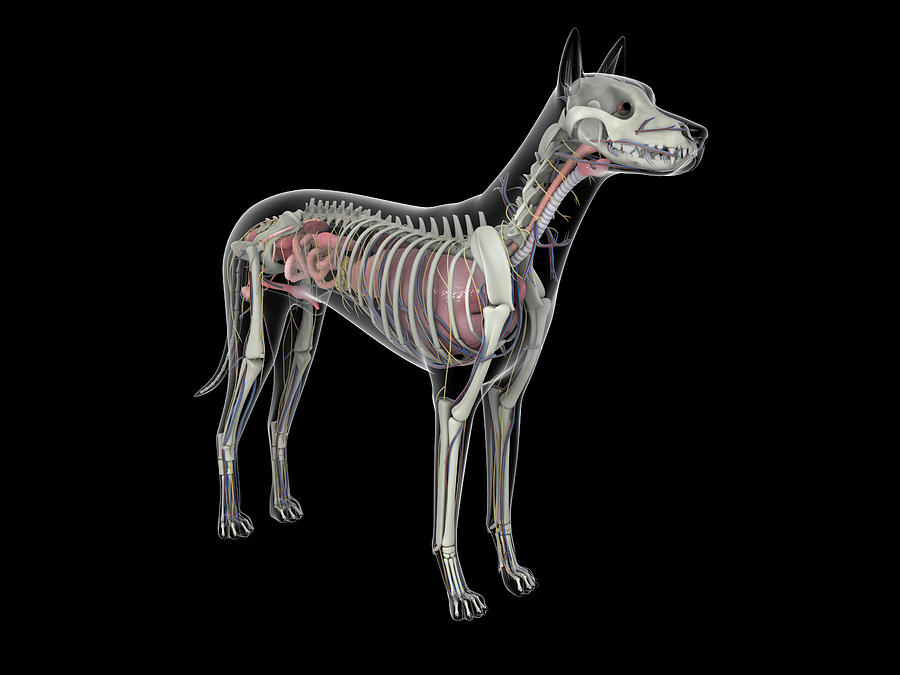
Dog Anatomy With Internal Organs Photograph by Stocktrek Images Fine Art America
Quick idea: in this article, you will learn the location of different organs from the different systems (like skeletal, digestive, respiratory, urinary, cardiovascular, endocrine, nervous, and special sense) of a dog with their important anatomical features.

A4 Veterinary Poster u00 Internal Organs Of The Dog (Animal Anatomy Pathology) Dog anatomy
Dogs, like all mammals, have eyes, a nose, a forehead, and ears. The only difference is that their noses are cold and wet, and their ears can be either dropped, erect, or cropped, depending on the breed. They also have a throat, a flew (the upper lip), chest, fore and hind legs, back, stomach, buttocks, and a tail.

Dog Anatomy Skeleton Animaltia
Anatomic Planes The main planes of motion for dogs are as follows (see Figure 5-1): • The sagittal plane divides the dog into right and left portions. If this plane were in the midline of the body, this is the median plane or median sagittal plane. • The dorsal plane divides the dog into ventral and dorsal portions.

Parts of a Dog Useful Dog Anatomy with Pictures • 7ESL
This module of vet-Anatomy is a basic atlas of normal imaging anatomy of the dog on radiographs. 51 sampled x-ray images of healthy dogs performed by Susanne AEB Borofka (PhD - dipl. ECVDI, Utrecht, Netherland) were categorized topographically into seven chapters (head, vertebral column, thoracic limb, pelvic limb, larynx/pharynx, thorax and abdomen/pelvis).
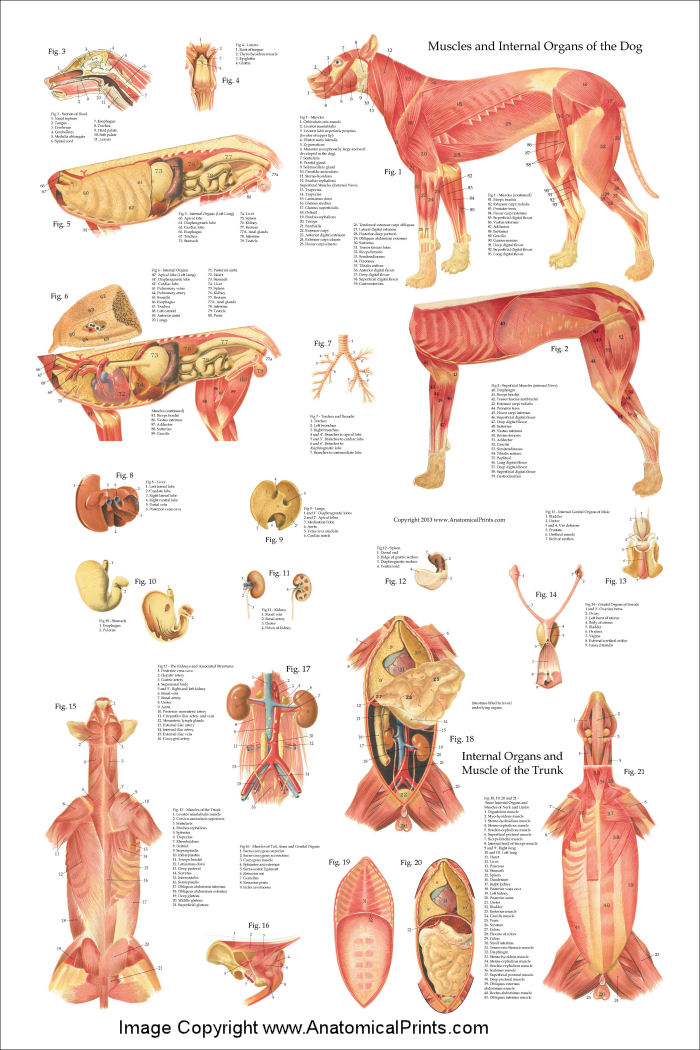
Dog Internal Anatomy Poster 24 x 36
Dog - Muscles Dog - Thorax/Abdomen/Pelvis Animal - Anatomy atlas: Cardiovascular system Veterinary anatomy - Animal: ANATOMICAL PARTS Abdomen Abdominal aorta Abdominal mammary gland Abdominal mammary region Accessory carpal bone Acromion Adductor muscle Ala of ilium; Wing of ilium Ala of nose Anconeus muscle Antebrachial region Aortic arch
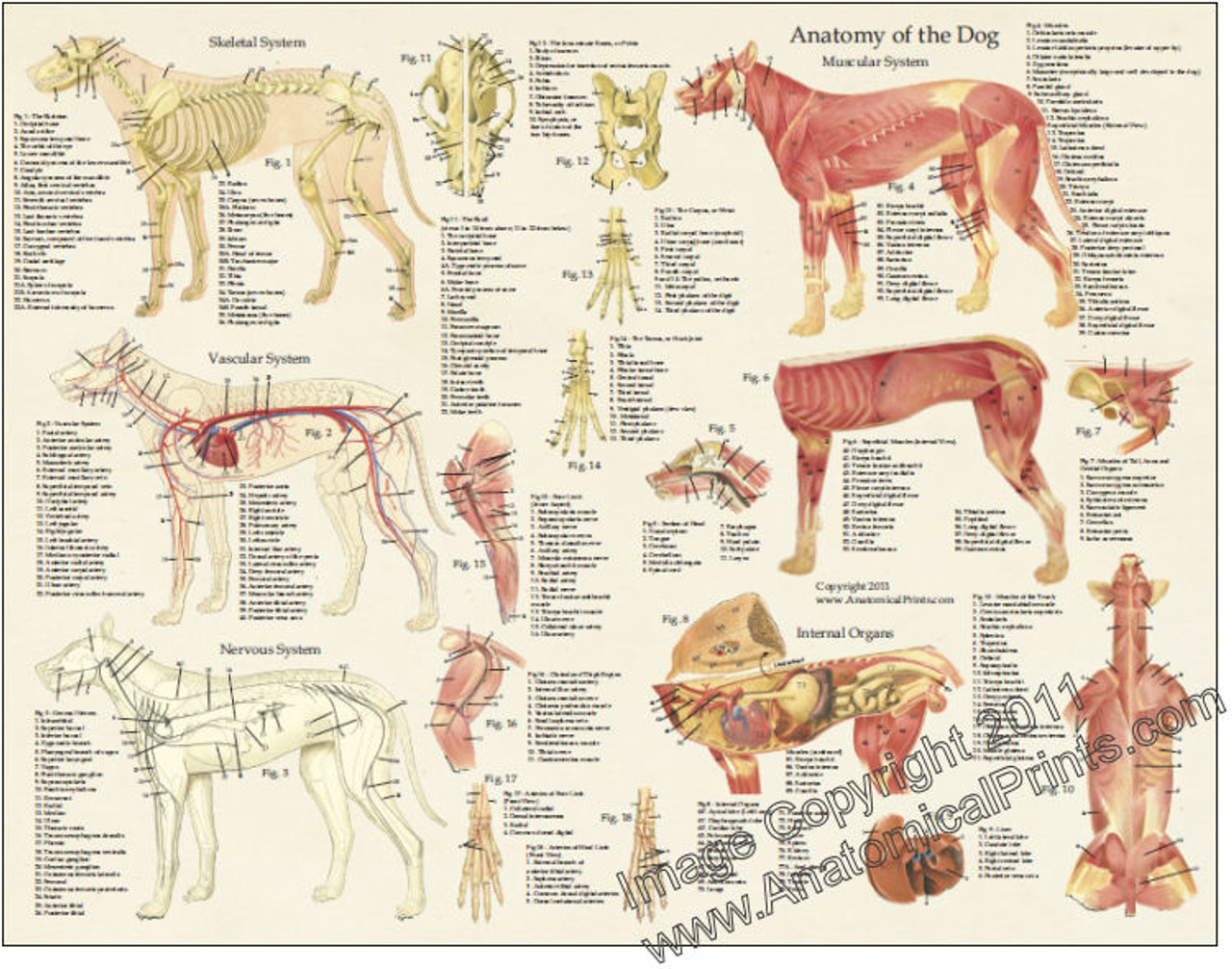
Dog Anatomy Laminated Poster Clinical Charts and Supplies
These include the head, ears, eyes, nose, mouth, neck, tail, legs, and paws. The head of a dog is one of its most distinguishing features. It includes the skull, jaw, and teeth. The ears can be upright or floppy, and they come in a variety of shapes and sizes. The eyes are usually round and can be brown, blue, or green.
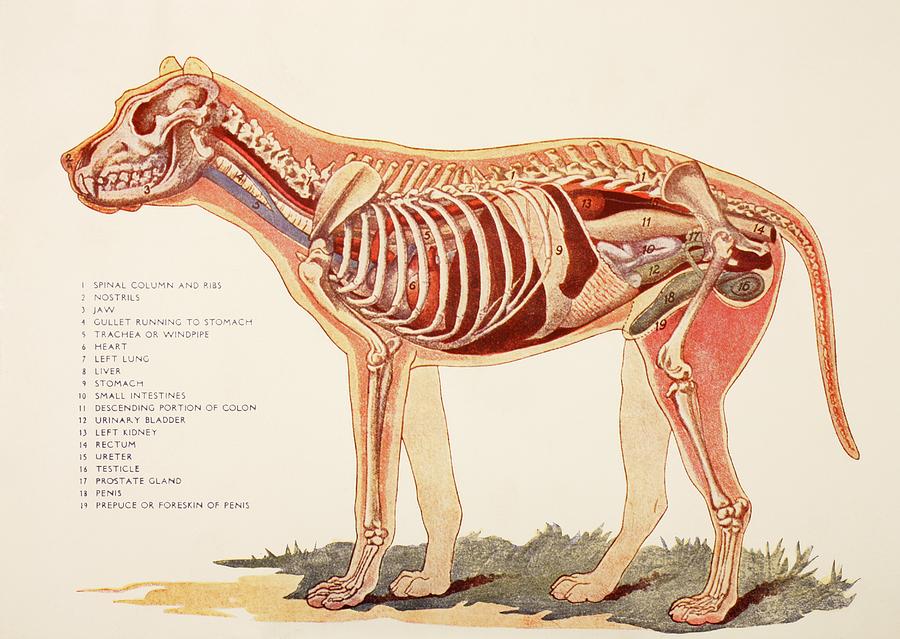
Internal Organs Of A Male Dog. From Photograph by Ken Welsh Pixels
A dog's physical anatomy is designed to help them navigate their environment and perform various tasks. Their bodies are made up of many different parts, including their skeleton, muscles and internal organs. One of the most important parts of a dog's anatomy is their skeleton.

Canine Internal Anatomy Chart. Anatomy of dog with inside organ structure examination vector
Common anatomical terminology Here are some common veterinary terms and their meanings: Pet senses Pets communicate in a very different way than people do. They have the same basic senses like sight, hearing, smell, touch, and taste, but they use them differently to communicate with the world.

Глубокие мышцы, внутренние органы собаки Dog Muscles & Internal Anatomy Собаки, Животные
What is dog anatomy. Dog anatomy is how a dog is built. In other words, a dog's anatomy includes all the parts of a dog's body like: Skeletal structure. Internal organs. Musculoskeletal system. Senses. Body systems. Each body part plays an important role in how your dog moves, breathes, eats, and reproduces.
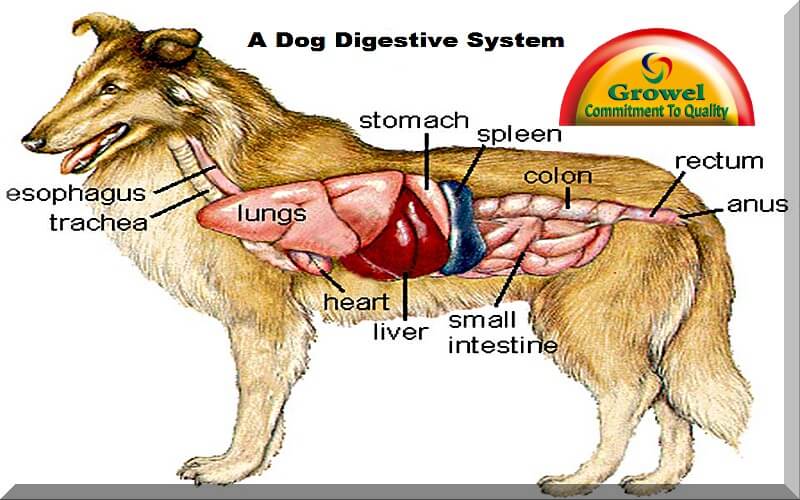
How is a Dog Digestive System Functioning? Growel Agrovet
Dog anatomy comprises the anatomical studies of the visible parts of the body of a domestic dog.Details of structures vary tremendously from breed to breed, more than in any other animal species, wild or domesticated, as dogs are highly variable in height and weight. The smallest known adult dog was a Yorkshire Terrier that stood only 6.3 cm (2.5 in) at the shoulder, 9.5 cm (3.7 in) in length.

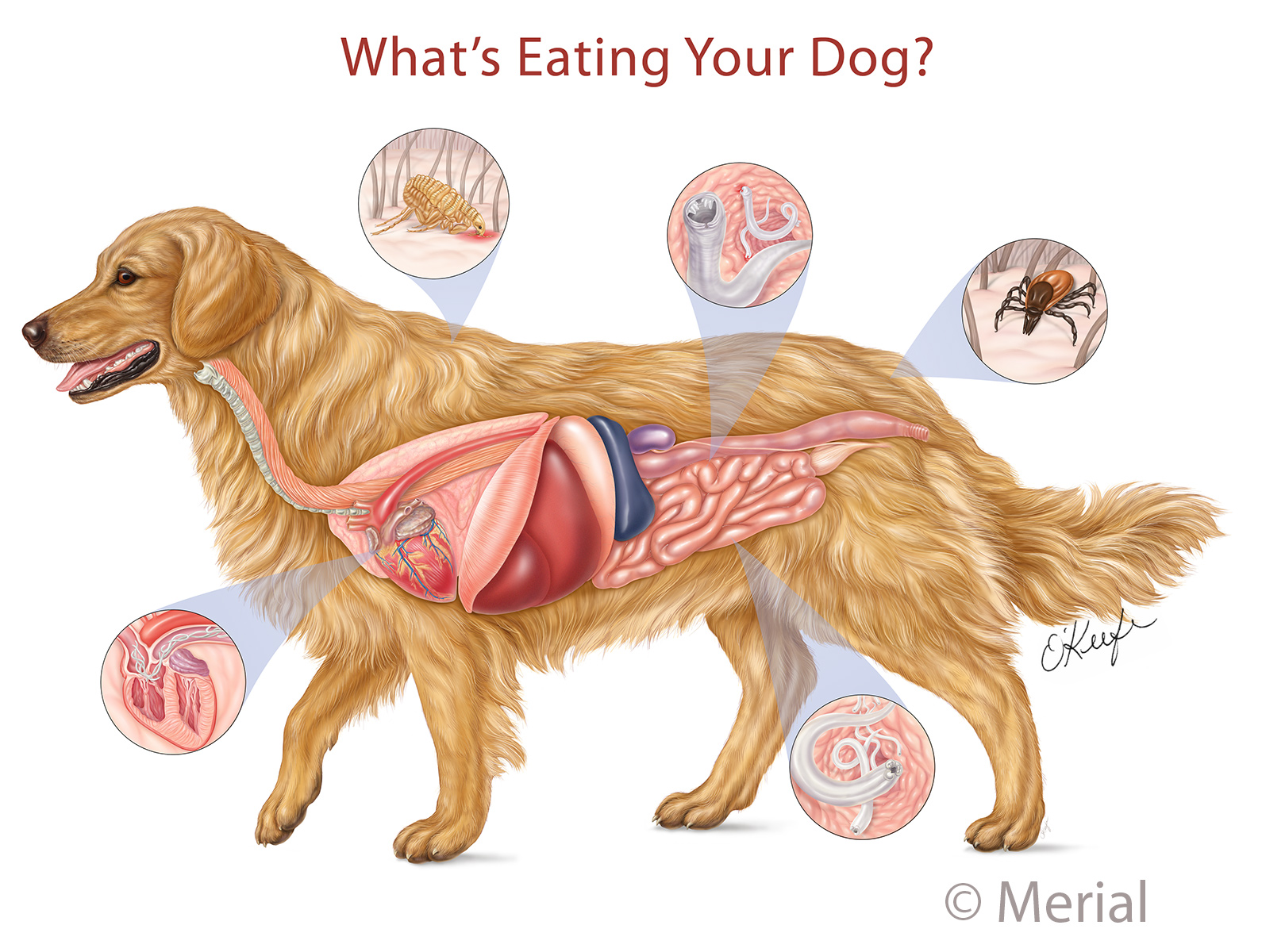
Dog anatomy4 views Illustration by Laurie O'Keefe Medical Illustration & Animation
On the left side view of a dog's internal organs, you can see the lungs, heart, liver, stomach, spleen, kidney, intestines, bladder, and the rectum in that order from front to back. You can also view the spinal column and the brain. Laurie O'Keefe Dog Anatomy Organs Right Side
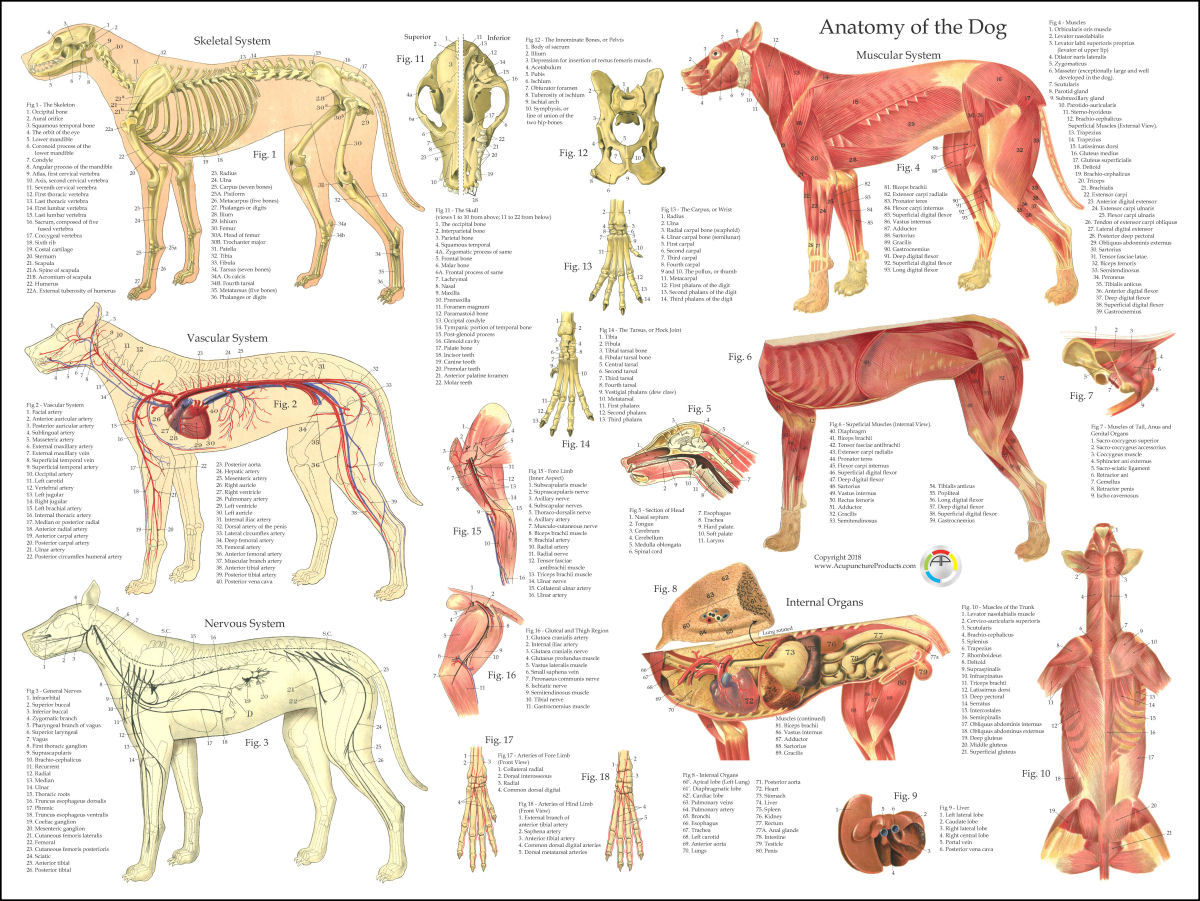
Dog Muscle Skeletal Veterinary Internal Anatomy Poster 18 X 24 Laminated Chart Art Posters
Our canine charts cover internal organ anatomy, the musculoskeletal system, common pathologies and guides to dog health and safety. Excellent wall displays in vet clinics, surgeries, dog groomers, and veterinary colleges. Our canine posters are suitable for both animal lovers and veterinary studies. Our canine model range covers detailed.
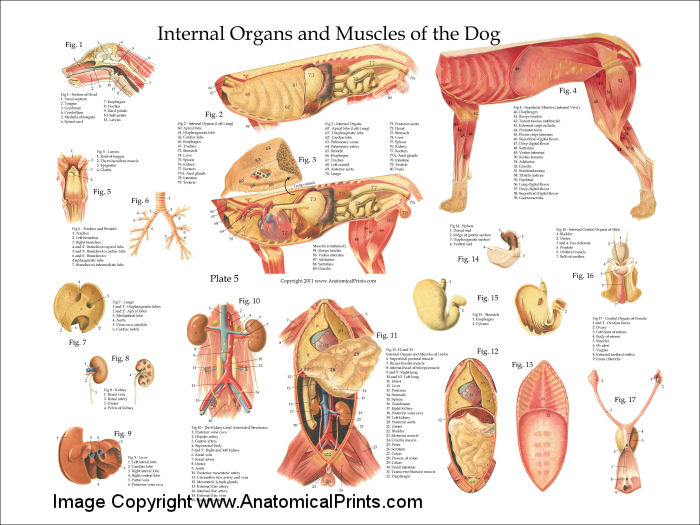
Dog Internal Anatomy Poster
This detailed canine internal anatomy wall chart has been laminated for easy cleaning and to enable wipeable marker pens to be used for notation. This is one of our bestselling veterinary charts in the canine anatomy series, which includes the canine muscular system and canine skeletal anatomy charts. Designed and printed in the UK.
Dog Internal Anatomy Anatomical Charts & Posters
Speaking of skeletons, a dog has 320 bones in their body (depending on the length of their tail) and around 700 muscles. Muscles attach to bones via tendons. Depending on the breed of dog, they will have different types of muscle fibers. You've probably heard about slow and fast twitch muscle fibers before.
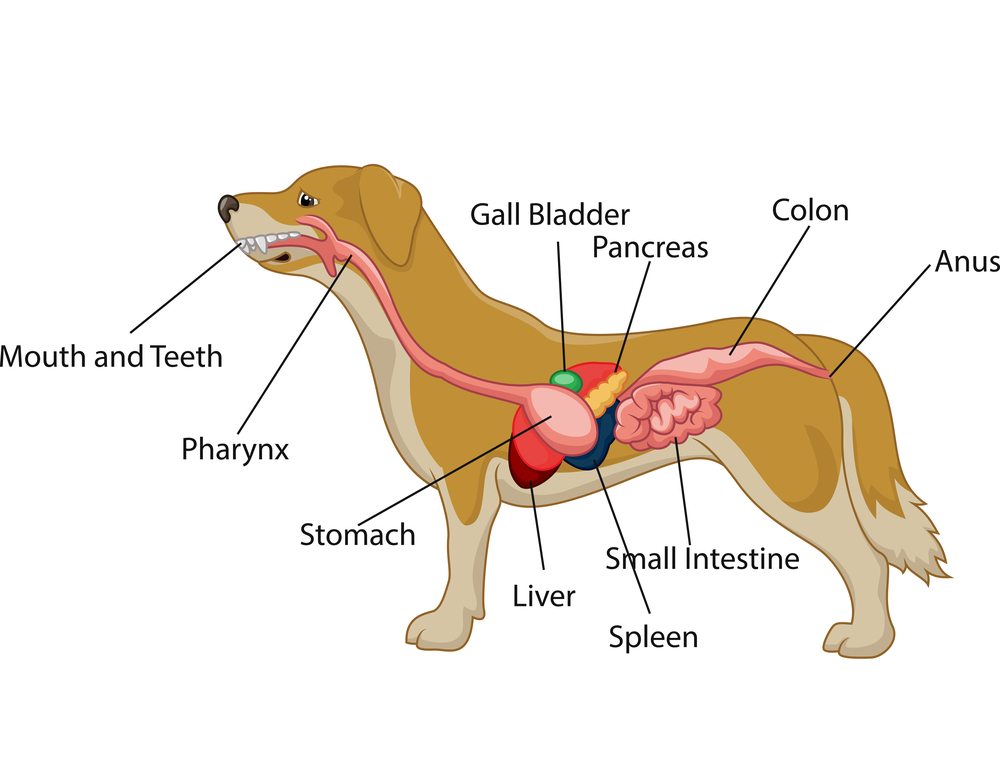
Dog Digestive Process and what the stages are and how it works
Dogs have 42 teeth. Six pairs of sharp incisor teeth are in front of the mouth, flanked by two pairs of large canine ('dog') teeth. The other teeth are premolars and molars. The incisors and the canines are very important because the dog bites and tears at its food with these teeth. Tongue
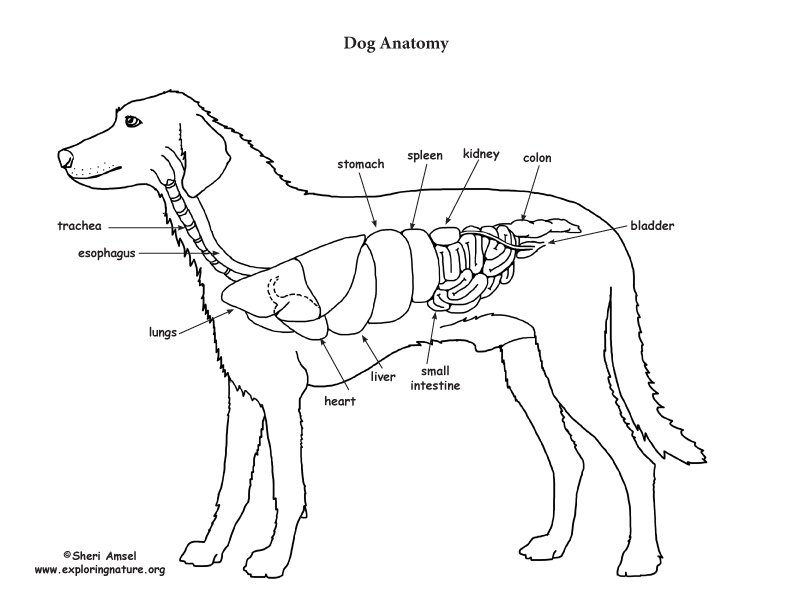
Dog Anatomy (Thoracic and Abdominal Organs)
Internal anatomy of a dog: carnivorous domestic mammal raised to perform various tasks for humans. Encephalon: seat of the intelluctual capacities of a gog. Spinal column: important part of the nervous system. Stomach: part of the digestive tract between the esophagus and the intestine. Spleen: hematopoiesis organ that produces lymphocytes.