be done when weight-bearing if your patient can manage it. 2. Review the bones. Work round the bones one by one (including the metatarsals). Start proximally and work your way down, going medial lateral.
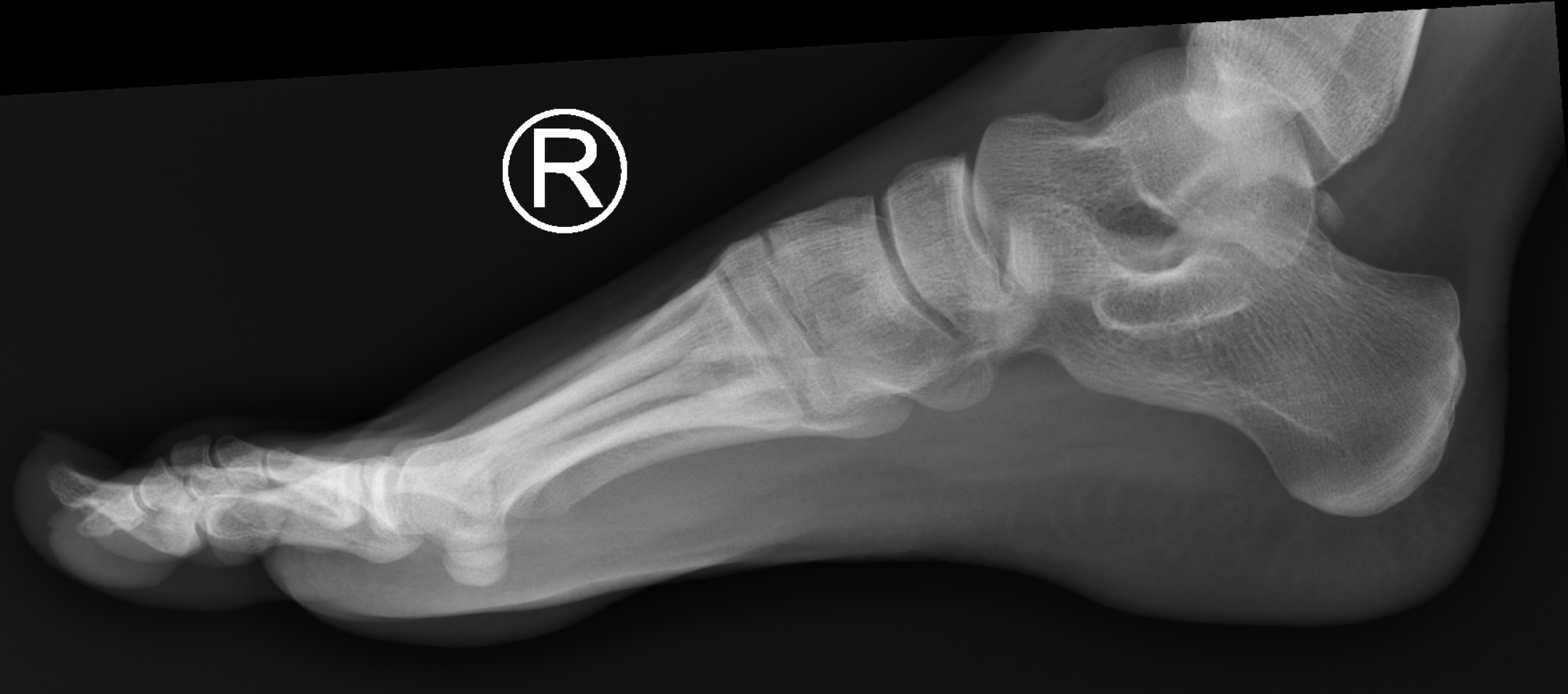
NORMAL FOOT 7
Tutorials Next » Trauma X-ray - Lower limb Foot Key points Carefully check the cortical edge of all bones on all views available Always check for alignment of bones at the mid-forefoot junction (tarsometatarsal joints) Injury to the Lisfranc ligament may not be visible on initial X-ray - follow up may be necessary
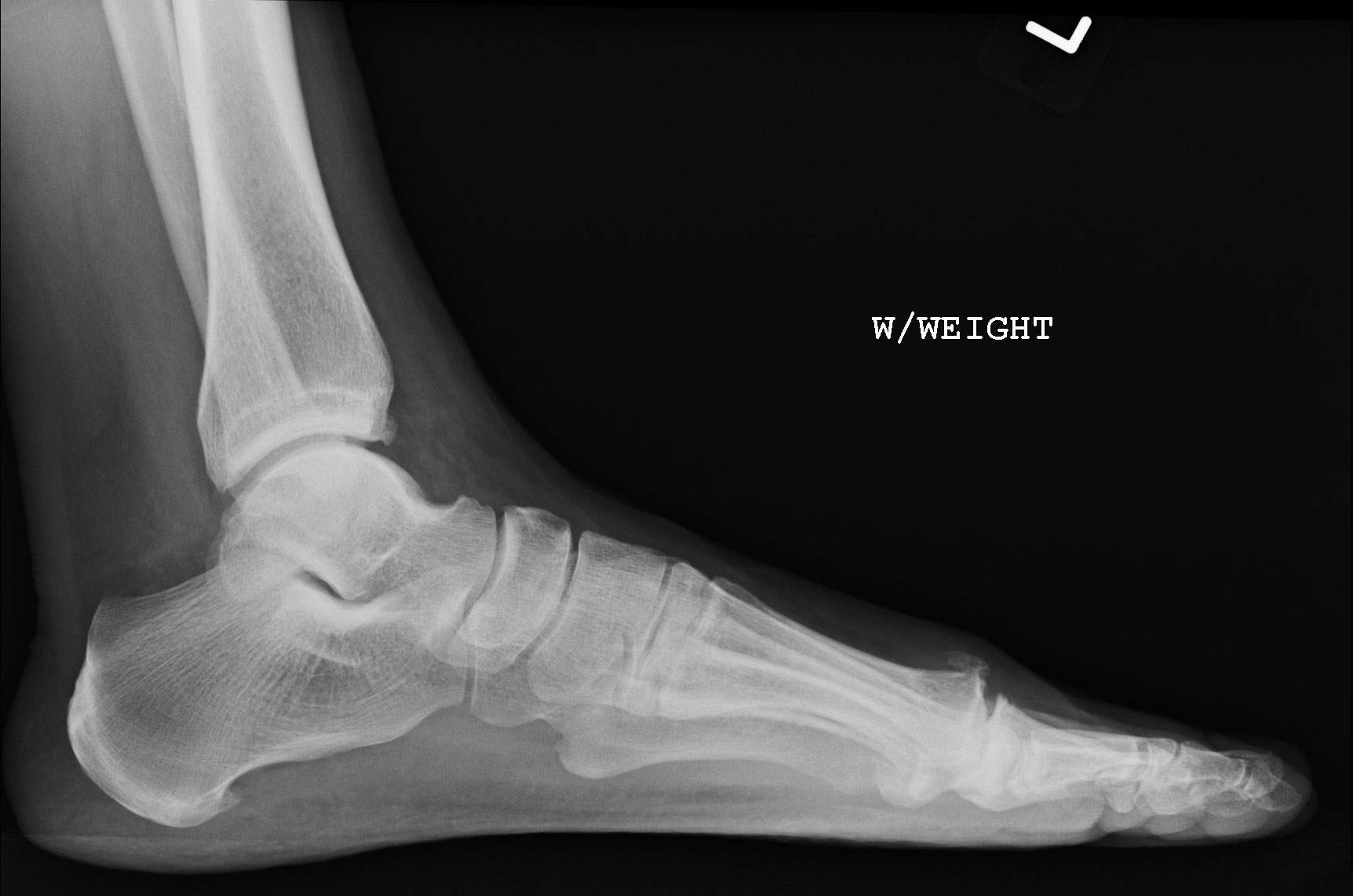
Figure 2
18 cm x 24 cm exposure 55-60 kVp 4-6 mAs SID 100 cm grid no Image technical evaluation the metatarsals are almost completely superimposed with only the tuberosity of the 5 th metatarsal seen in profile the domes of the superior aspect of the talus are superimposed tibiotalar joint is open Practical points

Image
Routine Radiographs. These include a series of ankle and foot X-rays. Fig. 2.1 (A and B) (A) Anteroposterior (AP) and (B) Lateral (LAT) views of ankle. • Oblique (mortise) views: Mortise view is 15-degree internal rotation view, which clearly shows ankle mortise in its true plane.
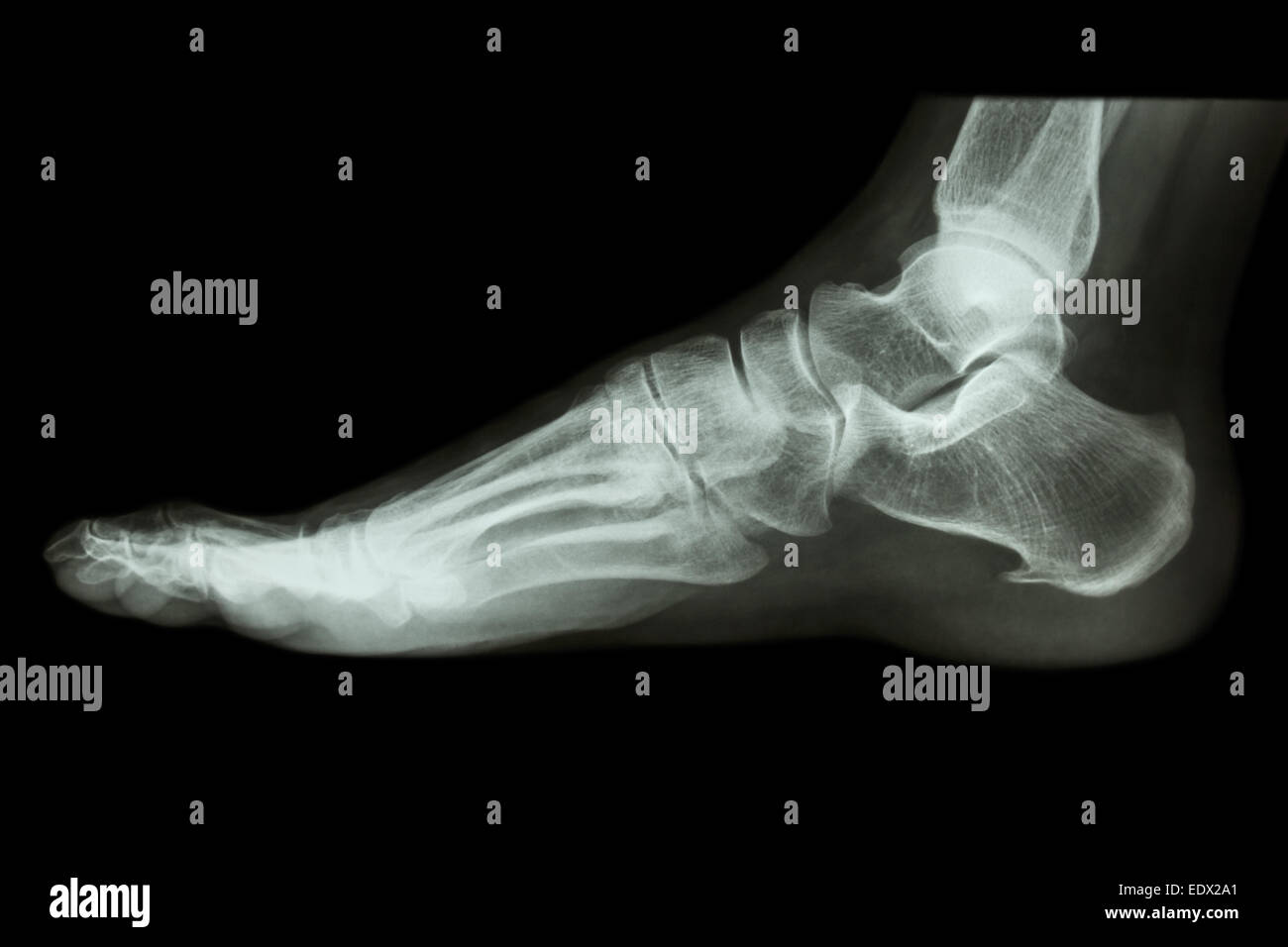
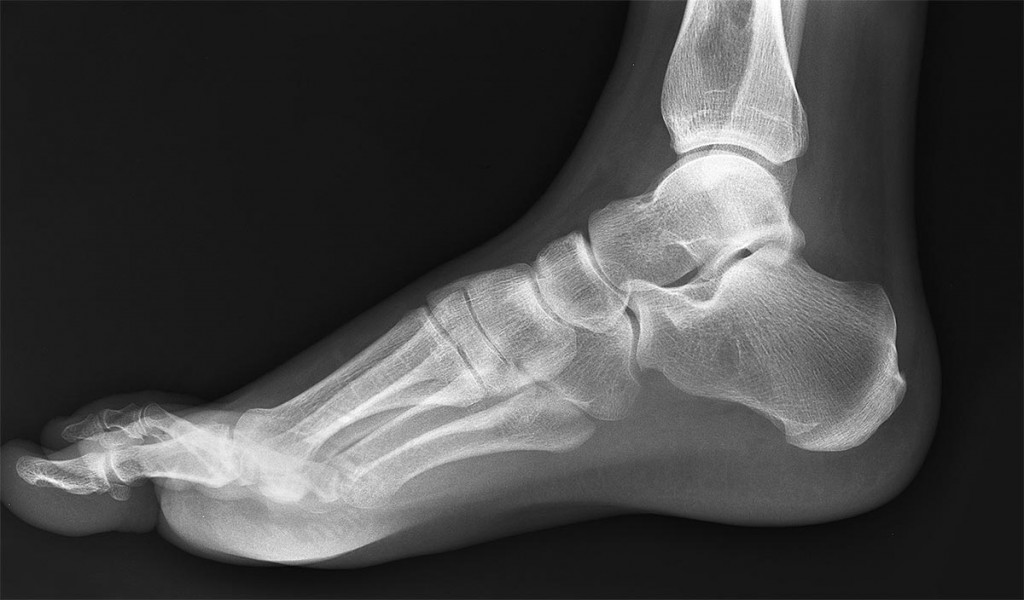
Xray normal human's foot lateral Stock Photo Alamy
Case Discussion. Important areas to review include midfoot alignment, which is lost in Lisfranc injuries, the metatarsals and navicular for stress fractures, and for an erosive arthropathy, such as in gout . A structured approach and checklists can be helpful when preparing for exams.
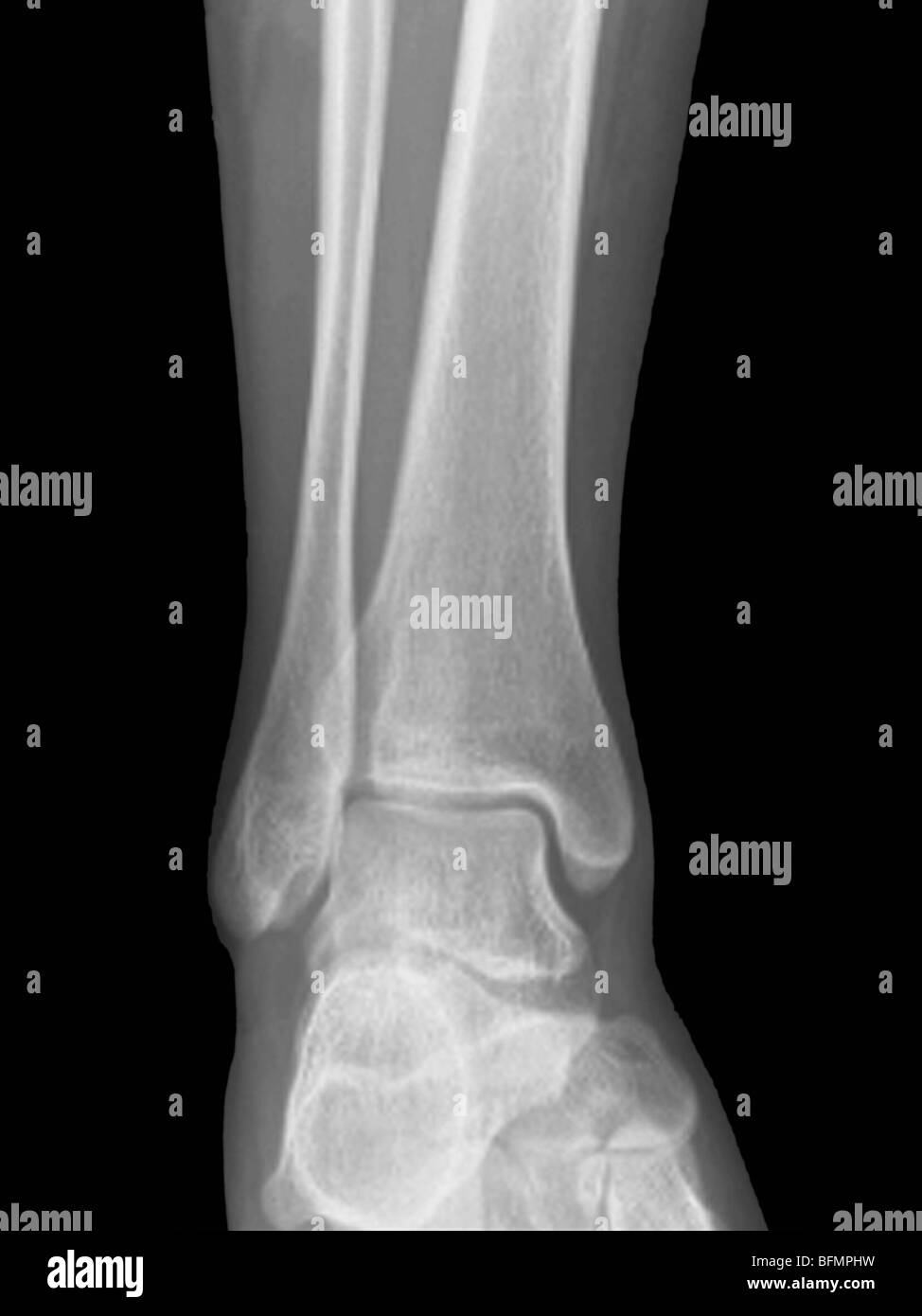
Normal ankle joint x ray fotografías e imágenes de alta resolución Alamy
If viewed from the front or exposure side, the side from which the X-ray beam originally entered the body, it will appear to be a left foot. But if the same image is looked upon from the back-the opposite surface or nonexposure side, the viewer sees the mirror image, which appears to be a right foot.