
Conductors and insulators
Method 2 - Testing Different Thicknesses of Insulator: Wrap five beakers in varying thicknesses of one insulating material e.g. wrap each beaker in newspaper using one more sheet per beaker. Fill each beaker with warm water, record the initial temperature and cover each beaker with paper lids. Repeat the experiment as before, measuring the.

Difference between Conductor Semiconductor and Insulator Electrical A2Z
In a conductor there are no band gaps between the valence and conduction bands. In some metals the conduction and valence bands partially overlap. This means that electrons can move freely between.
Structural diagrams of the four types of insulators. Download Scientific Diagram
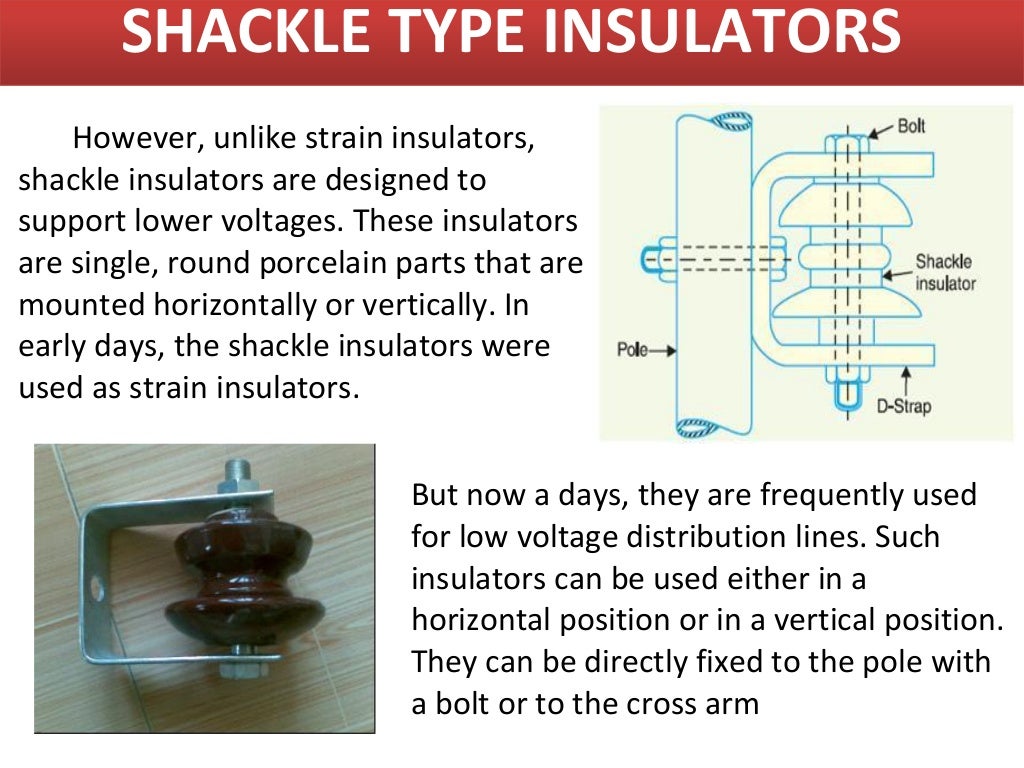
Suspension Insulator Strain Insulator Shackle Insulator Post-Insulator Stay Insulator Disc Insulator Pin Insulator This kind of insulator is used in distribution systems. The voltage capacity of this insulator is 11kV. It is designed with a high mechanical strength material. These are connected in vertical as well as horizontal positions.

Insulator, Conductor, Semiconductor Explained Shubhanshu yadav. YouTube
April 25, 2021 by Electrical4U Contents Type of Insulators Used in Transmission lines There are 5 types of insulators used in transmission lines as overhead insulation: Pin Insulator Suspension Insulator Strain Insulator Stay Insulator Shackle Insulator Pin, Suspension, and Strain insulators are used in medium to high voltage systems.

Conductors and Insulators Definition and Examples Electrical Academia
What are Insulators? 10 Types of Insulators [Uses, Function, Properties, Advantages & Disadvantages]: - Insulators are materials that prevent electricity from flowing freely through them. This implies they may be used to stop the flow of electricity in a circuit and protect persons and things from electrical shock.

PPT Insulators and Conductors PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3424925
3.5. Mott-Hubbard insulator. To carry the discussion we will start with an arrangement of monovalent atoms like hydrogen (H) in a cubic lattice with a lattice constant a as we have done earlier in section 3.2. The hydrogen atom at each lattice point carries one valence electron ( s electron) with it.

Conductor, Insulator and Semiconductor Play with electrons
The aim is to investigate the effectiveness of different materials as thermal insulators and the factors that may affect the thermal insulation properties of a material;. 6.2.4 Refraction Ray Diagrams; 6.2.5 Required Practical: Investigating Infrared Radiation; 6.2.6 EM Waves & Atoms; 6.2.7 Radio Waves; 6.2.8 Dangers of High-Energy EM Waves;

Different Types of Insulators Used In Power Transmission Lines
Revise electrical charges, free electrons and the direction of conventional current, using circuit symbols, components and simple circuit diagrams.
Electrical Revolution
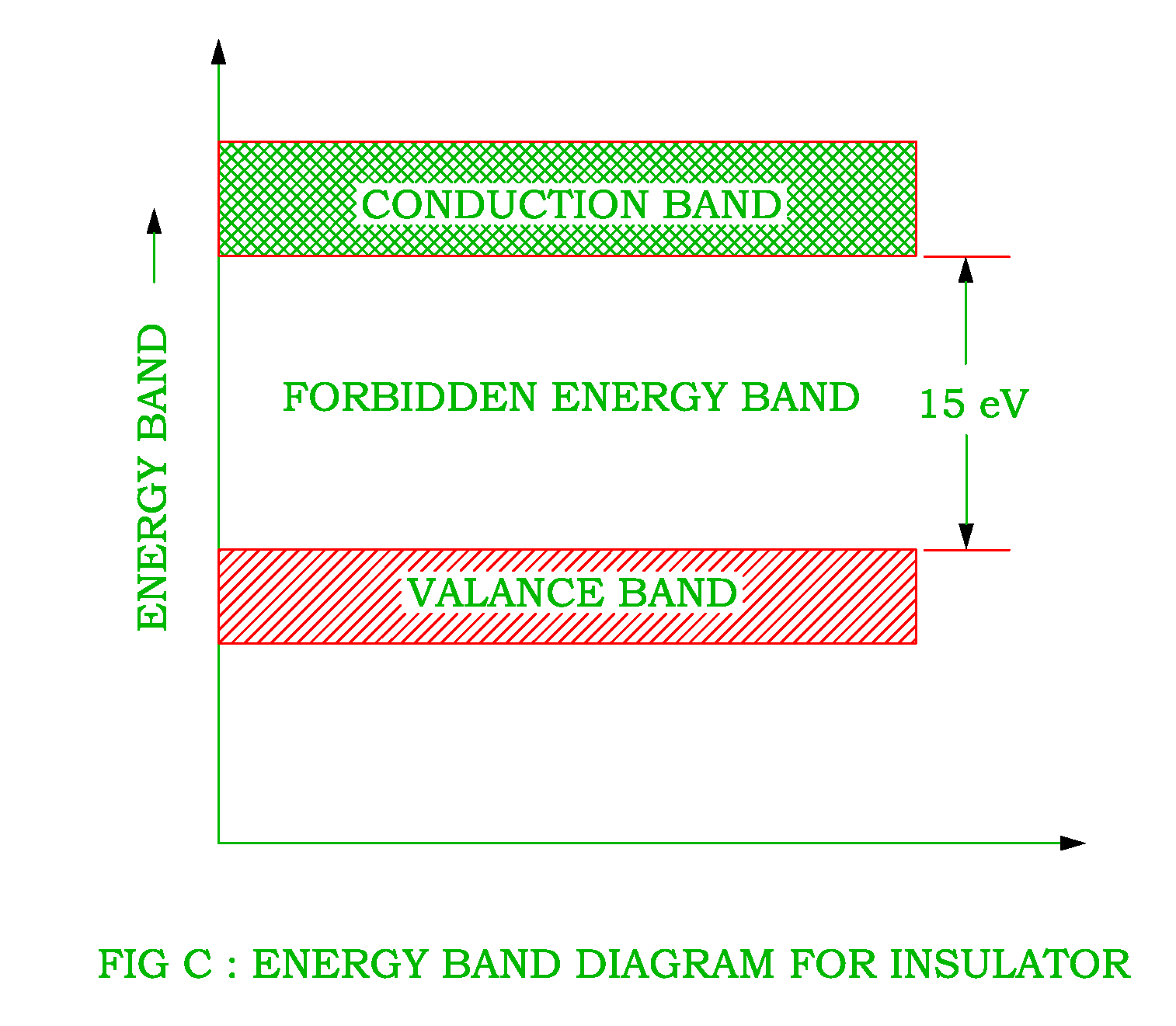
The Energy Band Diagram for Conductors Insulators and Semiconductors is shown in Fig. 1-13 show that insulators have a wide forbidden gap, semiconductors have a narrow forbidden gap, and conductors have no forbidden gap at all. In the case of insulators, there are practically no electrons in the conduction band, and the valence band is filled.
PPT Chapter 3 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3887454
Conductors allow for charge transfer through the free movement of electrons. In contrast to conductors, insulators are materials that impede the free flow of electrons from atom to atom and molecule to molecule. If charge is transferred to an insulator at a given location, the excess charge will remain at the initial location of charging.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/examples-of-electrical-conductors-and-insulators-608315_v3-5b609152c9e77c004f6e8892.png)
10 Examples of Electrical Conductors and Insulators
Insulators, Conductors and Semiconductors (with Band Diagram) Categories Basic Electrical, Electronics Solid state materials can be classified into three groups: insulators, semiconductors conductors. Insulators have no free charge carriers available with them under normal conditions.

Insulation The Science Behind It Insulation Essentials
A typical phase diagram for a metal-insulator transition is shown at the right for V 2 O 3. The octahedrally coordinated V 3+ ion has a d 2 electron count, so there are two unpaired spins per atom, and at low temperature the spins in the lattice order antiferromagnetically. As we learned in Chapter 8, above the Néel temperature an.

Cross section of suspension type porcelain insulator used for 154 kV... Download Scientific
The pin type insulator diagram is shown below. pin-insulator. These insulators are still used in 33 kV power distribution systems. These insulators are available in different parts like 1 part, 2 parts or 3 parts type based on the voltage of application. One part type is used in an 11 kV power distribution system where the entire insulator is a.

What is Passive House? A beginner's guide Insulation Superstore Help & Advice
A conductor is a material that allows electrons to flow freely through it, making it useful for carrying electric current. An insulatoris a material that resists the flow of electrons, so it does not allow electric current to pass through it. Learn about how conductors and insulators work and how they are effected by changes in electrical current.

Electrical Systems High Voltage Insulator
These insulators are mostly solid core insulators made of resin. In these insulators porcelain is also used. Bushings are used in transformers, Switchgears. Isolators etc. to take out live conductors through earthed tanks or metallic parts. In bushing design, the central conductor is in the form of brass or copper or stranded copper conductors.
INSULATORS AND ITS TYPES
The probability of finding an electron in the conduction band is shown by the equation: P = 1 eΔE/RT + 1 (6.8B.1) (6.8B.1) P = 1 e Δ E / R T + 1. The ∆E in the equation stands for the change in energy or energy gap. t stands for the temperature, and R is a bonding constant. That equation and this table below show how the bigger difference.