
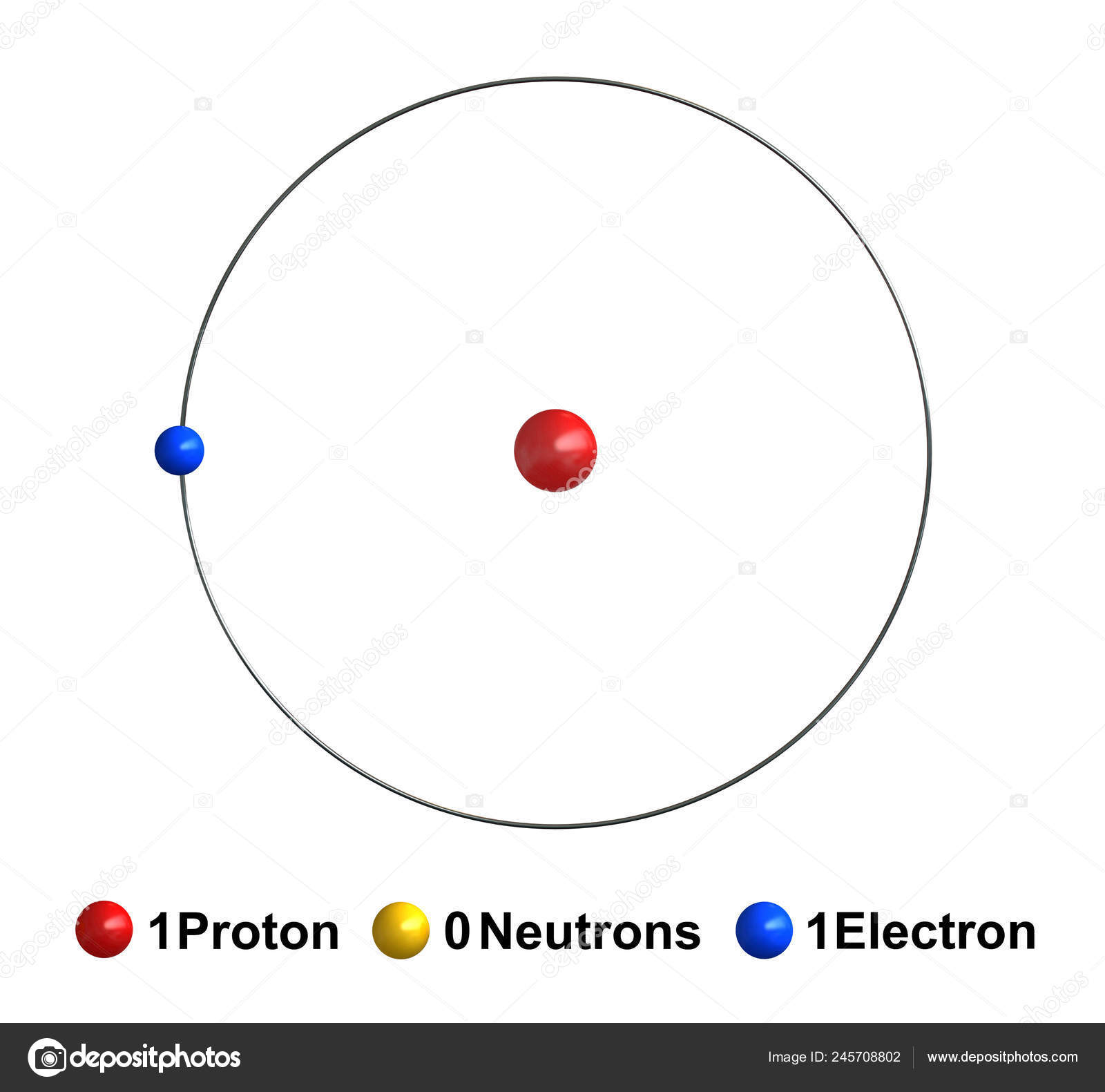
Bohr model scientific hydrogen atom Royalty Free Vector
hydrogen (H), a colourless, odourless, tasteless, flammable gaseous substance that is the simplest member of the family of chemical elements.The hydrogen atom has a nucleus consisting of a proton bearing one unit of positive electrical charge; an electron, bearing one unit of negative electrical charge, is also associated with this nucleus.Under ordinary conditions, hydrogen gas is a loose.

Hydrogen Boundless Chemistry
Model Atom Hidrogen - Mekanika Kuantum, Atom Hidrogen, Model Bohr - PhET. Lompat ke Isi Utama.
Render Atom Structure Hydrogen Isolated White Backgroun Stock Photo by ©oorka5 245708802
Depiction of a hydrogen atom showing the diameter as about twice the Bohr model radius. (Image not to scale) A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen.The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the baryonic mass of the.

Átomo de hidrógeno en el fondo blanco
Global hydrogen production by technology in the Net Zero Scenario, 2019-2030. IEA. Licence: CC BY 4.0. Dedicated hydrogen production today is primarily based on fossil fuel technologies, with around a sixth of the global hydrogen supply coming from "by-product" hydrogen, mainly in the petrochemical industry.

How to Learn About the Chemistry of the Hydrogen Atom 12 Steps
Figure 8.2.1: A representation of the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom. With the assumption of a fixed proton, we focus on the motion of the electron. In the electric field of the proton, the potential energy of the electron is. U(r) = − ke2 r, where k = 1 / 4πϵ0 and r is the distance between the electron and the proton.

Hydrogen Atom · Free vector graphic on Pixabay
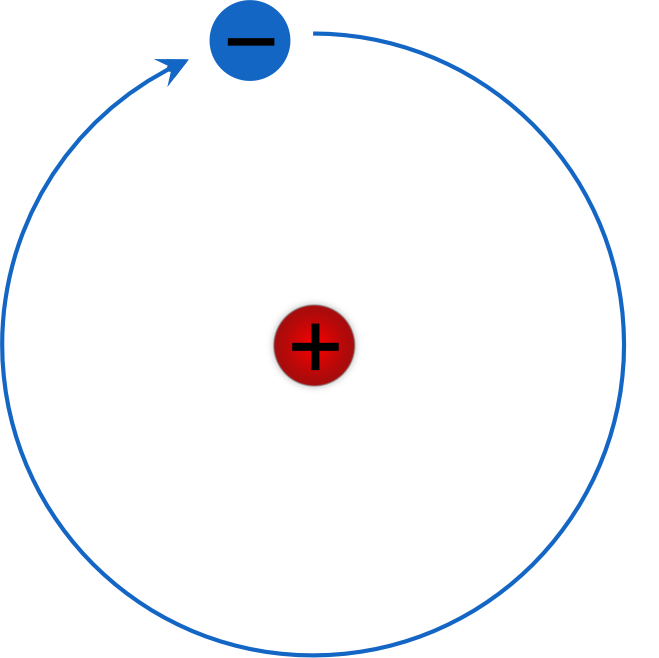
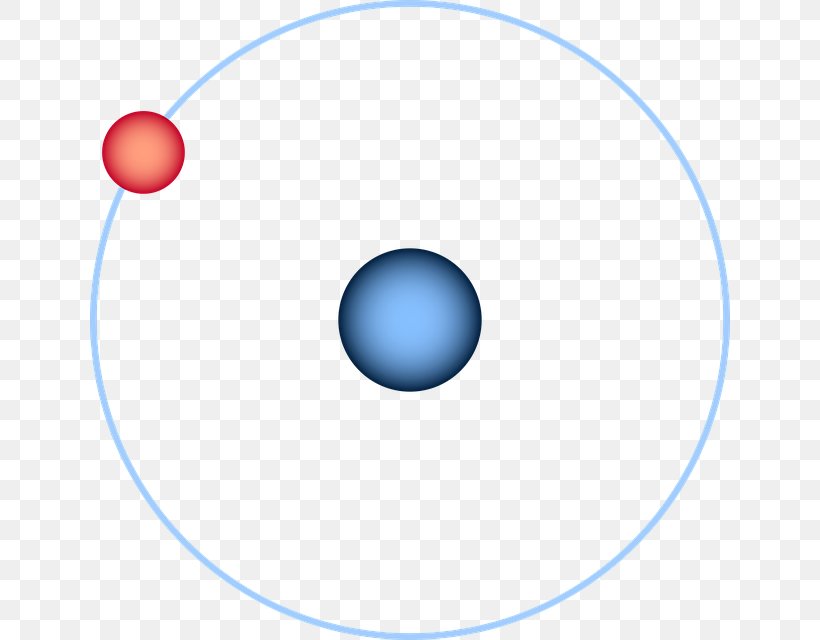
The hydrogen atom is the simplest atom in nature and, therefore, a good starting point to study atoms and atomic structure. The hydrogen atom consists of a single negatively charged electron that moves about a positively charged proton ().In Bohr's model, the electron is pulled around the proton in a perfectly circular orbit by an attractive Coulomb force.

Bohr Atomic Model Of Hydrogen
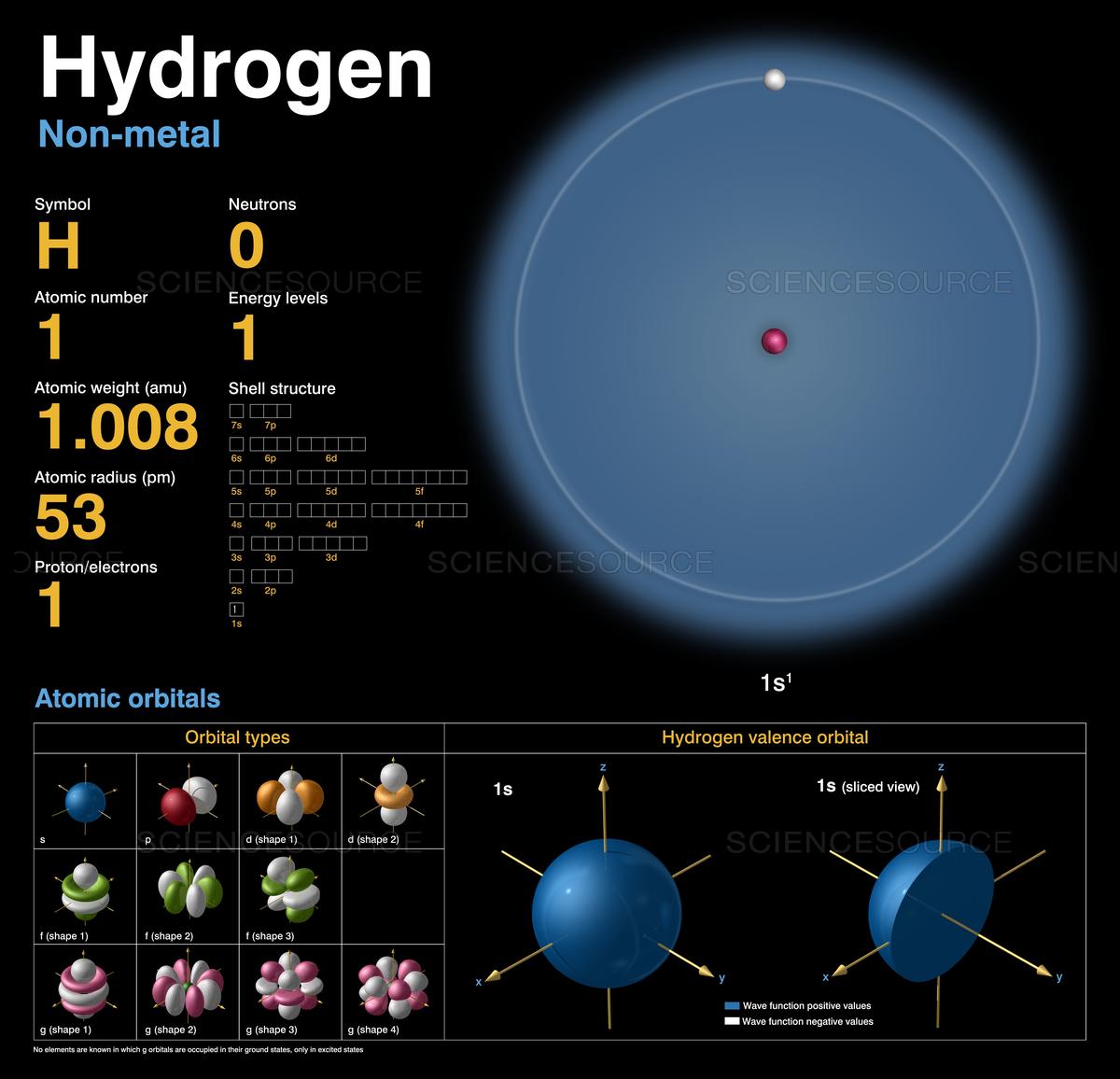
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest element and, at standard conditions, is a gas of diatomic molecules with the formula H2, sometimes called dihydrogen, [10] but more commonly called hydrogen gas, molecular hydrogen or simply hydrogen. It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, [11] non-toxic, and.
35 Gambar Struktur Atom Lengkap dengan Konfigurasi Elektron dan Diagram Orbitalnya MateriKimia
With sodium, however, we observe a yellow color because the most intense lines in its spectrum are in the yellow portion of the spectrum, at about 589 nm. Figure 7.3.1: The Emission of Light by Hydrogen Atoms. (a) A sample of excited hydrogen atoms emits a characteristic red light.

Hydrogen Definition, Structure, Properties & Uses Embibe
In this chapter we will consider the hydrogen atom as a proton fixed at the origin, orbited by an electron of reduced mass μ. The potential due to electrostatic attraction is: V(r) = − e2 4πε0r, where ε0 is the constant permittivity of vacuum. The kinetic energy term in the Hamiltonian is.
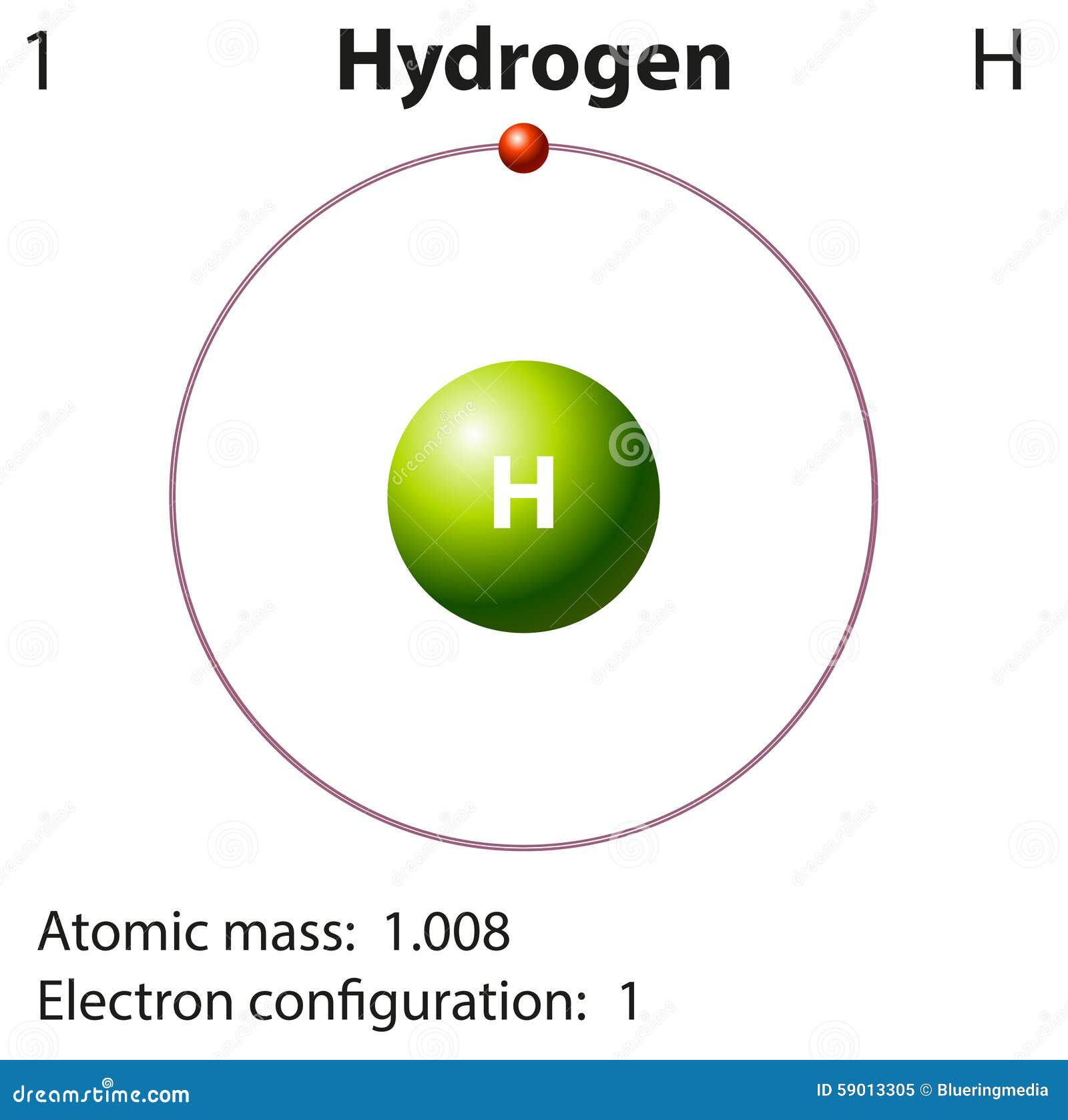
Diagram Representation Of The Element Hydrogen Stock Vector Image 59013305
The hydrogen atom consists of an electron and a proton bound together by the attractive electrostatic force between the negative and positive charges of these particles. Our experience with the one-dimensional particle in a box shows that a spatially restricted particle takes on only discrete values of the total energy. This conclusion carries.

A Hydrogen Atom with an Electron. Chemical Model of the Molecule. Stock Vector Illustration of
The mass of an atom relative to that of carbon-12. This is approximately the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Where more than one isotope exists, the value given is the abundance weighted average. Isotopes Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. CAS number
Atoms & Molecules echapter — The Biology Primer
Atomic hydrogen may be generated in aqueous solution through the solvation of electrons. e−(aq) +H3O+ ⇋ H. +H2O (2.4.3) (2.4.3) e ( a q) − + H 3 O + ⇋ H. + H 2 O. The formation equilibrium constant (K eq) is very small resulting in very low concentrations being generated (10 -5 M). As expected solvated atomic hydrogen is a strong.
Hydrogen Molecule Model
hydrogen, Lightest chemical element, chemical symbol H, atomic number 1.A colourless, odourless, tasteless, flammable gas, it occurs as the diatomic molecule H 2.Its atom consists of one proton (the nucleus) and one electron; the isotopes deuterium and tritium have an additional one and two nuclear neutrons, respectively. Though only the ninth most abundant element on Earth, it represents.

Describe Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom. bitWise Academy
6: The Hydrogen Atom. Page ID. 11783. The solution of the Schrödinger equation (wave equation) for the hydrogen atom uses the fact that the Coulomb potential produced by the nucleus is isotropic (it is radially symmetric in space and only depends on the distance to the nucleus). Although the resulting energy eigenfunctions (the orbitals) are.
Hydrogen Atom Electron Hydrogen Economy, PNG, 640x640px, Hydrogen Atom, Area, Atom, Atomic Mass
where h f h f is the energy of either an emitted or an absorbed photon with frequency f.The second quantization condition states that an electron's change in energy in the hydrogen atom is quantized. These three postulates of the early quantum theory of the hydrogen atom allow us to derive not only the Rydberg formula, but also the value of the Rydberg constant and other important properties.

Hydrogen atom diagram concept illustration Stock Vector Image & Art Alamy
The electron's speed is largest in the first Bohr orbit, for n = 1, which is the orbit closest to the nucleus. The radius of the first Bohr orbit is called the Bohr radius of hydrogen, denoted as a0. Its value is obtained by setting n = 1 in Equation 6.5.6: a0 = 4πϵ0 ℏ2 mee2 = 5.29 × 10 − 11m = 0.529 Å.